Role of RBC distribution width and its derived indicators in predicting the prognosis of sepsis
-
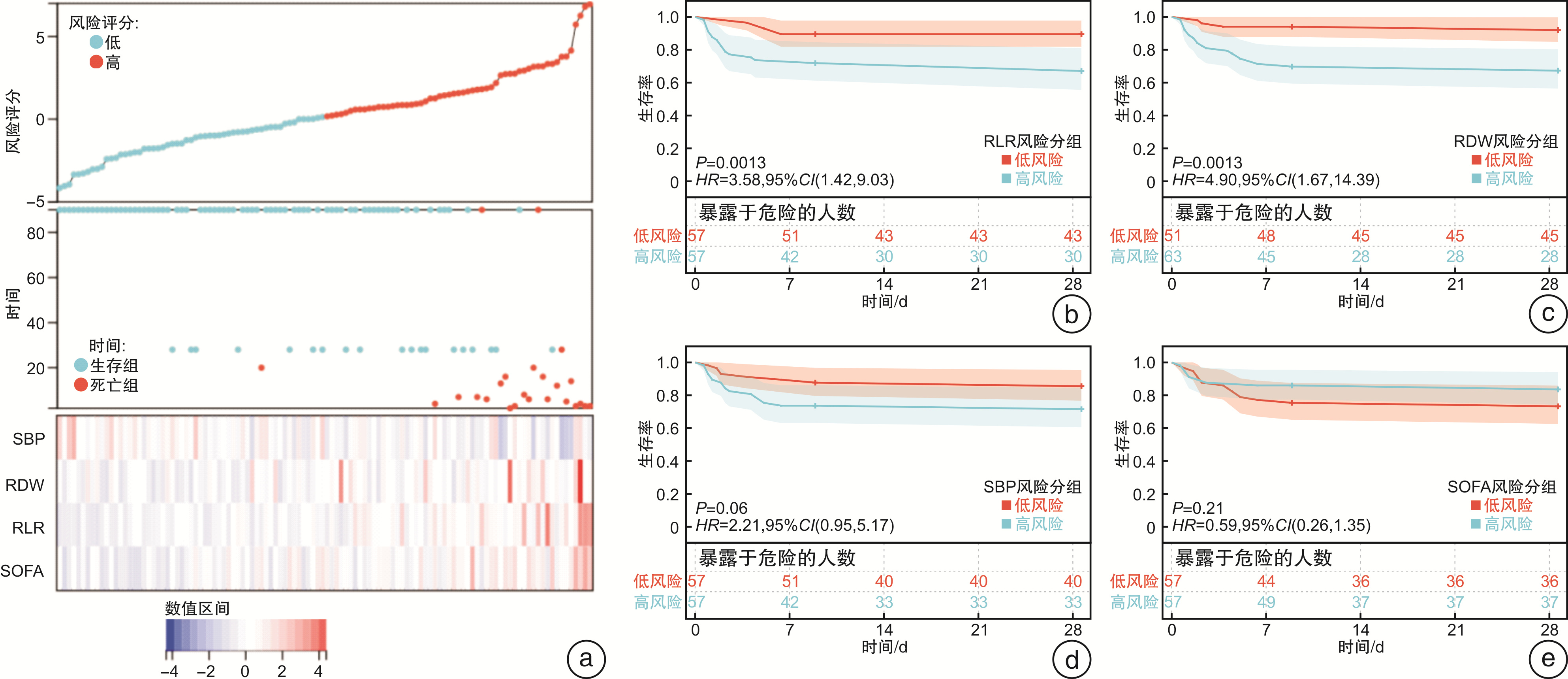
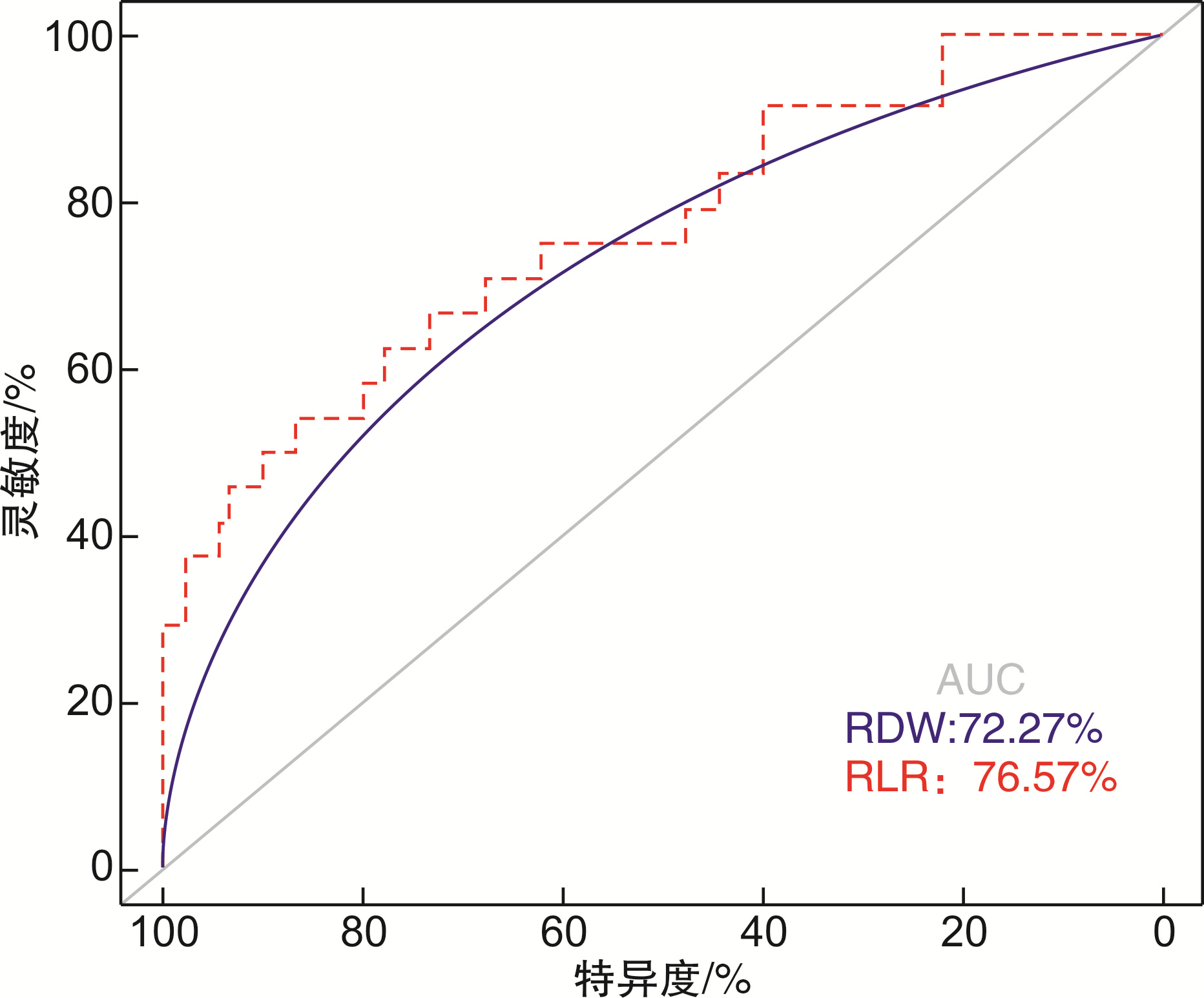
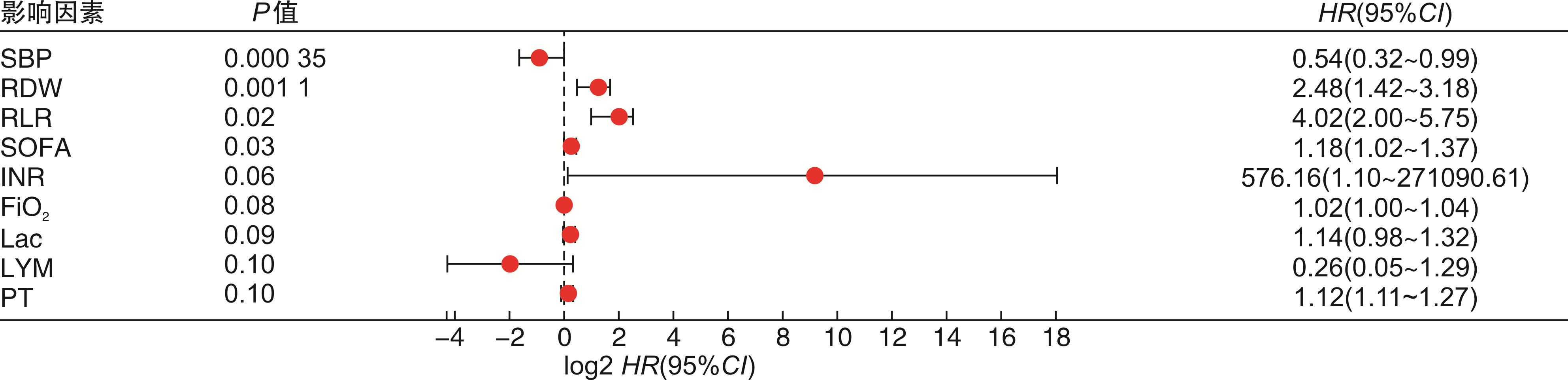
摘要: 目的 研究脓毒症患者红细胞分布宽度(RDW)及其衍生指标对早期死亡的影响并探讨其判断脓毒症预后的价值。方法 选取西京医院急诊科2021年10月1日—2022年4月30日的脓毒症患者114例,根据预后分为存活组和死亡组,对相关指标进行单因素分析,对单因素分析中差异有统计学意义的指标进行Cox回归和Kaplan-Meier生存曲线及预后相关性热图分析,最后对筛选出的指标进行ROC曲线评估预测价值。结果 114例患者根据预后分为存活组(90例)和死亡组(24例),对相关指标进行单因素分析提示中性粒细胞、淋巴细胞、收缩压、舒张压、凝血酶原时间、国际标准化比值、SOFA评分、NEWS评分、氧分压、吸氧浓度分数、氧合指数、血乳酸差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);RDW、红细胞分布宽度与淋巴细胞比值(RLR)显著高于存活组(P < 0.05)。Cox回归和Kaplan-Meier生存曲线及预后相关性热图分析提示RDW、RLR可能是影响脓毒症预后的指标,RDW、RLR与脓毒症预后的ROC曲线分析显示二者预测效能良好,其中RLR稍优于RDW。结论 RDW和RLR是影响脓毒症预后的相关因素,可用于临床判断脓毒症早期死亡风险。
-
关键词:
- 红细胞分布宽度 /
- 红细胞分布宽度/淋巴细胞 /
- 脓毒症 /
- 预后
Abstract: Objective To study the effect of red cell volume distribution width (RDW) and its derived indicators on early death in patients with sepsis, and to explore the value of RDW in predicting the prognosis of sepsis.Methods A total of 114 patients with sepsis in our department from October 1, 2021 to April 30, 2022 were selected and divided into survival group and death group based on prognosis. Univariate analysis was performed on the relevant indicators, and Cox regression models, Kaplan-Meier survival curves, and prognostic heatmap analyses were performed on the indicators with statistically significant differences in univariate analysis. Finally, we use the ROC curve to assess the predictive value of the selected metrics.Results According to the prognosis, 114 patients were divided into survival group (90 cases) and death group (24 cases). Univariate analysis of related indicators showed that there were significant differences in neutrophils, lymphocytes, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, prothrombin time, international standardized ratio, SOFA score, NEWS score, oxygen partial pressure, fraction of inspired oxygen, oxygenation index and blood lactic acid (P < 0.05); RDW, red cell volume distribution width to lymphocyte ratio (RLR) were significantly higher than those in survival group (P < 0.05). Cox regression, Kaplan-Meier survival curve and prognostic correlation heatmap analysis shed light on RDW and RLR as possible indicators affecting sepsis prognosis. Analysis of ROC curves for RDW, RLR and sepsis prognosis shows excellent predictive performance, and RLR is slightly better than RDW.Conclusion RDW and RLR are relevant factors affecting sepsis prognosis and can be used to determine the risk of early death in sepsis. -

-
表 1 脓毒症患者基础资料
例(%),X±S 基本信息 死亡组(n=24) 存活组(n=90) P 性别 0.65 女 9(7.89) 27(23.68) 男 15(13.16) 63(55.26) 高血压 8(7.02) 42(36.84) 0.35 糖尿病 7(6.14) 26(22.81) 0.97 一般情况 年龄/岁 55.71±17.10 57.81±14.05 0.54 住院天数/d 8.79±6.37 7.81±5.89 0.48 体温/℃ 36.40(36.00,39.20) 36.75(35.90,40.20) 0.24 呼吸频率/(次·min-1) 25.33±8.46 25.24±7.10 0.96 HR/(次·min-1) 100.75±27.52 101.03±22.55 0.96 DBP/mmHg 67.96±19.94 77.33±17.18 0.02 SBP/mmHg 116.38±39.44 133.89±28.55 0.02 注:1 mmHg=0.133 kPa。 表 2 脓毒症患者实验室检查指标
X±S,M(P25,P75) 实验室指标 死亡组(n=24) 存活组(n=90) P 炎症指标 NEU/(×109·L-1) 14.24±8.80 10.84±6.11 0.03 LYM/(×109·L-1) 0.77±0.42 1.21±0.60 0.02 RDW/fl 48.35±8.82 46.45±7.20 < 0.05 IL-6/(pg·mL-1) 133.11±200.947 81.70±87.2 0.23 PCT/(ng·mL-1) 0.79(0.03,73.53) 0.34(0.04,70.74) 0.88 比值 RLR 86.27±46.82 47.18±21.84 < 0.05 RPR 0.24(0.10,1.31) 0.26(0.09,1.21) 0.31 RAR 1.61±0.53 1.47±0.41 0.17 凝血功能 PLT/(×109·L-1) 197.71±126.78 198.87±94.72 0.96 PT/s 15.14±10.62 12.75±2.02 0.04 INR 1.34±1.00 1.09±0.17 0.03 APTT/s 17.45±3.05 16.40±2.24 0.61 D-D/(Ig·L-1) 4.32(0.39,71.48) 2.99(0.26,29.32) 0.07 疾病评分 qSOFA/分 1.96±0.75 1.73±0.70 0.17 SOFA/分 11.92±4.40 7.79±3.72 0.00 NEWS/分 9.42±3.78 6.82±3.35 0.01 肝脏功能 TBIL/(μmol·L-1) 20.30(9.70,339.40) 18.90(5.80,166.40) 0.27 ALB/(g·L-1) 34.61±8.26 32.74±6.95 0.26 ALT/(IU·L-1) 79.25±99.32 124.54±413.16 0.60 AST/(IU·L-1) 191.08±485.64 108.47±336.54 0.32 肺功能 SaO2/% 95.42±5.25 88.40±10.89 0.06 PO2/mmHg 81.27±32.70 61.19±27.82 0.04 FiO2/(pg·mL-1) 43.04±20.69 33.70±8.47 < 0.05 PaO2/FiO2/mmHg 184.71±127.75 254.25±119.18 0.02 PCO2/mmHg 32.92±13.85 31.93±12.40 0.74 CO2/mmHg 24.52±5.82 21.98±5.37 0.06 pH 7.44(7.06,7.62) 7.44(7.17,7.67) 0.49 循环功能 BNP/(pg·mL-1) 1417.00(47.53,35 000.00) 856.90(13.41,35 000.00) 0.18 CK-MB/(ng·mL-1) 3.55(0.60,189.30) 2.60(0.30,96.80) 0.39 CnT-I/(ng·mL-1) 2.27±5.92 0.71±2.89 0.07 Lac/(mmol·L-1) 3.81±3.62 2.44±2.53 0.04 MB/(ng·mL-1) 69.25(6.60,3131.00) 42.00(6.40,122 221.00) 0.39 LDH/(IU·L-1) 341.00(180.00,930.00) 304.50(107.00,4185.00) 0.61 肾脏功能 UA/(μmol·L-1) 335.83±157.53 312.90±172.17 0.54 Urea/(μmol·L-1) 13.41±9.56 10.41±8.31 0.13 CCr/(μmol·L-1) 98.42±76.82 112.10±146.19 0.66 注:NEU,中性粒细胞数值;LYM,淋巴细胞数值;IL-6,白介素-6;PCT,降钙素原;RLR,红细胞分布宽度/淋巴细胞;RPR,红细胞分布宽度/血小板;RAR,红细胞分布宽度/白细胞;PT,血浆凝血酶原时间;APTT,活化部分凝血活酶时间;INR,国际标准化比值;D-D,D-二聚体;PLT,血小板;qSOFA,快速脓毒症相关的器官衰竭评分;SOFA,脓毒症相关的器官衰竭评分;NEWS,英国早期预警评分;ALB,白蛋白;ALT,谷丙转氨酶;AST,谷草转氨酶;PO2,氧分压;FiO2,吸入氧浓度;PaO2/FiO2,氧合指数;PCO2,二氧化碳分压;CO2,二氧化碳含量;pH,酸碱值;SaO2,氧饱和度;BNP,脑钠肽;CK-MB,肌酸激酶同工酶;CnT-I,肌钙蛋白;MB,肌红蛋白;Lac,血乳酸;LDH,乳酸脱氢酶;TBIL,总胆红素;UA,尿酸;Urea,尿素;CCr,肌酐。 表 3 RDW和RLR预测脓毒症患者短期预后的ROC曲线分析
指标 AUC 95%CI P 约登指数 灵敏度/% 特异度/% RDW 0.723 0.604~0.843 0.001 0.389 66.67 72.22 RLR 0.766 0.653~0.879 <0.001 0.408 54.17 86.67 -
[1] Teng AK, Wilcox AB. A review of predictive analytics solutions for sepsis patients[J]. Appl Clin Inform, 2020, 11(3): 387-398. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1710525
[2] 黄昆鹏, 张进祥. 脓毒症的定义、诊断与早期干预——不可分割的三要素[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2021, 22(3): 221-226. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2021.03.015
[3] Wattanasit P, Khwannimit B. Comparison the accuracy of early warning scores with qSOFA and SIRS for predicting sepsis in the emergency department[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2021, 46: 284-288. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.07.077
[4] Deniz M, Ozgun P, Ozdemir E. Relationships between RDW, NLR, CAR, and APACHE Ⅱ scores in the context of predicting the prognosis and mortality in ICU patients[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 26(12): 4258-4267.
[5] Hu ZD, Lippi G, Montagnana M. Diagnostic and prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width in sepsis: a narrative review[J]. Clin Biochem, 2020, 77: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.01.001
[6] Moreno-Torres V, Royuela A, Múñez-Rubio E, et al. Red blood cell distribution width as prognostic factor in sepsis: a new use for a classical parameter[J]. J Crit Care, 2022, 71: 154069. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2022.154069
[7] Zhang L, Yu CH, Guo KP, et al. Prognostic role of red blood cell distribution width in patients with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. BMC Immunol, 2020, 21(1): 40. doi: 10.1186/s12865-020-00369-6
[8] Dankl D, Rezar R, Mamandipoor B, et al. Red cell distribution width is independently associated with mortality in sepsis[J]. Med Princ Pract, 2022, 31(2): 187-194. doi: 10.1159/000522261
[9] 李俊玉, 王雅慧, 刘慧珍, 等. 红细胞分布宽度与血小板计数比值对急诊脓毒症患者预后的预测价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2022, 23(2): 132-137. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2022.02.011
[10] 曹亚萍, 费素娟, 李莉. 红细胞分布宽度与淋巴细胞比值对结直肠癌的诊断价值[J]. 西部医学, 2021, 33(7): 1010-1015. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2021.07.015
[11] 周峰, 刘志祯, 蔡华忠, 等. 红细胞分布宽度/白蛋白比值在急性中毒患者中的应用研究[J]. 岭南急诊医学杂志, 2022, 27(4): 314-316. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNJZ202204004.htm
[12] Pinna A, Carlino P, Serra R, et al. Red cell distribution width(RDW)and complete blood cell count-derived measures in non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(10): 2239-2244. doi: 10.7150/ijms.53668
[13] Soliz J, Schneider-Gasser EM, Arias-Reyes C, et al. Coping with hypoxemia: could erythropoietin(EPO)be an adjuvant treatment of COVID-19?[J]. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2020, 279: 103476. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2020.103476
[14] Ramachandran P, Gajendran M, Perisetti A, et al. Red blood cell distribution width in hospitalized COVID-19 patients[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2022, 8: 582403.
[15] Otero TMN, Yeh DD, Bajwa EK, et al. Elevated red cell distribution width is associated with decreased ventilator-free days in critically ill patients[J]. J Intensive Care Med, 2018, 33(4): 241-247. doi: 10.1177/0885066616652612
[16] Lee JJ, Montazerin SM, Jamil A, et al. Association between red blood cell distribution width and mortality and severity among patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Med Virol, 2021, 93(4): 2513-2522. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26797
[17] Uffen JW, Oomen P, de Regt M, et al. The prognostic value of red blood cell distribution width in patients with suspected infection in the emergency department[J]. BMC Emerg Med, 2019, 19(1): 76. doi: 10.1186/s12873-019-0293-7
[18] Zhang XY, Wang DW, Chen ZM, et al. Red cell distribution width-to-lymphocyte ratio: a novel predictor for HBV-related liver cirrhosis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2020, 99(23): e20638.
[19] Wu J. RDW, NLR and RLR in predicting liver failure and prognosis in patients with hepatitis E virus infection[J]. Clin Biochem, 2019, 63: 24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.11.012
[20] Hannarici Z, Yilmaz A, Buyukbayram ME, et al. A novel prognostic biomarker for cutaneous malignant melanoma: red cell distribution width(RDW)to lymphocyte ratio[J]. Melanoma Res, 2021, 31(6): 566-574. doi: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000785
[21] Huang YY, Jiang SW, Li WJ, et al. Establishment and effectiveness evaluation of a scoring system-RAAS(RDW, AGE, APACHE Ⅱ, SOFA)for sepsis by a retrospective analysis[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2022, 15: 465-474.
[22] Venet F, Monneret G. Advances in the understanding and treatment of sepsis-induced immunosuppression[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2018, 14(2): 121-137.
[23] 徐燕, 谢建刚. 脓毒症免疫功能特点及检测方法的研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(5): 462-466. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBFM202005014.htm
[24] Huang Z, Fu Z, Huang W, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: a meta-analysis[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2020, 38(3): 641-647.
-




 下载:
下载: