Construction of a scoring tool for early screening sepsis in emergency department based on the NEWS with biomarkers
-
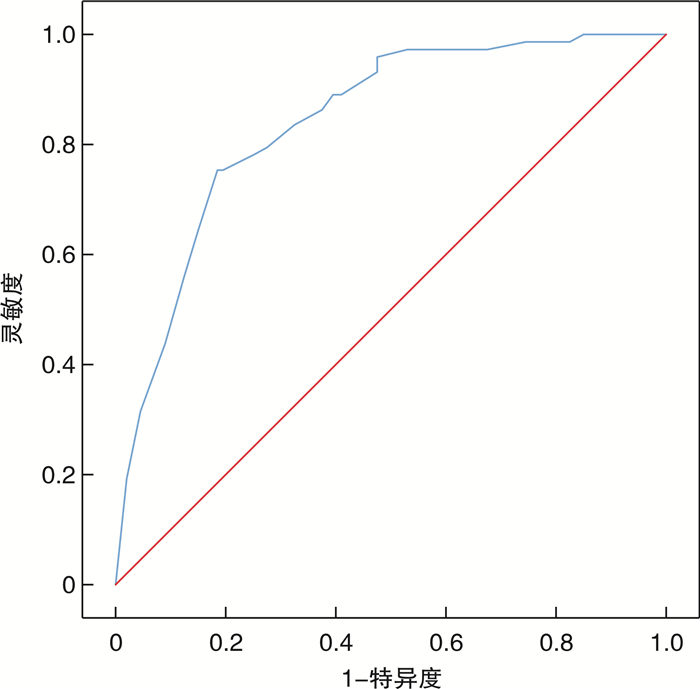
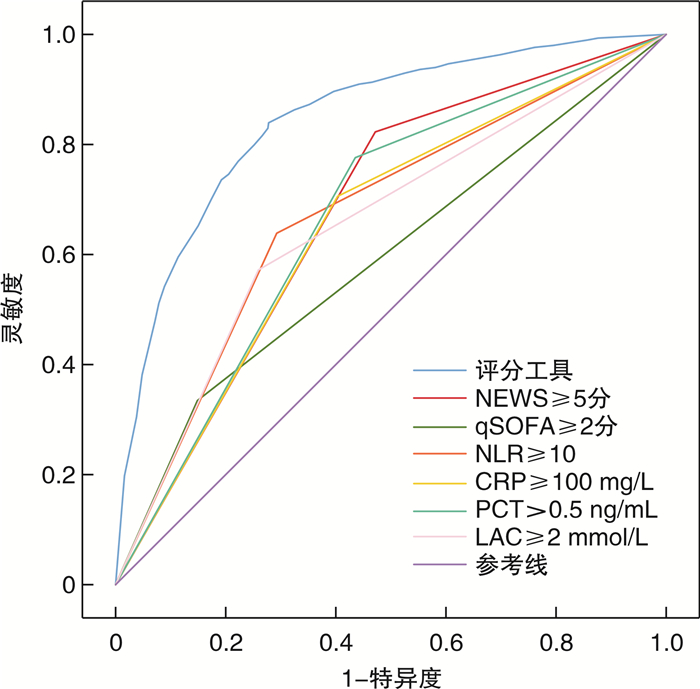
摘要: 目的 构建国家早期预警评分(national early warning score,NEWS)联合生物标志物的急诊筛查脓毒症的评分工具,并验证其诊断效能。方法 本研究采用整群抽样法,连续收集2020年1月1日—2022年10月31日苏州大学附属第二医院急诊抢救室救治的986例急性感染患者临床资料。按照2016版Sepsis 3.0诊断标准分为脓毒症组(299例)和非脓毒症感染组(687例)。采用单因素和多因素logistic回归分析(逐步回归前进法)筛选独立危险因素,根据各诊断指标β值构建急诊筛查脓毒症评分工具。使用受试者工作特征(receiver operating curve,ROC)曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)和Hosmer-Lemeshow(H-L)检验评价评分工具的区分度和校准度;然后,收集苏州九龙医院2021年1月1日-2022年10月31日急诊救治的273例急性感染患者(其中脓毒症73例),对评分工具进行外部验证。结果 单因素分析发现糖尿病、尿毒症、慢性阻塞性肺部疾病(chronic obstructive pulmonary disease,COPD)、恶性肿瘤、昏迷(glasgow coma scale,GCS)评分、心率、呼吸频率、收缩压、舒张压、平均动脉压(mean arterial pressure,MAP)、中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞、中性粒细胞与淋巴细胞比值(neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio,NLR)、血小板、D-二聚体、C-反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)、降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、血乳酸(blood lactic acid,LAC)以及国家早期预警评分(national early warning score,NEWS)是急诊脓毒症发生的危险因素;经多因素logistic回归分析,最终评分工具由NEWS≥5分赋值3分,NLR≥10、CRP≥100 mg/L、PCT>0.5 ng/mL以及LAC≥2 mmol/L各赋值2分组成,总分11分。该评分工具预测急诊脓毒症正确率为79.9%,AUC为0.845(95%CI:0.816~0.869);当最佳截断值为7分时,灵敏度为83.9%,特异度为72.2%。H-L检验χ2=4.129,P=0.845。外部验证AUC为0.841(95%CI:0.792~0.891),灵敏度为75.5%,特异度为80.9%。结论 NEWS联合生物标志物构建的急诊筛查脓毒症评分工具,其临床诊断效能良好,可辅助急诊识别脓毒症患者。Abstract: Objective To construct a scoring tool for screening sepsis in emergency department based on the national early warning score(NEWS) with biomarkers, and to validate its diagnostic efficacy.Methods In this study, the clinical data of patients with acute infections treated in the emergency room of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University during the period from January 1, 2020 to October 31, 2022 were consecutively included using the whole cluster sampling method. They were categorized into sepsis(299 cases)and non-sepsis infection groups(687 cases)according to the 2016 edition of Sepsis 3. 0 diagnostic criteria. Independent risk factors were screened using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses(stepwise regression forward method), and an emergency screening sepsis scoring tool was constructed based on the β-value of each diagnostic index. The area under curve(AUC) of receiver operating characteristics(ROC) and the Hosmer-Lemeshow(H-L) test were used to evaluate the differentiation and calibration of the scoring tool. Then, 273 patients with acute infections(73 of them with sepsis) treated in the emergency department of Suzhou Kowloon Hospital of Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine from January 1, 2021, to October 31, 2022, were included to externally validate the scoring tool.Results A total of 986 patients with acute infections were included, including 299 with sepsis and 687 with non-septic infections. Univariate analysis identified diabetes mellitus, uremia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD), malignancy, glasgow coma scale(GCS), heart rate, respiratory rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial pressure(MAP), neutrophils, lymphocytes, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio(NLR), platelets, D-dimer, C-reactive protein(CRP), procalcitonin(PCT), blood lactate(LAC), and the NEWS as risk factors for the development of emergency sepsis. After multifactorial logistic regression analysis, the final scoring tool consisted of 3 points assigned to NEWS ≥5, and 2 points assigned to each of NLR ≥10, CRP ≥100 mg/L, PCT>0.5 ng/mL, and LAC ≥2 mmol/L, with a total score of 11 points. The scoring tool predicted emergency sepsis correctly in 79.9% of cases with an AUC of 0.845(95%CI: 0.816-0.869); the sensitivity was 83.9% and the specificity was 72.2% when the optimal cut-off value was 7. The H-L test chi-square value was 4.129, P=0.845. The external validation AUC was 0.841(95%CI: 0.792-0.891), with a sensitivity of 75.5% and a specificity of 80.9%.Conclusion The clinical diagnostic efficacy of the NEWS combined with biomarker-constructed emergency screening sepsis scoring tool is good and can assist in identifying patients with sepsis in the emergency department.
-
Key words:
- national early warning score /
- biomarkers /
- emergency department /
- screening /
- sepsis /
- scoring system
-

-
表 1 脓毒症组与非脓毒症感染组患者临床基线资料
M(P25,P75) 影响因素 总体(986例) 脓毒症组(299例) 非脓毒症感染组(687例) χ2/Z/t P 年龄/岁 74(65,80) 73(63,81) 75(67,80) -0.952 0.341 性别/例(%) 0.809 0.369 男 598(60.6) 175(58.5) 423(61.6) 女 388(39.4) 124(41.5) 264(38.4) 基础疾病/例(%) 高血压 0.424 0.515 否 625(63.4) 185(61.9) 440(64.0) 是 361(36.6) 114(38.1) 247(36.0) 糖尿病 4.791 0.029 否 640(64.9) 179(59.9) 461(67.1) 是 346(35.1) 120(40.1) 226(32.9) 尿毒症 12.562 <0.01 否 807(81.8) 225(75.3) 582(84.7) 是 179(18.2) 74(24.7) 105(15.3) 脑卒中后遗症 0.028 0.867 否 868(88.0) 264(88.3) 604(87.9) 是 118(12.0) 35(11.7) 83(12.1) COPD 3.794 0.051 否 852(86.4) 268(89.6) 584(85.0) 是 134(13.6) 31(10.4) 103(15.0) 恶性肿瘤 3.091 0.079 否 853(86.5) 250(83.6) 603(87.8) 是 133(13.5) 49(16.4) 84(12.2) 感染部位/例(%) 7.016 0.135 肺部感染 486(49.3) 133(44.5) 353(51.4) 腹部感染 220(22.3) 79(26.4) 141(20.5) 泌尿系感染 178(18.1) 59(19.7) 119(17.3) 皮肤软组织 70(7.1) 21(7.0) 49(7.1) 其他 32(3.3) 7(2.3) 25(3.6) 生命体征 体温/℃ 38.2(36.8,39.2) 38.0(36.9,39.1) 38.3(36.7,39.2) -0.649 0.516 心率/(次/min) 104(88,120) 110(95,126) 101(86,116) -5.922 <0.001 收缩压/mmHga) 116(105,128) 107(88.5,129) 117(109,128) -5.786 <0.01 舒张压/mmHg 71(63,78.0) 66(56,78) 72(6,78.0) -5.918 <0.01 MAP/mmHg 86(78,94.0) 80(66,94.0) 87(81,93.0) -6.059 <0.01 RR/(次/min) 21(19,26) 22(20,29) 21(18,25) -4.760 <0.001 SPO2/% 96(91,99) 96(91,99) 96(91,99) -0.351 0.725 GCS评分 15.0(14.0,15.0) 15.0(12.0,15.0) 15.0(15.0,15.0) -3.768 <0.01 实验室检测 WBC/(×109/L) 13.0(9.40,17.2) 12.6(8.10,19.1) 13.1(10.0,17.0) -0.945 0.345 N/(×109/L) 8.70(5.70,12.0) 9.60(5.75,14.0) 8.40(5.70,11.5) -3.433 <0.01 L/(×109/L) 1.05(0.75,1.35) 0.80(0.60,1.20) 1.20(0.75,1.38) -7.601 <0.01 NLR 8.45(5.01,13.7) 13.5(6.79,18.5) 7.48(4.81,10.6) -9.094 <0.01 PLT/(×109/L) 171(120,224) 143(94.5,214) 181(133,227) -5.028 <0.01 D-Dimer/(mg/L) 2.70(1.34,5.35) 3.52(2.18,7.30) 2.27(1.08,4.34) -7.670 <0.01 CRP/(mg/L) 99.2(38.9,161) 142(90.8,204) 74.3(30.1,133) -10.147 <0.01 PCT/(ng/mL) 0.51(0.16,9.64) 0.74(0.50,14.3) 0.42(0.13,0.57) -10.269 <0.01 LAC/(mmol/L) 1.60(1.00,2.60) 2.40(1.45,4.30) 1.40(1.00,2.00) -9.817 <0.01 脏器功能评分 NEWS评分 5.00(3.00,7.00) 7.00(5.00,9.00) 4.00(3.00,6.00) -11.507 <0.01 注:a)1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 连续型变量截断值及二分类赋值
变量 理论截断值 最佳截断值 赋值情况 心率/(次/min) ≥105 ≥105 ≥105=1,<105=0 收缩压/mmHg ≤100.5 ≤100 ≤100=1,>100=0 舒张压/mmHg ≤62.5 ≤60 ≤60=1,>60=0 MAP/mmHg ≤72.3 ≤70 ≤70=1,>70=0 RR/(次/min) ≥22 ≥22 ≥22=1,<22=0 N/(×109/L) >11.95 ≥12 ≥12=1,<12=0 L/(×109/L) <0.85 <0.85 <0.8=1,≥0.8=0 NLR ≥10.47 ≥10 ≥10=1,<10=0 PLT/(×109/L) ≤140.5 ≤140 ≤140=1,>140=0 D-Dimer/(mg/L) ≥2.06 ≥2 ≥2=1,<2=0 CRP/(mg/L) ≥102.1 ≥100 ≥100=1,<100=0 PCT/(ng/mL) >0.52 >0.5 >0.5=1,≤0.5=0 LAC/(mmol/L) ≥2.15 ≥2 ≥2=1,<2=0 GCS评分 ≤14 ≤14 ≤14=1,>14=0 NEWS评分 ≥5 ≥5 ≥5=1,<5=0 表 3 多因素logistic回归分析筛选急诊脓毒症独立危险因素
诊断指标 β SE Wald P OR(95%CI) NLR≥10 1.191 0.170 49.066 <0.01 3.289(2.357~4.589) CRP≥100 mg/L 1.069 0.174 37.927 <0.01 2.913(2.073~4.093) PCT>0.5 ng/mL 1.184 0.181 42.885 <0.01 3.268(2.293~4.658) LAC≥2 mmol/L 1.007 0.172 34.432 <0.01 2.737(1.955~3.831) NEWS≥5分 1.512 0.191 62.509 <0.01 4.537(3.118~6.600) 常量 -4.126 0.261 249.554 <0.01 0.016 表 4 急诊筛查脓毒症各诊断指标β值及相应分值
诊断指标 β 比值 分值/分 NLR≥10 1.191 2.36 2 CRP≥100 mg/L 1.069 2.12 2 PCT>0.5 ng/mL 1.184 2.28 2 LAC≥2 mmol/L 1.007 2.00 2 NEWS≥5分 1.512 3.00 3 总分/分 11 表 5 评分工具及各诊断指标早期筛查急诊脓毒症效能情况
指标 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 约登指数 最佳截断值 AUC(95%CI) 评分工具 83.90 72.20 0.297 7.0 0.845(0.818~0.871) NEWSa) 67.60 61.40 0.290 5.0 0.676(0.642~0.712) qSOFAa) 33.40 85.20 0.374 2.0 0.593(0.554~0.634) NLRa) 65.20 70.90 0.335 10.0 0.681(0.644~0.718) CRPa) 70.60 59.70 0.305 100.0 0.651(0.613~0.687) PCTa) 77.60 56.50 0.330 0.5 0.670(0.634~0.705) LACa) 57.20 74.10 0.345 2.0 0.656(0.618~0.695) a)各指标与评分工具差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 -
[1] Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 47(11): 1181-1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y
[2] Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10219): 200-211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
[3] Liu VX, Lu Y, Carey KA, et al. Comparison of Early Warning Scoring Systems for Hospitalized Patients With and Without Infection at Risk for In-Hospital Mortality and Transfer to the Intensive Care Unit[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(5): e205191. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.5191
[4] Turgman O, Schinkel M, Wiersinga WJ. Host Response Biomarkers for Sepsis in the Emergency Room[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27(1): 97-104. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04367-z
[5] 王仲, 魏捷, 朱华栋, 等. 中国脓毒症早期预防与阻断急诊专家共识[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2020, 21(7): 517-529. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2020.07.001
[6] Singer M, Deutsschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock(Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
[7] Seymour CW, Gesten F, Prescott HC, et al. Time to Treatment and Mortality during Mandated Emergency Care for Sepsis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(23): 2235-2244. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1703058
[8] Churpek MM, Snyder A, Han X, et al. Quick Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment, Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome, and Early Warning Scores for Detecting Clinical Deterioration in Infected Patients outside the Intensive Care Unit[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2017, 195(7): 906-911. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201604-0854OC
[9] 陈正钢, 刘励军. 急诊脓毒症患者早期筛查生物标志物的研究现状与展望[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(2): 99-104. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.02.010
[10] Zhang K, Zhang X, Ding W, et al. National Early Warning Score Does Not Accurately Predict Mortality for Patients With Infection Outside the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2021, 8: 704358-704373.
[11] Pierrakos C, Velissaris D, Bisdorff M, et al. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 287-302. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02993-5
[12] Buonacera A, Stancanelli B, Colaci M, et al. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(7): 3636-3645. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073636
[13] Rubio I, Osuchowski MF, Shankar-Hari M, et al. Current gaps in sepsis immunology: new opportunities for translational research[J]. Lancet Infect Dis, 2019, 19(12): e422-e436. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(19)30567-5
[14] Jiang J, Liu R, Yu X, et al. The neutrophil-lymphocyte count ratio as a diagnostic marker for bacteraemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2019, 37(8): 1482-1489. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2018.10.057
[15] Opal SM, Wittebole X. Biomarkers of Infection and Sepsis[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2020, 36(1): 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2019.08.002
[16] Huang YH, Chen CJ, Shao SC, et al. Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracies of Monocyte Distribution Width, Procalcitonin, and C-Reactive Protein for Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis[J]. Crit Care Med, 2023, 51(5): e106-e114. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005820
[17] Chen H, Zhao C, Wei Y, et al. Early lactate measurement is associated with better outcomes in septic patients with an elevated serum lactate level[J]. Crit Care, 2019, 23(1): 351. doi: 10.1186/s13054-019-2625-0
[18] Vincent JL, Bakker J. Blood lactate levels in sepsis: in 8 questions[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2021, 27(3): 298-302. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000824
[19] Sivayoham N, Hussain AN, Shabbo L, et al. An observational cohort study of the performance of the REDS score compared to the SIRS criteria, NEWS2, CURB65, SOFA, MEDS and PIRO scores to risk-stratify emergency department suspected sepsis[J]. Ann Med, 2021, 53(1): 1863-1874. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1992495
[20] Lin SF, Lin HA, Pan YH, et al. A novel scoring system combining Modified Early Warning Score with biomarkers of monocyte distribution width, white blood cell counts, and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio to improve early sepsis prediction in older adults[J]. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2023, 61(1): 162-172. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2022-0656
-




 下载:
下载: