The value of P16INK4a, IL-37 and Cys-C combined detection of acute kidney injury in sepsis
-
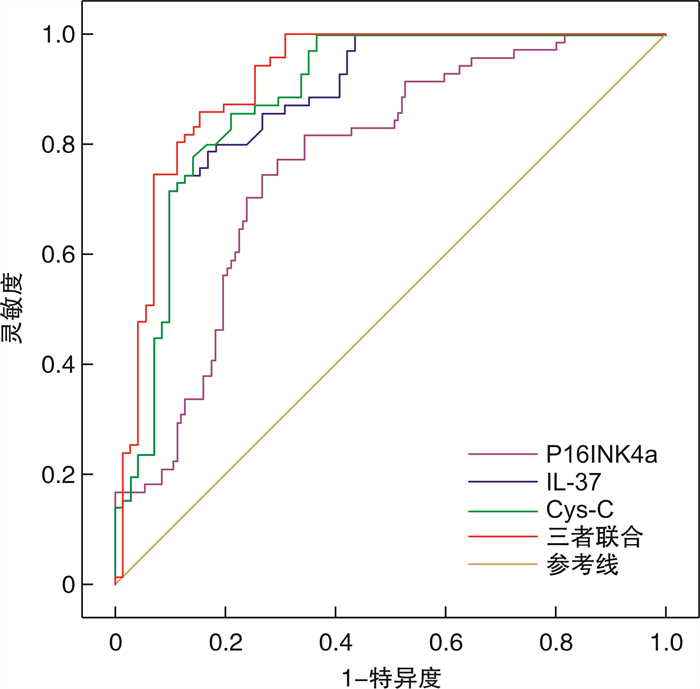
摘要: 目的 探讨P16INK4a、白介素37(interleukin-37,IL-37)和胱抑素C(Cys-C)联合检测在脓毒症急性肾损伤中的早期诊断价值。方法 前瞻性选取2021年3月—2023年9月海军军医大学海军特色医学中心收治的脓毒症患者193例,根据是否发生急性肾损伤,将患者分为急性肾损伤组(71例)和单纯脓毒症组(122例)。对比两组的基线资料,采用二元logistic回归分析脓毒症发生急性肾损伤的影响因素,Pearson相关分析P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C与炎症因子、肾功能的相关性,绘制受试者工作特征曲线分析P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C的诊断效能。结果 本研究共计纳入193例脓毒症患者,急性肾损伤的发生率为36.79%(71/193);急性肾损伤组和单纯脓毒症组的年龄、性别、原发感染部位、高血压、糖尿病、高脂血症和糖尿病对比差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而急性肾损伤组中的序贯器官功能衰竭评分、急性生理学和慢性健康状况评分及肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)、IL-6、血小板压积(procalcitonin,PCT)、肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)、尿素氮(blood urea nitrogen, BUN)、P16INK4a、Cys-C水平明显高于单纯脓毒症组,IL-37水平明显低于单纯脓毒症组,均差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);二元logistic回归分析结果显示,TNF-α、IL-6、PCT、Scr、BUN、P16INK4a、IL-37、Cys-C是脓毒症患者发生急性肾损伤的影响因素;P16INK4a、Cys-C水平与炎症因子TNF-α、IL-6、PCT呈正相关(P < 0.05),与肾功能指标Scr、BUN也呈正相关(P < 0.05);IL-37水平与炎症因子TNF-α、IL-6、PCT呈负相关(P < 0.05),与肾功能指标Scr、BUN也呈负相关(P < 0.05);当P16INK4a截断值为1.535时,曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)值为0.765,灵敏度为77.40%,特异度为69.60%;当IL-37截断值为101.46 mmol/L时,AUC值为0.871,灵敏度为79.95%,特异度为74.65%;当Cys-C截断值为1.72 mg/L时,诊断脓毒症急性肾损伤的AUC值为0.884,灵敏度为80.28%,特异度为76.06%;三者联合诊断的AUC值为0.916,灵敏度为93.96%,特异度为83.10%;三者联合诊断的AUC值、灵敏度、特异度分别高于P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C单独检测(P < 0.05)。结论 血清P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C三者联合检测在早期识别脓毒症急性肾损伤方面具有较高的预测能力,能够有效地提高早期脓毒症急性肾损伤的检出率。Abstract: Objective To investigate the value of combined detection of P16INK4a, interleukin-37(IL-37)and Cys-C in the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in sepsis.Methods One hundred and ninty-three patients with sepsis care were admitted in Naval Medicine Center from March 2021 to September 2023 were prospectively included in the study. They were divided to two groups according to whether acute kidney injury occurred (n=71) and simple sepsis(n=122). The baseline data of the two groups were compared, and the influencing factors of acute kidney injury in sepsis were analyzed by binary logistic regression, and the correlations of P16INK4a, IL-37 and Cys-C with inflammatory factors and renal function were analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis. Receiver operating characteristic curves were drawn to analyze the P16INK4a, IL-37 and Cys-C.Results In the total of 193 patients with sepsis, the incidence of acute kidney injury was 36.79%(71/193). There were no significant differences in primary infection site, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and diabetes between acute kidney injury group and sepsis group(P>0.05). The levels of sequential organ failure assessment, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation score, tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), IL-6, procalcitonin(PCT), serum creatinine(Scr), blood urea nitrogen(BUN), P16INK4a and Cys-C in acute renal injury group were significantly higher than those in simple sepsis group, and IL-37 level was significantly lower than that in simple sepsis group(P < 0.05). Binary logistic regression analysis showed that TNF-α, IL-6, PCT, Scr, BUN, P16INK4a, IL-37, Cys-C were the influential factors of acute kidney injury in sepsis patients. The levels of P16INK4a and Cys-C were positively correlated with inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6 and PCT(P < 0.05), and were also positively correlated with renal function indexes Scr and BUN(P < 0.05). IL-37 levels were negatively correlated with inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6 and PCT(P < 0.05), and were also negatively correlated with renal function indexes Scr and BUN(P < 0.05). When the cutoff value of P16INK4a was 1.535, the area under the curve(AUC) value for diagnosing acute renal injury in sepsis was 0.765, the sensitivity was 77.40%, and specificity 69.60%. When the IL-37 cut-off value was 101.46 mmol/L, the AUC value, sensitivity and specificity were 0.871, 79.95% and 74.65% respectively. When the cutoff value of Cys-C was 1.72 mg/L, the AUC value for diagnosing acute kidney injury in sepsis was 0.884, the sensitivity was 80.28%, and the specificity was 76.06%. The AUC value of the combined diagnosis was 0.916, the sensitivity was 93.96% and the specificity was 83.10%. The AUC value, sensitivity and specificity of the combined diagnosis were higher than those of P16INK4a, IL-37 and Cys-C alone(P < 0.05).Conclusion The combined detection of serum P16INK4a, IL-37 and Cys-C has high predictive ability in early identification of sepsis acute kidney injury, and can effectively improve the detection rate of early sepsis acute kidney injury.
-
Key words:
- sepsis /
- acute kidney injury /
- P16INK4a /
- IL-37 /
- Cys-C /
- diagnostic value
-

-
表 1 两组患者基线资料对比
项目 急性肾损伤组(71例) 单纯脓毒症组(122例) χ2/t P 年龄/岁 52.71±10.54 50.71±9.83 1.327 0.186 性别/例(%) 0.026 0.872 男 41(57.75) 69(56.56) 女 30(42.25) 53(43.44) 体重指数/(kg/m2) 24.59±2.86 24.01±2.79 1.379 0.169 原发感染部位/例(%) 0.976 0.807 呼吸系统 28(39.44) 46(37.70) 泌尿系统 18(25.35) 28(22.95) 消化系统 16(22.54) 26(21.31) 皮肤软组织/其他 9(12.68) 22(18.03) 合并基础疾病/例(%) 高血压 34(47.89) 52(42.62) 0.503 0.478 糖尿病 28(39.44) 45(36.89) 0.124 0.724 高脂血症 13(18.31) 19(15.57) 0.243 0.622 糖尿病 25(35.21) 37(30.33) 0.491 0.484 SOFA评分/分 8.03±2.31 5.47±1.24 10.019 < 0.001 APACHE Ⅱ评分/分 23.51±4.18 14.62±4.06 14.511 < 0.001 TNF-α/(pg/mL) 179.46±11.74 132.86±9.95 29.338 < 0.001 IL-6/(pg/mL) 142.87±11.82 119.53±8.79 15.624 < 0.001 PCT/(μg/L) 15.91±3.76 10.05±4.17 9.755 < 0.001 Scr/(μmol/L) 339.84±45.32 71.82±13.95 60.665 < 0.001 BUN(mmol/L) 9.93±2.45 7.05±1.42 10.347 < 0.001 P16INK4a mRNA 2.49±0.67 0.51±0.09 32.305 < 0.001 IL-37/(mmol/L) 92.79±26.87 113.54±30.72 4.905 < 0.001 Cys-C/(mg/L) 2.36±0.29 1.59±0.18 22.765 < 0.001 表 2 脓毒症有无急性肾损伤患者的二元logistic回归分析
变量 β SE Wald χ2 P OR(95%CI) SOFA评分 0.724 0.403 3.797 0.074 0.873(0.537~1.294) APACHE Ⅱ评分 0.629 0.398 3.380 0.116 0.916(0.642~1.078) TNF-α 1.275 0.224 10.805 < 0.001 2.185(1.524~4.793) IL-6 1.396 0.413 8.493 0.001 1.546(1.321~3.754) PCT 1.263 0.351 9.736 < 0.001 1.947(1.436~4.629) Scr 1.203 0.526 5.798 0.023 1.189(1.034~3.327) BUN 1.342 0.429 8.241 0.002 1.386(1.127~3.576) P16INK4a 1.196 0.416 7.988 0.005 1.243(1.104~3.418) IL-37 -1.693 0.279 11.181 < 0.001 0.476(0.295~1.206) Cys-C 1.438 0.524 6.875 0.007 1.196(1.094~3.392) 表 3 P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C水平与炎症因子、肾功能的相关性
指标 P16INK4a IL-37 Cys-C r P r P r P TNF-α 0.316 < 0.001 -0.227 < 0.001 0.359 < 0.001 IL-6 0.473 < 0.001 -0.303 < 0.001 0.471 < 0.001 PCT 0.358 < 0.001 -0.286 < 0.001 0.368 < 0.001 Scr 0.406 < 0.001 -0.312 < 0.001 0.401 < 0.001 BUN 0.314 < 0.001 -0.343 < 0.001 0.472 < 0.001 表 4 P16INK4a、IL-37和Cys-C对脓毒症急性肾损伤的诊断效能
指标 AUC值 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 约登指数 截断值 95%CI P P16INK4a 0.765 77.40 69.60 0.679 1.535 0.686~0.844 < 0.001 IL-37 0.871 80.28 76.06 0.824 101.46 mmol/L 0.812~0.931 < 0.001 Cys-C 0.884 79.95 74.65 0.718 1.72 mg/L 0.826~0.942 < 0.001 三者联合 0.916 93.96 83.10 0.882 - 0.868~0.965 < 0.001 -
[1] 李晓玲, 周文杰, 邓伟, 等. 凝血指标联合血清胱抑素C对脓毒症急性肾损伤患者预后的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2023, 39(1): 81-85.
[2] Oh DJ. A long journey for acute kidney injury biomarkers[J]. Ren Fail, 2020, 42(1): 154-165. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2020.1721300
[3] Costa NA, Gut AL, Azevedo PS, et al. Protein carbonyl concentration as a biomarker for development and mortality in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Biosci Rep, 2018, 38(1): BSR20171238. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171238
[4] 沙丽恒· 阿布德克, 吕欣炜, 郭仁楠, 等. 脓毒症相关急性肾损伤启动肾脏替代治疗时机探讨[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(1): 41-45. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.01.008
[5] 李锴, 赵明. 旱莲草下调P16~(INK4a)抑制LPS诱导的肾小球系膜细胞增殖及炎症反应[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2021, 22(11): 989-992. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2021.11.014
[6] 顾鹏, 陶维雄, 彭伟, 等. IL-37调控miR-106b-5p/PTEN抑制肾细胞癌细胞生物学行为[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(8): 1694-1699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2023.08.023
[7] 韦先锋, 李静, 王硕. 脑梗死患者Cys-C、UA及Hcy水平与预后相关性分析[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2023, 15(7): 1275-1278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6929.2023.07.043
[8] Munyendo C, Admani B, Mburugu P, et al. Prevalence of acute kidney injury and its characteristics among neonates with suspected sepsis in a tertiary hospital in Kenya[J]. Afr Health Sci. 2023, 23(1): 704-710. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v23i1.75
[9] Pan HC, Yang SY, Chiou TY, et al. Comparative accuracy of biomarkers for the prediction of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Crit Care, 2022, 26(1): 349. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04223-6
[10] 陈旋. 脓毒症并发急性肾损伤患者外周血单个核细胞中微小RNA-16-5 p、干扰素诱导跨膜蛋白3表达及临床意义[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志, 2023, 23(1): 45-51.
[11] Nusshag C, Rupp C, Schmitt F, et al. Cell Cycle Biomarkers and Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor for the Prediction of Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Requiring Renal Replacement Therapy: A Prospective, Exploratory Study[J]. Crit Care Med, 2019, 47(12): 999-1007. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004042
[12] 李佳, 袁野, 罗娟娟, 等. 联合肾动脉阻力指数和β2微球蛋白及降钙素原水平构建脓毒症合并急性肾损伤患者预后模型的验证评价[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2022, 23(10): 727-732. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2022.10.008
[13] 庹林蓉, 黄小军, 汤红平, 等. p16INK4a免疫染色对子宫颈细胞学筛查鳞状上皮病变检测的临床价值[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2022, 37(22): 4266-4269.
[14] Jurisic V, Obradovic J, Nikolic N, et al. Analyses of P16INK4a gene promoter methylation relative to molecular, demographic and clinical parameters characteristics in non-small cell lung cancer patients: A pilot study[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2023, 50(2): 971-979.
[15] Wu D, Tan H, Su W, et al. MZF1 mediates oncogene-induced senescence by promoting the transcription of p16INK4A[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(3): 414-426.
[16] 高胜男, 林江涛. IL-37的抗炎作用机制及其在哮喘中的研究进展[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2021, 41(6): 488-492.
[17] Bai J, Li Y, Li M, et al. IL-37 As a Potential Biotherapeutics of Inflammatory Diseases[J]. Current Drug Targets, 2020, 21(9): 855-863.
[18] Yu L, Fu H, Zhang H. The diagnostic value of combined detection of microRNA-155, TNF-α and IL-37 for active pulmonary tuberculosis in the elderly[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2022, 14(12): 9018-9024.
[19] 段刘剑, 章顺, 张林, 等. 外周血免疫指标对肾癌术前诊断与分期的临床意义[J]. 临床泌尿外科杂志, 2023, 38(2): 120-123, 127.
[20] 张娟娟, 杜云, 陈群, 等. 血清Cys-c、NLR、TFF3对妊娠期糖尿病早期肾功能损伤的预测价值[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2023, 15(12): 2117-2120.
[21] 武道荣, 方磊, 李睿, 等. APACHEⅡ评分联合血清RBP和Cys-C在ICU脓毒症性急性肾损伤患者中的评估价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2021, 22(8): 563-568. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2021.08.011
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 355
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: