Evaluation value of early sequential organ failure score changes after admission for short-term prognosis of elderly sepsis
-
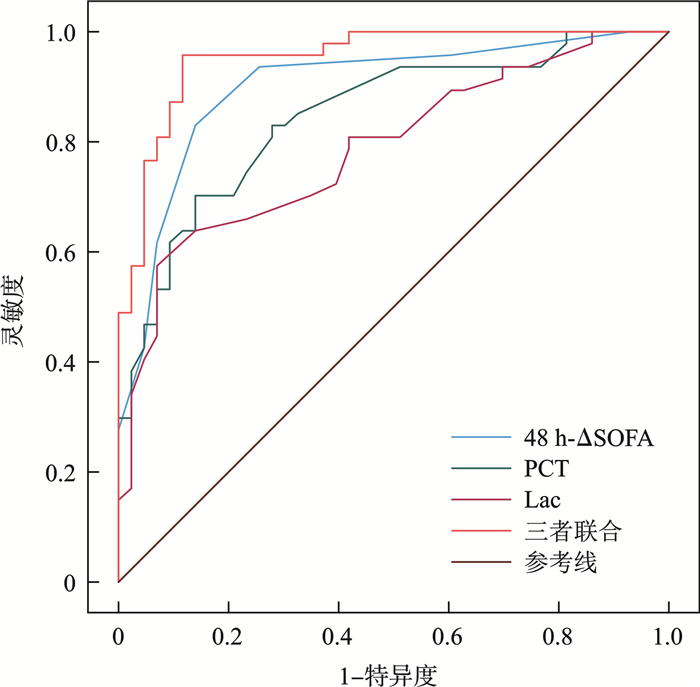
摘要: 目的 探讨入院后早期序贯器官衰竭评分(sequential organ failure assessment,SOFA)变化(ΔSOFA)对老年脓毒症短期预后的评估价值。方法 回顾性分析我院急诊重症监护病房(EICU)2016年1月—2019年12月收治的90例老年脓毒症患者的临床资料,根据28 d生存状况,分成生存组和死亡组,收集并分析一般资料和相关实验室指标。采用logistic回归分析筛选老年脓毒症患者28 d内死亡的危险因素;绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,探讨48 h-ΔSOFA对老年脓毒症28 d预后的评估价值。结果 90例老年脓毒症患者中,28 d内死亡47例,生存43例。单因素分析显示,死亡组入院即刻SOFA、48 h-ΔSOFA、血降钙素原和乳酸水平高于生存组,血清Ca2+水平低于生存组,差异均有统计学意义(均P < 0.05)。多因素二元logistic回顾分析显示,48 h-ΔSOFA是老年脓毒症28 d死亡的独立危险因素(OR=2.383,95%CI:1.535~3.702,P < 0.01);应用绘制ROC曲线分析显示,入院48 h-ΔSOFA预测老年脓毒症患者28 d预后的曲线下面积为0.900(95%CI:0.834~0.967,P < 0.01)。结论 48 h-ΔSOFA在入院早期评估老年脓毒症病情严重程度及短期预后方面具有良好、可靠的预测价值。Abstract: Objective To explore the value of early changes in sequential organ failure assessment(SOFA) after admission(ΔSOFA) in evaluating the short-term prognosis of elderly sepsis.Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 90 elderly sepsis patients admitted to the emergency intensive care unit(EICU) of our hospital from January 2016 to December 2019. Based on their 28 day survival status, they were divided into a survival group and a death group. General information and relevant laboratory indicators were collected and analyzed. Using logistic regression analysis to screen risk factors for mortality within 28 days in elderly sepsis patients; Draw receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curves to explore the evaluation value of 48 h-ΔSOFA in the 28 day prognosis of elderly sepsis.Results Among 90 elderly sepsis patients, 47 cases died within 28 days and 43 cases survived. Univariate analysis showed that the levels of SOFA, 48 h-ΔSOFA, procalcitonin and lactate in the death group were higher than those in the survival group upon admission, while the serum Ca2+ level was lower than that in the survival group, and the differences were statistically significant(all P < 0.05). Multivariate binary logistic review analysis showed that 48 h-ΔSOFA was an independent risk factor for 28 day mortality in elderly sepsis(OR=2.383, 95%CI: 1.535-3.702, P < 0.01). The application of ROC curve analysis showed that the area under the curve for predicting the 28 day prognosis of elderly sepsis patients with 48 h-ΔSOFA after admission was 0.900(95%CI: 0.834-0.967, P < 0.01).Conclusion 48 h-ΔSOFA has good and reliable predictive value in evaluating the severity and short-term prognosis of elderly sepsis in the early stage of admission.
-
Key words:
- sepsis /
- elderly /
- prognosis /
- sequential organ failure assessment
-

-
表 1 受试者一般情况和临床特征比较
M(P25,P75),X±S 项目 总数(90例) 生存(43例) 死亡(47例) χ2/t/Z P 年龄/岁 82.9±7.3 81.3±8.0 84.3±6.3 1.930 0.058 性别/例(%) 0.040 0.844 男 64(71.1) 31(48.4) 33(51.6) 女 26(28.9) 12(46.2) 14(53.8) 体温/℃ 36.7(36.5~37.0) 36.7(36.5~37.2) 36.6(36.4~36.9) -0.552 0.581 平均动脉压/mmHg 103.6±17.2 100.7±14.1 89.9±17.2 2.490 0.118 心率/(次/min) 88.0(78.0,95.3) 87.0(78.0,95.0) 90.0(77.0,97.0) -0.480 0.470 呼吸频率/(次/min) 18.0(18.0,20.0) 18.0(18.0,20.0) 19.0(18.0,20.0) -0.920 0.358 高血压/例(%) 0.700 0.404 是 44(48.9) 23(52.3) 21(47.7) 否 46(51.1) 20(43.5) 26(56.5) 糖尿病/例(%) 0.270 0.605 是 29(32.2) 15(51.7) 14(48.3) 否 61(67.8) 28(45.9) 33(54.1) 呼吸系统疾病/例(%) 2.780 0.095 是 24(26.7) 8(33.3) 16(66.7) 否 66(73.3) 35(53.0) 31(47.0) 心血管系统疾病/例(%) 0.840 0.360 是 65(48.2) 33(50.8) 32(49.2) 否 25(27.8) 10(40.0) 15(60.0) 神经系统疾病/例(%) 0.700 0.402 是 29(32.2) 12(41.4) 17(58.6) 否 61(67.8) 31(50.8) 30(49.2) PCT/(ng/mL) 0.14(0.09,0.23) 0.1(0.07,0.13) 0.26(0.13,0.44) 5.650 < 0.001 Lac/(mmol/L) 1.98(1.25,2.70) 1.39(1.02,2.00) 2.6(1.60,3.50) 4.699 < 0.001 Ca2+/(mmol/L) 2.07(1.98,2.15) 2.15(1.99,2.18) 2.03(1.93,2.10) -3.84 < 0.001 即刻SOFA/分 3.00(2.00,3.25) 2.00(2.00,3.00) 3.00(2.00,4.00) 2.552 0.011 48 h-ΔSOFA 0.50(-1.00,2.25) -1.00(-2.00,0) 2.00(1.00,4.00) 6.596 < 0.001 注:1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 预测老年脓毒症短期预后的logistic回归模型
项目 β OR P 95%CI 48 h-ΔSOFA 0.869 2.383 < 0.001 1.535~3.702 PCT 9.782 17.709 0.004 2.400~127.478 Lac 1.178 3.249 0.009 1.334~7.914 表 3 研究指标的AUC和界值
项目 AUC cut-off值 灵敏度 特异度 约登指数 PCT 0.846 0.160 ng/mL 0.702 0.860 0.562 Lac 0.787 2.400 mmol/L 0.570 0.930 0.504 48 h-ΔSOFA 0.900 0.500 0.830 0.860 0.690 三者联合 0.953 0.393 0.957 0.884 0.841 -
[1] Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 47(11): 1181-1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
[2] Yealy DM, Mohr NM, Shapiro NI, et al. Early care of adults with suspected sepsis in the emergency department and out-of-hospital environment: a consensus-based task force report[J]. Ann Emerg Med, 2021, 78(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2021.02.006
[3] Fleischmann-Struzek C, Mellhammar L, Rose N, et al. Incidence and mortality of hospital-and ICU-treated sepsis: results from an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2020, 46(8): 1552-1562. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06151-x
[4] Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10219): 200-211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
[5] 王睿之, 禹茜, 蔡强, 等. 脓毒症患者血清IL-3的表达情况及其临床意义[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2020, 40(2): 322-326.
[6] 刘超, 毛智, 周飞虎. 老年脓毒症的研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2017, 42(6): 563-568.
[7] Kingren MS, Starr ME, Saito H. Divergent sepsis pathophysiology in older adults[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2021, 35(16): 1358-1375. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0056
[8] 张新超, 温伟, 董士民. 老年脓毒症诊断与治疗中的困难与挑战[J]. 中国急救医学, 2024, 44(5): 376-384.
[9] Mankowski RT, Anton SD, Ghita GL, et al. Older adults demonstrate biomarker evidence of the persistent inflammation, immunosuppression, and catabolism syndrome(PICS)after sepsis[J]. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, 2022, 77(1): 188-196. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab080
[10] Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ, et al. Assessment of clinical criteria for sepsis: for the third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock(sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 762-774. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0288
[11] 丁佳, 皋源. PCT清除率与ΔSOFA在复杂腹腔感染中的预测价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2016, 32(24): 4034-4037.
[12] 朱梦莉, 王智超, 张婧, 等. 全身炎症反应综合征评分、序贯器官衰竭评分、快速脓毒症相关器官功能障碍评分对急诊感染性疾病预后的评估价值[J]. 安徽医药, 2021, 25(2): 261-264.
[13] 刘炳炜, 徐燕平, 席绍松, 等. SOFA评分联合PCT检测对脓毒症患者病情及其预后的临床评估价值[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(3): 391-393.
[14] 高磊, 鲍万国, 齐翀, 等. 降钙素原及其变化率联合序贯器官衰竭评分对脓毒症病情与预后判别的临床价值[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2019, 35(17): 2789-2793.
[15] Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, et al. The SOFA(Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment)score to describe organ dysfunction/failure[J]. Intensive Care Med, 1996, 22(7): 707-710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751
[16] 谢俊涛, 陈钦桂. 序贯器官衰竭评估评分对老年脓毒症患者预后的预测价值[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2020, 39(8): 914-918.
[17] 李梅. C-反应蛋白与白细胞介素-6及降钙素原联合检测在感染性疾病中的应用[J]. 实用检验医师杂志, 2023, 15(3): 266-269.
[18] Dong XX, Zhang QQ, Yu XY, et al. Metabolic lactate production coordinates vasculature development and progenitor behavior in the developing mouse neocortex[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2022, 25(7): 865-875. doi: 10.1038/s41593-022-01093-7
[19] 孟鹏飞, 石正松, 陈亚君, 等. 血清乳酸、降钙素原、内毒素对脓毒症及感染性休克预后的预测价值[J]. 分子诊断与治疗杂志, 2023, 15(3): 527-530, 535.
[20] Do SN, Dao CX, Nguyen TA, et al. Sequential organ failure assessment(SOFA)score for predicting mortality in patients with sepsis in Vietnamese intensive care units: a multicentre, cross-sectional study[J]. BMJ Open, 2023, 13(3): e064870. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064870
[21] 刘辉, 祝筱梅, 姚咏明. 深化对血乳酸在脓毒症中作用与意义的新认识[J]. 中国急救医学, 2024, 44(8): 668-671.
[22] Assicot M, Gendrel D, Carsin H, et al. High serum procalcitonin concentrations in patients with sepsis and infection[J]. Lancet, 1993, 341(8844): 515-518. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)90277-N
[23] Kyriazopoulou E, Liaskou-Antoniou L, Adamis G, et al. Procalcitonin to reduce long-term infection-associated adverse events in sepsis. A randomized trial[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2021, 203(2): 202-210. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1201OC
[24] 卢苏, 孙健, 童朝阳. 乳酸与48 h乳酸清除率对脓毒症患者预后的预测价值[J]. 中国临床医学, 2023, 30(1): 91-96.
[25] Chen RX, Wu ZQ, Li ZY, et al. Prognostic predictors in patients with sepsis after gastrointestinal tumor surgery: a retrospective study[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2021, 13(3): 256-266. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v13.i3.256
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 85
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: