Prognostic value of critical ultrasound score and CT score combined with APACHE Ⅱ score in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
-
摘要: 目的 分析重症超声与CT评分联合急性生理与慢性健康评分(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation,APACHE Ⅱ)对重症急性胰腺炎(severe acute pancreatitis,SAP)患者预后的评估价值。方法 回顾分析2020年1月—2024年1月同济大学附属第十人民医院综合ICU收治的180例SAP患者临床资料,对所有患者进行重症超声、CT检查及APACHE Ⅱ评分评估,按照患者临床预后的不同分为好转组(126例)和加重组(54例),比较两组患者一般临床资料、超声评分、CT评分及APACHE Ⅱ评分,分析SAP预后的影响因素。采用受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)曲线预测3种检测手段对SAP患者预后评估的价值。结果 两组患者年龄、入院前腹痛时间、病因、性别等一般临床资料比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);但加重组患者的超声评分、CT评分及APACHE Ⅱ评分分别为(9.12±2.46)分、(3.18±0.84)分、(47.59±11.16)分,显著高于好转组的(5.88±1.23)分、(2.22±0.66)分、(40.61±10.21)分,两组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。logistic回归分析显示,重症超声评分、CT评分与APACHE Ⅱ评分均是SAP预后情况的影响因素(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线结果显示,重症超声、CT评分、APACHE Ⅱ评分三者联合检测的诊断效能最大:灵敏度为88.89%,特异度为92.86%,AUC为0.909。结论 重症超声、CT评分及APACHE Ⅱ评分可影响SAP预后,对SAP患者的预后具有一定的预估价值,3种检测方式联合预测对SAP患者诊治具有临床指导价值,值得临床重视。
-
关键词:
- 重症超声 /
- CT评分 /
- 急性生理与慢性健康评分 /
- 重症急性胰腺炎 /
- 预后评估
Abstract: Objective To analyze the prognostic value of critical ultrasound score and CT score combined with the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation(APACHE) Ⅱ score in patients with severe acute pancreatitis(SAP).Methods The clinical data of 180 patients with SAP who were admitted to comprehensive ICU of the hospital from January 2020 to January 2024 were analyzed retrospectively. All patients underwent critical ultrasound examination, CT examination and APACHE Ⅱ evaluation. They were divided into the improvement group(n=126) and the exacerbation group(n=54) according to the prognosis. General clinical data, ultrasound scores, CT scores and APACHE Ⅱ scores of the two groups were comparatively analyzed. The factors influencing the prognosis of SAP were analyzed. The receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves were used to evaluate the prognostic value of the three methods in patients with SAP.Results There was no statistically significant difference in general clinical data such as age, duration of abdominal pain before admission, cause of disease and gender between the two groups(P>0.05). Ultrasound score, CT score and APACHE Ⅱ score of the exacerbation group([9.12±2.46], [3.18±0.84], [47.59±11.16]) were significantly higher than those of the improvement group([5.88±1.23], [2.22±0.66], [40.61±10.21]) (P < 0.05). logistic regression analysis showed that critical ultrasound score, CT score and APACHE Ⅱ score were factors influencing the prognosis of SAP(P < 0.05). ROC curve analysis results showed that the prognostic efficacy of the combination of critical ultrasound score, CT score and APACHE Ⅱ score was the highest. The sensitivity, specificity and AUC were 88.89%, 92.86% and 0.909, respectively.Conclusion Critical ultrasound score, CT score and APACHE Ⅱ score influence the prognosis of SAP, and they have certain value in predicting the prognosis of SAP. Joint prediction with the three above is of guiding value in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with SAP, which deserves attention in clinic. -

-
表 1 SAP患者超声的评分标准
评分项 0分 1分 2分 3分 4分 胰腺大小 胰头≤20 mm 胰头为21~25 mm 胰头为26~30 mm 胰头为31~35 mm 胰头≥35 mm 胰体≤15 mm 胰体为16~20 mm 胰体为21~25 mm 胰体为26~30 mm 胰体≥30 mm 胰腺实质回声 正常 均匀性减低 不均匀减低 高低不均 有局灶性无回声区 胰腺轮廓 清晰光滑 欠光滑 模糊不光滑 轮廓不规整 部分消失 胰周积液(前后深度) 无 局限性积液≤5 mm 1处积液6~15 mm 2处积液16~30 mm 2处以上积液或>30 mm 表 2 好转组与加重组一般临床资料比较
X±S 指标 好转组(126例) 加重组(54例) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 49.17±4.39 49.55±4.63 0.524 0.601 入院前腹痛时间/h 9.03±2.14 9.28±2.35 0.697 0.487 吸烟史/例(%) 68(53.97) 30(55.56) 0.038 0.845 饮酒史/例(%) 52(41.27) 23(42.59) 0.061 0.805 高血压史/例(%) 40(31.75) 21(38.89) 0.861 0.354 病因/例(%) 6.370 0.095 脂源性 21(16.70) 6(11.11) 胆源性 55(44.00) 34(62.96) 酒精性 14(11.11) 5(9.26) 其他 36(28.57) 9(16.67) 性别/例(%) 0.128 0.720 男 64(50.79) 29(53.70) 女 62(49.21) 25(46.30) 重症超声评分/分 5.88±1.23 9.12±2.46 11.770 < 0.001 CT评分/分 2.22±0.66 3.18±0.84 8.217 < 0.001 APACHE Ⅱ评分/分 40.61±10.21 47.59±11.16 4.086 < 0.001 抗菌药使用时间/d 15.84±4.65 17.16±4.79 1.730 0.085 升压药使用时间/d 4.23±1.17 4.62±1.52 1.867 0.064 住院时间/d 12.37±2.92 15.79±3.49 6.781 < 0.001 ICU住院时间/d 3.78±1.14 7.09±2.22 13.191 < 0.001 表 3 SAP预后情况的影响因素分析
指标 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI 重症超声评分 1.258 0.497 6.407 0.012 3.518 1.328~9.320 CT评分 0.587 0.263 4.982 0.026 1.799 1.074~3.012 APACHE Ⅱ评分 2.268 1.123 4.079 0.044 9.660 1.069~87.276 住院时间 1.154 1.028 1.260 0.262 3.171 0.423~23.781 ICU住院时间 0.269 0.154 3.051 0.081 1.309 0.968~1.770 表 4 重症超声、CT评分、APACHE Ⅱ评分及联合检测预测SAP预后情况的ROC特征
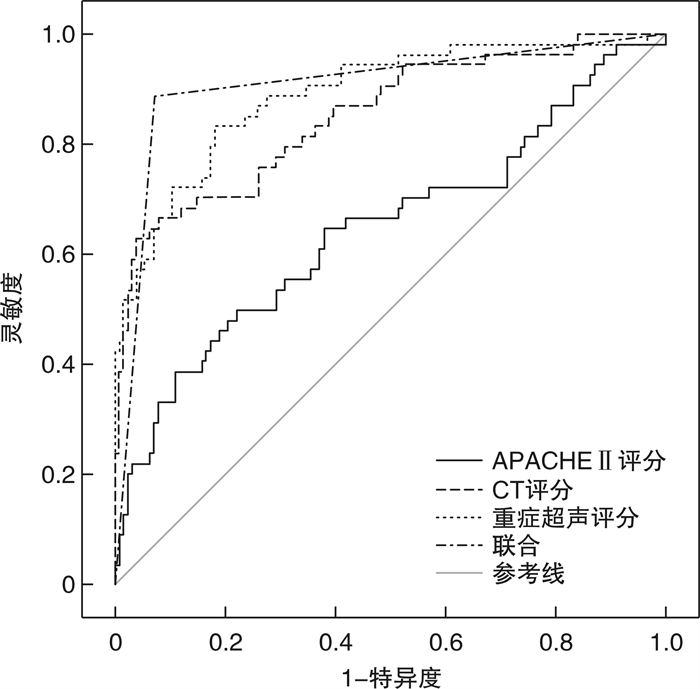
检测方法 截断值 灵敏度/% 特异度/% AUC 95%CI 约登指数 重症超声评分 6.761 83.33 81.75 0.890 0.835~0.932 0.651 CT评分 3.072 62.96 96.03 0.851 0.791~0.900 0.590 APACHE Ⅱ评分 50.033 50.00 77.78 0.647 0.742~0.934 0.278 三者联合检测 - 88.89 92.86 0.909 0.857~0.946 0.818 -
[1] 段荣, 赵晨, 唐飞飞. qSOFA联合血小板平均体积对老年急性重症胰腺炎预后的预测价值[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(6): 1336-1339.
[2] Boxhoorn L, Voermans RP, Bouwense SA, et al. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10252): 726-734. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31310-6
[3] 杨威, 黄咏宁, 吕元博, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎患者外周血TLR4、TRAF6的表达及与并发肝损伤的关系[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2023, 33(12): 18-23.
[4] 何俊娜, 申素芳, 陈洪. 血清载脂蛋白B与载脂蛋白A比值对重症急性胰腺炎患者预后的预测价值[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2023, 51(9): 1029-1032.
[5] 蒋奎荣, 袁昊, 苗毅. 影像学在胆源性胰腺炎诊治中价值及评价[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40(11): 1266-1270.
[6] 陶京, 方琦, 常剑, 等. 可溶性程序性死亡配体1对重症急性胰腺炎患者并发持续炎症-免疫抑制-分解代谢综合征的预测价值[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2020, 37(3): 537-540.
[7] 王思盼, 张珏, 张珂, 等. 内脏脂肪指数对高脂血症性急性胰腺炎患者病情严重程度的预测价值[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2023, 30(4): 453-457.
[8] 甄品, 张昆鹏, 左长增, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎继发肺部感染患者血清炎症细胞因子水平的变化及临床价值[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2020, 30(8): 1240-1243.
[9] 杨琼英, 叶茜, 李永静, 等. 重症胰腺炎患者超声评分与白蛋白-胆红素评分的关系及对死亡风险的联合预测价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2023, 18(7): 905-909.
[10] 程炯炯, 李琳琳, 赵浩东, 等. CRRT联合血浆置换救治高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎患者的疗效分析[J]. 天津医药, 2023, 51(8): 855-859.
[11] 李莉, 宁华英, 刘晖, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎患者营养风险筛查与临床结局的相关性?凹壑堤教諿J]. 重庆医学, 2020, 49(9): 1413-1416.
[12] 杨君, 马亚南, 陆莉莉, 等. 徐州地区急性胰腺炎病因及临床特征分析[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(9): 470-475. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.09.006
[13] 周哲, 平立英, 郑洋, 等. 清热通腑化瘀方结合血液净化治疗急性胰腺炎的疗效分析[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2023, 31(7): 567-572.
[14] 郭丰. 重症急性胰腺炎合并感染的诊断和抗生素使用[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2020, 40(7): 444-447.
[15] 刘英, 帅佳颖, 杨治宇, 等. 肺超声评分鉴别急性胰腺炎病情危重程度及预后评估[J]. 中华实验外科杂志, 2023, 40(7): 1397-1400.
[16] 汪涛, 丁娟娟, 冒秀宏, 等. MSCT与超声联合S-AMY、LPS检测对重症急性胰腺炎的诊断价值研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2021, 19(11): 132-134.
[17] 陆贝, 蔡阳, 殷俊杰, 等. 经引流管窦道超声气压弹道碎石清石系统辅助无麻醉胰腺坏死清除术12例[J]. 中华普通外科杂志, 2021, 36(9): 702-704.
[18] 胡洁, 覃伶伶, 吴汤娜, 等. 胰腺炎胰周血管并发症的超声诊断[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2020, 36(6): 574-576.
[19] 杨淑洁. CT严重指数结合APACHE-Ⅱ评分对急性胰腺炎严重程度及预后的评估[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(2): 98-101.
[20] 温福兴, 王丽双, 张静. Balthazar CT分级联合红细胞分布宽度与重症急性胰腺炎患者预后的相关性[J]. 国际老年医学杂志, 2022, 43(6): 649-654.
[21] 何海航, 张亚欣, 陈琳, 等. Balthazar CT分级联合中性粒细胞淋巴细胞比值在重症急性胰腺炎患者预后的预测作用[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2021, 26(10): 1303-1307.
[22] 孙志辉, 杨伟, 刘秦勤, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎并发腹腔感染耐碳青霉烯类肠杆菌科细菌类型及影响因素分析[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2024, 19(4): 454-458.
[23] 谷阁, 王润之, 张梦辉, 等. 血清淀粉样蛋白A联合APACHE Ⅱ评分对急性胰腺炎预后的预测价值[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2022, 17(12): 1626-1629.
[24] 徐玉龙, 叶淳娟, 谈冰. 腹膜后间隙炎症浸润、胸腔积液、胰周积液评估急性胰腺炎严重度的临床价值[J]. 天津医药, 2023, 51(11): 1242-1244.
-




 下载:
下载: