Prognostic value of RDW/ALB and CRP/ALB in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia
-
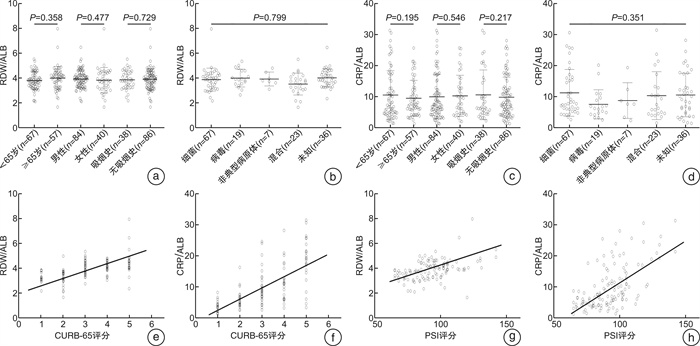
摘要: 目的 探究红细胞分布宽度/白蛋白比值(RDW/ALB)、C反应蛋白/白蛋白比值(CRP/ALB)预测重症社区感染性肺炎(sCAP)患者院内死亡的临床价值。方法 选取2018年6月-2021年3月期间我院重症监护病房收治的124例成人sCAP患者作为研究对象,另外招募120例年龄和性别相匹配的健康受试者作为正常对照组。获得患者特征数据和实验室数据,并计算CUR-65评分和肺炎严重程度指数(PSI)。根据血清ALB、CRP水平和RDW计算RDW/ALB比值和CRP/ALB比值。根据30 d院内病死率,将124例患者分为存活组和死亡组,应用多因素COX比例风险回归模型和受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价RDW/ALB、CRP/ALB比值与sCAP患者30 d死亡风险的相关性。结果 sCAP组患者RDW/ALB比值、CRP/ALB比值均高于对照组(P < 0.05);对于sCAP组患者,RDW/ALB比值、CRP/ALB比值与CURB-65评分(rs=0.608,0.669,P < 0.001)、PSI评分(rs=0.569,0.490,P < 0.001)呈正相关性。30 d病死率为37.10%(46/124)。死亡组患者RDW/ALB比值、CRP/ALB比值、CURB-65评分、PSI评分均高于存活组(P < 0.05)。经单因素和多因素COX回归模型分析,RDW/ALB比值[危险比(95%CI):2.635(1.237~5.614)]和CRP/ALB比值[危险比(95%CI):1.273(1.158~1.399)]是sCAP患者30 d内生存预后不良的强独立预测因子(P < 0.05)。联合检测RDW/ALB比值和CRP/ALB比值可进一步提高CURB-65评分+PSI评分预测sCAP患者30 d内死亡风险的曲线下面积(Z=-4.959,P < 0.05)。结论 RDW/ALB比值、CRP/ALB比值明显升高与sCAP疾病严重程度较高和30 d内生存预后不良有关,且增加这两项指标的检测结果可进一步提高CURB-65评分+PSI评分对sCAP的预后预测能力。
-
关键词:
- 红细胞分布宽度/白蛋白 /
- C反应蛋白/白蛋白 /
- 重症社区获得性肺炎 /
- CURB-65 /
- 预后
Abstract: Objective To investigate the prognostic value of red cell distribution width/albumin(RDW/ALB) ratio, C-reactive protein/albumin(CRP/ALB) ratio in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia(sCAP).Methods A total of 124 adult sCAP patients admitted to the intensive care unit of our hospital from June 2018 to March 2021 were selected as the research subjects, another 120 healthy age-and sex-matched subjects were recruited as normal controls. Data of patient characteristics and laboratory data were obtained and CURB-65, pneumonia severity index(PSI) was calculated. RDW/ALB ratio and CRP/ALB ratio was calculated based on serum RDW, CRP and ALB. 124 patients were divided into survival group and death group according to 30-day mortality in hospital. Multivariate COX proportional hazards regression model and receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve were used to evaluate the association between RDW/ALB ratio, CRP/ALB ratio and 30-day mortality of sCAP patients.Results RDW/ALB and CRP/ALB in sCAP group were higher than those in control group(P < 0.05), and in sCAP group, RDW/ALB ratio and CRP/ALB ratio were both positively correlated with CURB-65 score(rs=0.608, 0.669, P < 0.001) and PSI score(rs=0.569, 0.490, P < 0.001). The mortality of 30 days was 37.10%(46/124). RDW/ALB, CRP/ALB, CURB-65 and PSI were higher in death group than in survival group(P < 0.05). Univariate and multivariate COX models were used to analyze, RDW/ALB[risk ratio(95%CI): 2.635(1.237~5.614)]and CRP/ALB[risk ratio(95%CI): 1.273(1.158~1.399)]were strong independent predictors of poor survival within 30 days of sCAP patients(P < 0.05). The combination of RDW/ALB and CRP/ALB increased the area under the curve of CURB-65 + PSI to predict the 30 d mortality risk of sCAP patients(Z=-4.959, P < 0.05).Conclusion The higher RDW/ALB ratio and CRP/ALB ratio were associated with the higher disease severity of sCAP and the poor prognosis within 30 days. The predictive ability of CURB-65 + PSI score to the prognosis of sCAP could be further improved by increasing the results of these two indexes. -

-
表 1 两组一般临床资料比较
x±S,例(%),M(Q1,Q3) 指标 对照组(120例) sCAP组(124例) t/χ2/Z P 年龄/岁 62.89±10.12 64.02±8.76 0.934 0.352 男性 75(62.50) 84(67.74) 0.738 0.390 BMI 25.31±2.59 24.90±3.43 1.051 0.294 合并症 糖尿病史 15(12.50) 19(15.32) 0.405 0.525 高血压病史 24(20.0) 31(25.0) 0.873 0.350 冠心病史 19(15.83) 25(20.16) 0.773 0.379 实验室指标 WBC/(×109·L-1) 6.24(5.46,7.67) 8.77(6.76,11.57) -2.350 < 0.001 NEU/(×109·L-1) 3.47(3.02,3.85) 6.22(5.15,8.04) -3.189 < 0.001 LYM/(×109·L-1) 2.35(2.07,2.59) 1.79(1.52,2.16) -3.173 < 0.001 PLT/(×109·L-1) 247.34±48.73 195.01±72.81 6.576 < 0.001 HGB/(g·dL-1) 142.31±14.58 140.09±22.41 0.914 0.362 RDW/% 13.95±0.94 14.01±2.24 0.271 0.787 CRP/(mg·dL-1) 0.29(0,2.67) 27.50(17.50,48.79) -12.850 < 0.001 ALB/(g·dL-1) 4.89±0.29 3.67±0.50 23.209 < 0.001 RDW/ALB 2.81±0.34 3.88±0.83 13.008 < 0.001 CRP/ALB 0.051(0.019,0.064) 7.56(4.72,13.03) -9.404 < 0.001 表 2 存活组和死亡组sCAP患者一般临床资料比较
x±S,例(%) 指标 存活组(n=78) 死亡组(n=46) t/χ2/Z P 年龄/岁 62.68±7.81 66.28±9.84 2.248 0.026 男性 55(70.51) 29(63.04) 0.739 0.390 BMI 24.97±3.03 24.78±3.26 0.328 0.744 有创机械通气 5(6.41) 16(34.78) 16.561 < 0.001 感染性休克 4(5.13) 10(21.74) 7.972 0.005 共病 糖尿病史 9(11.54) 10(21.74) 2.321 0.128 高血压病史 15(19.23) 16(34.78) 3.732 0.053 冠心病史 15(19.23) 10(21.74) 0.113 0.737 基线生命体征 MAP/mmHg 91(84,98) 91(78,102) -0.694 0.605 呼吸频率/(次·mim-1) 20.91±1.99 28.89±4.46 13.691 < 0.001 心率/(次·mim-1) 84(78,95) 93(83,106) -1.409 0.013 体温/℃ 38.2(36.9,39.1) 38.3(37.0,39.7) -0.582 0.719 实验室指标 WBC/(×109·L-1) 8.60(6.63,11.18) 8.97(7.20,13.50) -1.141 0.254 NEU/(×109·L-1) 5.85(5.15,7.85) 6.57(5.48,8.16) -1.182 0.237 LYM/(×109·L-1) 1.80(1.44,2.18) 1.83(1.54,2.10) -0.008 0.994 PLT/(×109·L-1) 198.11±70.75 189.74±76.69 0.617 0.539 HGB/(g·dL-1) 139.26±21.42 142.60±22.76 0.822 0.413 RDW/% 13.63±2.14 14.66±2.28 2.527 0.013 CRP/(mg·dL-1) 21.55(15.0,31.0) 46.0(37.50,67.50) -6.470 < 0.001 ALB/(g·dL-1) 3.76±0.50 3.52±0.58 2.432 0.017 RDW/ALB 3.67±0.67 4.24±0.93 3.951 < 0.001 CRP/ALB 5.95(4.05,8.12) 13.82(10.82,20.18) -6.849 < 0.001 CURB-65评分/分 3.0(2.0,3.0) 4.0(3.0,5.0) -6.240 < 0.001 PSI评分/分 84.83±11.56 106.98±14.23 9.448 < 0.001 注:MAP, 平均动脉压。 表 3 影响sCAP患者30d生存预后不良的多因素COX比例风险回归分析
因素 单因素分析 多因素分析 HR 95%CI P HR 95%CI P 年龄 0.985 0.945~1.027 0.486 性别(以男性为参照) 1.402 0.648~3.032 0.391 感染性休克 5.139 1.508~17.512 0.009 0.903 0.311~2.618 0.581 病原学分布(以细菌感染为参照) 0.154 病毒vs.细菌 2.241 0.915~5.075 0.098 非典型病原体vs.细菌 2.612 0.771~8.786 0.217 混合vs.细菌 2.364 0.932~5.998 0.097 未知vs.细菌 2.018 0.672~9.031 0.319 吸烟史 1.029 0.998~1.021 0.057 糖尿病 3.920 0.475~8.933 0.474 高血压 2.871 0.079~21.372 0.550 冠心病 1.735 0.232~12.958 0.591 WBC 1.078 0.969~1.099 0.166 NEU 1.075 0.923~1.252 0.354 LYM 0.866 0.480~1.563 0.634 PLT 0.998 0.993~1.004 0.535 HGB 1.023 0.994~1.043 0.129 RDW/ALB 2.851 1.556~5.223 0.001 2.635 1.237~5.614 0.012 CRP/ALB 1.278 1.168~1.398 < 0.001 1.273 1.158~1.399 < 0.001 表 4 RDW/ALB比值和CRP/ALB比值单独或联合CURB-65评分+PSI评分预测30d死亡的ROC曲线分析结果
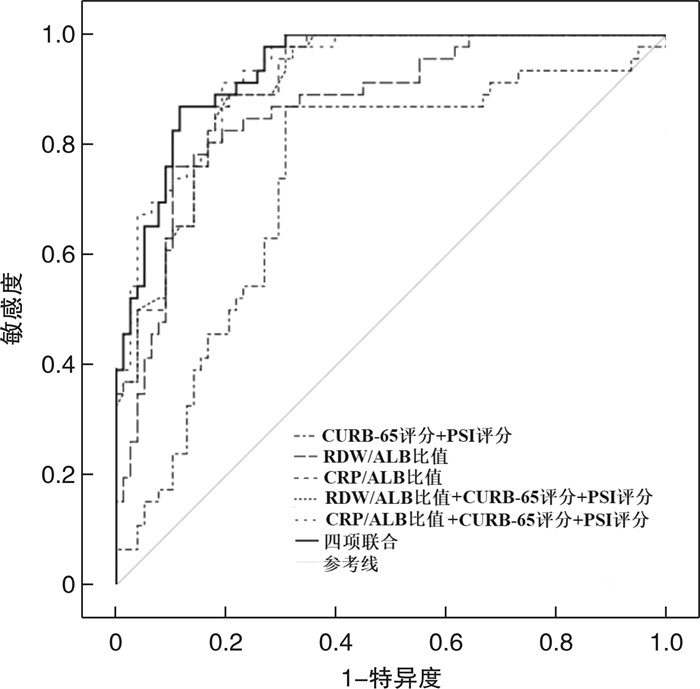
指标 AUC 95%CI 敏感度/% 特异度/% 最佳截断值 约登指数 CURB-65评分+PSI评分 0.735 0.641~0.828 87.0 69.2 0.349 0.562 RDW/ALB比值 0.869 0.804~0.934 76.1 89.7 3.858 0.658 CRP/ALB比值 0.909 0.860~0.957 89.1 79.5 10.736 0.686 RDW/ALB比值+CURB-65评分+PSI评分 0.909 0.860~0.957 89.1 79.5 0.344 0.686 CRP/ALB比值+CURB-65评分+PSI评分 0.928 0.886~0.970 88.1 80.8 0.323 0.689 四项指标联合 0.938 0.899~0.976 87.0 88.5 0.460 0.755 -
[1] Wu X, Li Y, Zhang M, et al. Etiology of Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults Based on Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing: A Prospective Multicenter Study[J]. Infect Dis Ther, 2020, 9(4): 1003-1015. doi: 10.1007/s40121-020-00353-y
[2] Wang C, Zhang H, Cao X, et al. Red cell distribution width(RDW): a prognostic indicator of severe COVID-19[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(19): 1230. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-6090
[3] 侯彦丽, 金旭婷, 李佳媚, 等. 红细胞分布宽度与危重症患者病死率的相关性研究[J]. 中国急救医学, 2021, 41(2): 111-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJJY202102004.htm
[4] 张鹏, 齐保龙, 孙耕耘. 血清C-反应蛋白和红细胞分布宽度在AECOPD与稳定期的变化及意义[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2015, 20(1): 16-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFK201501008.htm
[5] Horta-Baas G, Romero-Figueroa M. Clinical utility of red blood cell distribution width in inflammatory and non-inflammatory joint diseases[J]. Int J Rheum Dis, 2019, 22(1): 47-54. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13332
[6] 郭红玲, 欧阳艳红, 王圣, 等. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者的hs-CRP/ALB变化对预后的预测价值[J]. 中国急救医学, 2020, 40(2): 102-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJJY202002004.htm
[7] 中华医学会呼吸分会. 中国成人社区获得性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2016)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2016, 39(4): 241-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KGYY202003009.htm
[8] Brabrand M, Henriksen DP. CURB-65 Score is Equal to NEWS for Identifying Mortality Risk of Pneumonia Patients: An Observational Study[J]. Lung, 2018, 196(3): 359-361. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0105-y
[9] Fine MJ, Auble TE, Yealy DM, et al. A prediction rule to identify low-risk patients with community-acquired pneumonia[J]. N Engl J Med, 1997, 336(4): 243-50. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199701233360402
[10] 郭云, 杜紫燕, 王振, 等. 老年社区获得性肺炎预后评估方法[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(1): 63-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202101016.htm
[11] Lee H, Kim I, Kang BH, et al. Prognostic value of serial neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio measurements in hospitalized community-acquired pneumonia[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(4): e0250067.
[12] 秦志均, 刘磊, 孙群, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者外周血细胞动态变化特征及预测价值[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2020, 19(5): 457-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHW202005010.htm
[13] Viasus D, Garcia-Vidal C, Simonetti A, et al. Prognostic value of serum albumin levels in hospitalized adults with community-acquired pneumonia[J]. J Infect, 2013, 66(5): 415-423.
[14] Lee J, Kim K, Jo YH, et al. Severe thinness is associated with mortality in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a prospective observational study[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2015, 33(2): 209-213.
[15] 陈丽, 陆晓晔, 朱长清. 白蛋白对重症社区获得性肺炎预后的评估价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2019, 20(7): 537-540. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZLC201907008.htm
[16] 钟海潮, 莫瑛. 血清C反应蛋白/白蛋白水平与老年重症肺炎所致急性呼吸窘迫综合征及血管内皮通透性的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(17): 4214-4217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLXZ201917039.htm
[17] Efe SÇ, Özdemir CÖ, Gündo an C, et al. Value of C-reactive Protein/Albumin Ratio for Predicting Ischemia in Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy[J]. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther, 2020, 29(3): 112-117.
[18] Yoo JW, Ju SM, Lee SJ, et al. Red cell distribution width/albumin ratio is associated with 60-day mortality in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Infect Dis(Lond), 2020, 52(4): 266-270.
-




 下载:
下载: