The correlation between serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 levels and organ function damage in sepsis patients
-
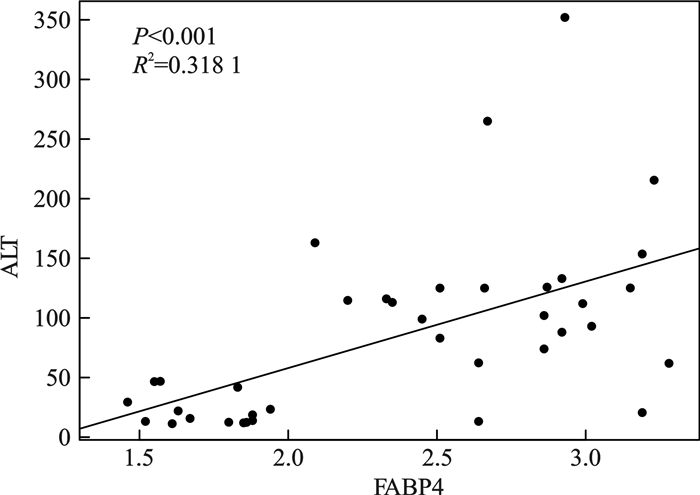
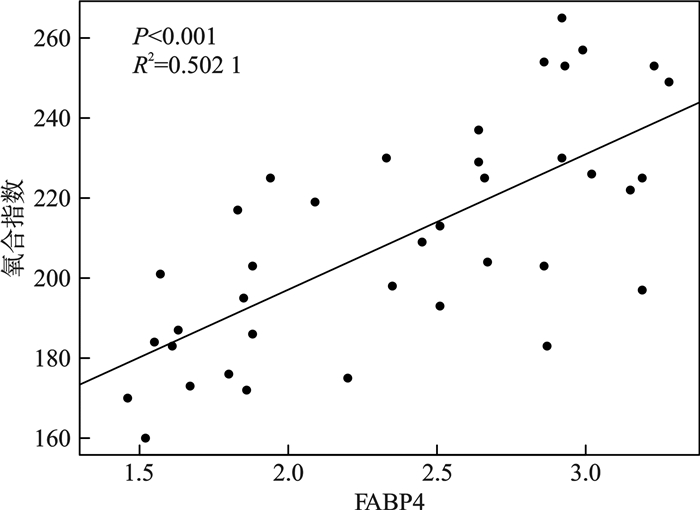
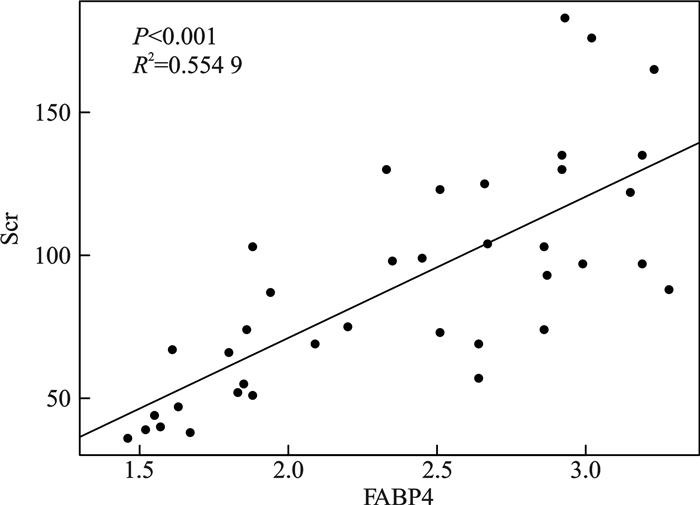
摘要: 目的 探究脓毒症患者中血清脂肪酸结合蛋白(fatty acid binding protein,FABP)表达水平与脓毒症患者脏器功能损伤的相关性。方法 收集自2024年6月—2024年10月就诊于北京清华长庚医院急诊医学科的38例脓毒症患者,依据Sepsis 3.0标准将入组患者分为脓毒症组(20例)及脓毒症休克组(18例),收集患者一般资料进行统计学分析。结果 脓毒症组及脓毒症休克组患者的年龄、性别、感染部位、心率、N末端B型利钠肽原(N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide,NT-proBNP)、FABP4、血肌酐(serum creatinine,Scr)、尿素氮、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(aspartate aminotransferase,AST)、白细胞计数、血小板计数、氧合指数、降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、序贯器官衰竭评分(sequential organ failure assessment,SOFA)及格拉斯哥昏迷评分(Glasgow coma scale,GCS)统计学分析结果显示,两组患者年龄、性别、感染部位、心率、NT-proBNP、尿素氮、AST、血小板计数、GCS评分间差异无统计学意义。两组患者血清FABP4水平、Scr、ALT、白细胞计数、氧合指数、PCT及SOFA评分差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。回归分析显示脏器相关损伤标记物Scr、ALT及氧合指数水平与FABP4水平存在正相关,其中Scr(R2=0.554 9,P < 0.001),ALT(R2=0.318 1,P < 0.001),氧合指数(R2=0.502 1,P < 0.001)。结论 研究结果显示,血清FABP4水平与器官功能损伤存在相关性。Abstract: Objective To investigate the correlation between serum fatty acid binding protein-4(FABP4) expression levels and organ function damage in patients with sepsis.Methods Patients with sepsis who visited the Emergency Medicine Department of Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital from June 2024 to October 2024 were collected. Based on the Sepsis 3.0 criteria, the enrolled patients were divided into a sepsis group(n=20) and a septic shock group(n=18). General patient information was collected for statistical analysis.Results A total of 38 patients were included in this study. Statistical analysis was performed on age, gender, infection site, heart rate, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide(NT-proBNP), FABP4, serum creatinine(Scr), urea nitrogen, alanine transaminase(ALT), aspartate aminotransferase(AST), white blood cell count, platelet count, oxygenation index, procalcitonin(PCT), sequential organ failure assessment(SOFA) score, and Glasgow coma scale(GCS) score between the two groups. The results showed no statistically significant differences in age, gender, infection site, heart rate, NT-proBNP, urea nitrogen, AST, platelet count, and GCS score between the two groups. However, there were statistically significant differences in serum FABP4 levels, Scr, ALT, white blood cell count, oxygenation index, PCT, and SOFA scores between the two groups(P < 0.05). Regression analysis revealed a positive correlation between organ-related injury markers(Scr, ALT, and oxygenation index) and FABP4 levels, with Scr(R2=0.554 9, P < 0.001), ALT(R2=0.318 1, P < 0.001), and oxygenation index(R2=0.502 1, P < 0.001).Conclusion The study results indicate a correlation between serum FABP4 levels and organ function damage.
-
Key words:
- sepsis /
- fatty acid binding protein /
- organ dysfunction /
- correlation analysis
-

-
表 1 脓毒症组与脓毒症休克组一般资料 X±S,M(P25,P75)
临床资料 脓毒症(20例) 脓毒症休克(18例) P 年龄/岁 74.90±9.36 79.53±8.85 0.932 性别/例 1.000 男 12 10 女 8 8 感染部位/例 1.000 腹腔 9 9 肺部 11 9 心率/(次/min) 82.35±15.17 88.33±13.15 0.064 NT-proBNP/(pg/mL) 260.50(222.50,307.50) 299.79(213.74,396.79) 0.007 FABP4/(ng/mL) 1.65±0.27 2.85±0.34 < 0.001 肌酐/(μmol/L) 60.40±21.38 122.56±58.99 < 0.001 尿素氮/(mmol/L) 10.05±4.17 13.73±8.33 0.065 ALT/(U/L) 28.20±9.06 92.00±18.56 0.003 AST/(U/L) 28.26±13.05 31.41±16.85 0.106 白细胞计数/(×109/L) 6.92±3.93 13.20±4.63 0.002 血小板计数/(×109/L) 228.05±62.14 183.61±91.10 0.085 氧合指数/mmHg 230.50±35.06 182.83±28.87 0.001 PCT/(ng/mL) 0.91±0.47 2.35±0.64 < 0.001 SOFA评分/分 5.43±1.02 9.13±1.41 < 0.001 GCS评分/分 10.75±2.16 9.00±2.94 0.079 -
[1] Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 47(11): 1181-1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
[2] Font MD, Thyagarajan B, Khanna AK. Sepsis and Septic Shock-Basics of diagnosis, pathophysiology and clinical decision making[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2020, 104(4): 573-585. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2020.02.011
[3] Gauer R, Forbes D, Boyer N. Sepsis: diagnosis and management[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2020, 101(7): 409-418.
[4] Piva S, Bertoni M, Gitti N, et al. Neurological complications of sepsis[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2023, 29(2): 75-84. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000001022
[5] Yan MY, Gustad LT, Nytrø Ø. Sepsis prediction, early detection, and identification using clinical text for machine learning: a systematic review[J]. J Am Med Inform Assoc, 2022, 29(3): 559-575. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocab236
[6] Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: from cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2013, 13: 862-874. doi: 10.1038/nri3552
[7] Shand H, Patra S, Ghorai S. Fatty acid binding protein as a new age biomarker[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2025, 565: 120029. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2024.120029
[8] Huang X, Zhou YC, Sun YW, et al. Intestinal fatty acid binding protein: a rising therapeutic target in lipid metabolism[J]. Prog Lipid Res, 2022, 87: 101178. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101178
[9] Furuhashi M. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2019, 26(3): 216-232. doi: 10.5551/jat.48710
[10] Glaser ST, Jayanetti K, Oubraim S, et al. Fatty acid binding proteins are novel modulators of synaptic epoxyeicosatrienoic acid signaling in the brain[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 15234. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42504-4
[11] Xiao Y, Shu LL, Wu XP, et al. Fatty acid binding protein 4 promotes autoimmune diabetes by recruitment and activation of pancreatic islet macrophages[J]. JCI Insight, 2021, 6(7): e141814. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141814
[12] Trojnar M, Patro-Małysza J, Kimber-Trojnar, et al. Associations between fatty acid-binding protein 4-A proinflammatory adipokine and insulin resistance, gestational and type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(3): 227. doi: 10.3390/cells8030227
[13] Aleksandrova K, Drogan D, Weikert C, et al. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 and risk of type 2 diabetes, myocardial infarction, and stroke: a prospective cohort study[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2019, 104(12): 5991-6002.
[14] Sun J, Esplugues E, Bort A, et al. Fatty acid binding protein 5 suppression attenuates obesity-induced hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting ferroptosis and intratumoral immune rewiring[J]. Nat Metab, 2024, 6(4): 741-763. doi: 10.1038/s42255-024-01019-6
[15] Hajizadeh M, Saboor-Yaraghi A A, Meamar A R, et al. The fatty acid-binding protein(FABP)decreases the clinical signs and modulates immune responses in a mouse model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis(EAE)[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 96: 107756. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107756
[16] Guo D, Lin CX, Lu YH, et al. FABP4 secreted by M1-polarized macrophages promotes synovitis and angiogenesis to exacerbate rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Bone Res, 2022, 10(1): 45. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00211-2
[17] Wang B, Xu J, Ren Q, et al. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 is a therapeutic target for septic acute kidney injury by regulating inflammatory response and cell apoptosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(4): 333. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04794-w
[18] Xuan WX, Wu X, Zheng LC, et al. Gut microbiota-derived acetic acids promoted sepsis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome by delaying neutrophil apoptosis through FABP4[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2024, 81(1): 438. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05474-y
[19] Zhang YQ, Zhao XT, Deng LL, et al. High expression of FABP4 and FABP6 in patients with colorectal cancer[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2019, 17(1): 171. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1714-5
[20] Vincent JL. Current sepsis therapeutics[J]. EBioMedicine, 2022, 86: 104318. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104318
[21] Li X, Lin Z, Xu SY, et al. Knockdown of KBTBD7 attenuates septic lung injury by inhibiting ferroptosis and improving mitochondrial dysfunction[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 133: 112129. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112129
[22] Li ZF, Wang YC, Feng QR, et al. Inhibition of the C3a receptor attenuates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by suppressing pyroptosis of the pulmonary vascular endothelial cells[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 184: 208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.02.032
[23] Aslani MR, Ghazaei Z, Ghobadi H. Correlation of serum fatty acid binding protein-4 and interleukin-6 with airflow limitation and quality of life in stable and acute exacerbation of COPD[J]. Turk J Med Sci, 2020, 50(2): 337-345.
[24] Qi SS. Inhibition of FABP4 ameliorates IL-13-induced inflammatory response and barrier dysfunction in nasal mucosal epithelial cells through the regulation of ferroptosis[J]. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2024.
[25] Gong YQ, Yu ZH, Gao Y, et al. FABP4 inhibitors suppress inflammation and oxidative stress in murine and cell models of acute lung injury[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 496(4): 1115-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.150
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 82
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: