ROC analysis of the relationship between high mobility group protein B1, microRNA-223 and emergency infection and the prognosis of severe pneumonia
-
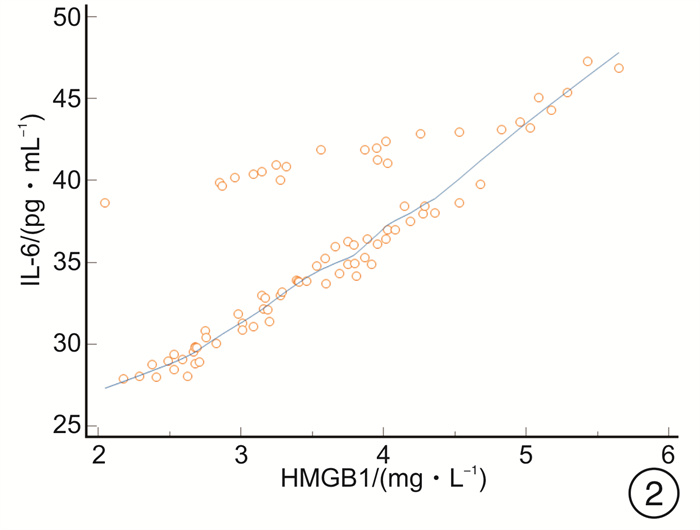
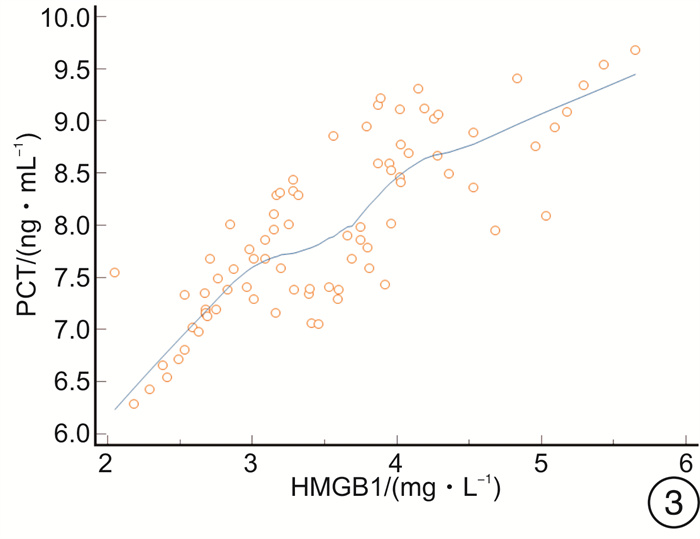
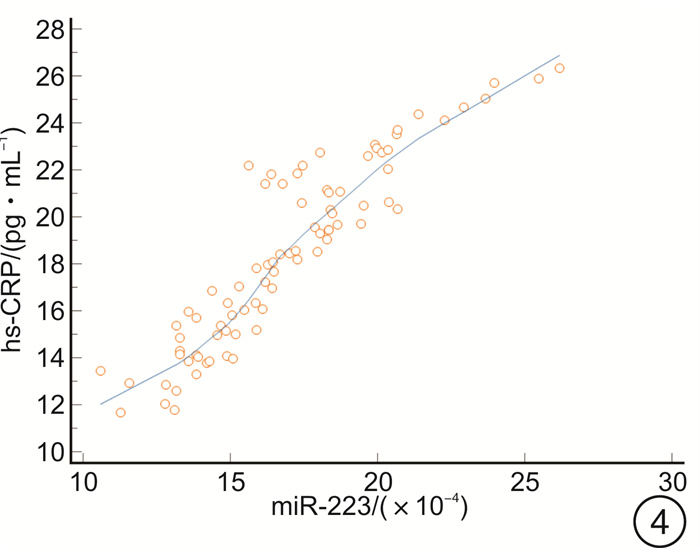
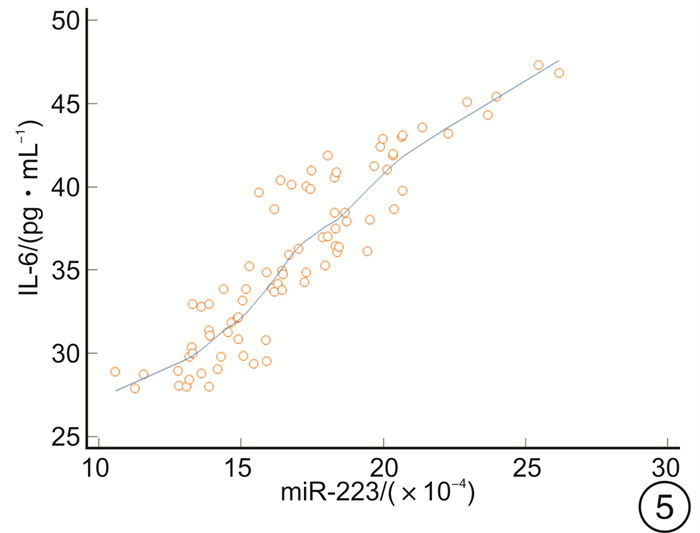
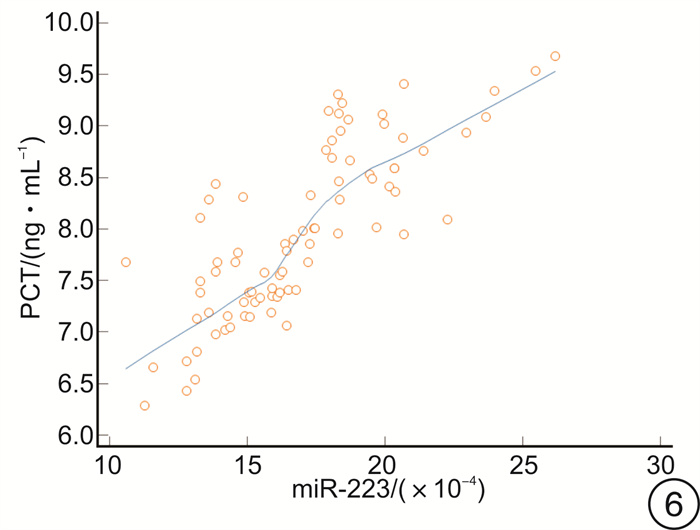
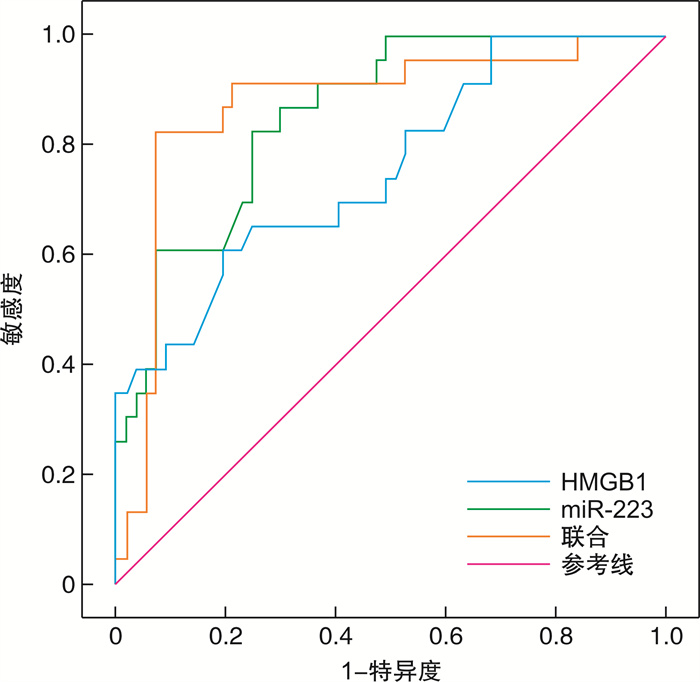
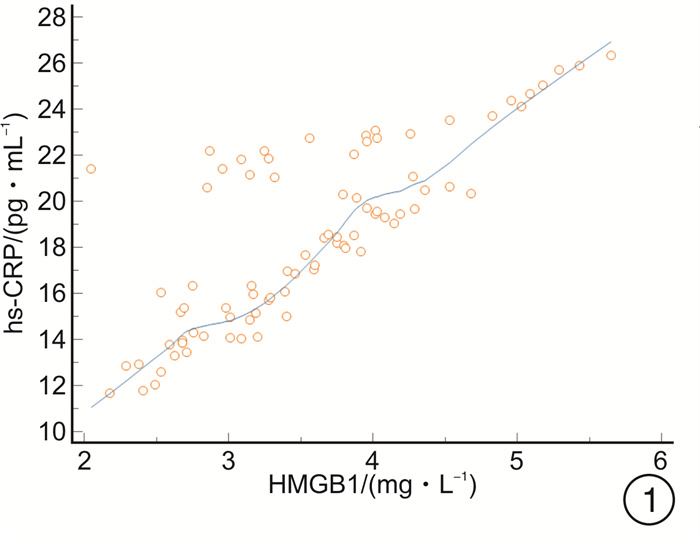
摘要: 目的 探讨高迁移率族蛋白B1(HMGB1)、微小RNA-223(miR-223)与急诊感染三项[超敏C-反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、IL-6、降钙素原(PCT)]的关系,及对重症肺炎(SP)预后的预测价值。方法 选取2018年2月-2020年8月82例SP患者为观察组,根据年龄、性别匹配普通肺炎患者(82例)为对照1组,健康体检人群(82例)为对照2组。比较3组HMGB1、miR-223及急诊感染三项的水平,分析观察组HMGB1、miR-223与急诊感染三项的关系,logistic回归分析HMGB1、miR-223及急诊感染三项与SP的关联性,受试者工作特征曲线分析HMGB1、miR-223对SP预后的预测价值。结果 观察组HMGB1、miR-223及IL-6、PCT、hs-CRP水平均高于对照1组、对照2组,对照1组高于对照2组(P< 0.05);观察组患者HMGB1、miR-223均与hs-CRP、IL-6、PCT呈正相关(P< 0.05);logistic回归分析显示,HMGB1、miR-223及急诊感染三项均与SP相关(P< 0.05);死亡者HMGB1、miR-223及hs-CRP、IL-6、PCT水平高于好转者(P< 0.05);HMGB1、miR-223联合预测SP预后的曲线下面积最大,为0.889,对应的敏感度为95.65%,特异度为70.11%。结论 SP患者HMGB1、miR-223异常高表达,且与急诊感染三项水平关系密切,可为临床评估SP的预后提供参考。Abstract: Objective To explore the relationship between high mobility group protein B1(HMGB1), microRNA-223(miR-223) and emergency infections, and their predictive value for the prognosis of severe pneumonia(SP).Methods From February 2018 to August 2020, 82 cases of SP patients in our hospital were selected as the observation group, 82 cases of common pneumonia matched by age and sex were selected as the control group 1 and 82 cases of healthy people were selected as the control group 2. The levels of HMGB1, miR-223 and emergency infection in the two groups were compared, the relationship between HMGB1, miR-223 and emergency infection in the observation group was analyzed, the association between HMGB1, miR-223 and emergency infection and SP was analyzed by logistic regression model, and the predictive value of HMGB1 and miR-223 on the prognosis of SP was analyzed by receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve.Results The observation group HMGB1, miR-223, interleukin-6(IL-6), procalcitonin(PCT), and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP) levels were higher than those of the control group 1 and control group 2, the control group 1 was higher than the control group 2(P< 0.05); HMGB1 and miR-223 in SP patients were positively correlated with hs-CRP, IL-6, and PCT(P< 0.05); logistic regression analysis showed that HMGB1, miR-223 and emergency infection were all related to SP(P< 0.05); the levels of HMGB1, miR-223, hs-CRP, IL-6, and PCT of the dead were higher than those who had improved(P< 0.05); the maximum AUC of HMGB1 and miR-223 predicting the prognosis of SP was 0.889, the corresponding sensitivity was 95.65%, and the specificity is 70.11%.Conclusion HMGB1 and miR-223 are abnormally highly expressed in SP patients, and are closely related to the three levels of emergency infection, which can provide references for clinical evaluation of the prognosis of SP.
-

-
表 1 3组HMGB1、miR-223水平及急诊感染三项水平的比较
X±S 组别 例数 HMGB1/ (mg·L-1) miR-223/ (×10-4) hs-CRP/ (pg·mL-1) IL-6/ (pg·mL-1) PCT/ (ng·mL-1) 观察组 82 3.59±0.84 17.04±4.86 18.39±4.57 35.74±6.36 7.86±0.83 对照1组 82 1.93±0.58 11.35±3.94 10.86±3.27 21.52±5.84 5.32±0.76 对照2组 82 0.76±0.35 6.17±2.04 4.37±1.06 12.69±2.85 1.09±0.51 F 427.196 167.926 370.340 402.414 1 884.759 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 2 HMGB1、miR-223及急诊感染三项与SP的关联性
变量 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI HMGB1 1.299 0.374 12.066 < 0.001 3.666 1.961~6.854 miR-223 1.258 0.351 12.841 < 0.001 3.519 2.141~5.783 hs-CRP 1.043 0.476 4.798 0.037 2.837 1.254~6.417 IL-6 1.046 0.321 10.610 < 0.001 2.845 1.362~5.943 PCT 1.239 0.382 10.524 < 0.001 3.453 2.016~5.914 表 3 观察组不同预后患者HMGB1、miR-223及急诊感染三项水平比较
X±S 组别 例数 HMGB1/ (mg·L-1) miR-223/ (×10-4) hs-CRP/ (pg·mL-1) IL-6/ (pg·mL-1) PCT/ (ng·mL-1) 死亡 25 4.15±1.12 20.25±4.37 22.61±5.76 41.28±7.29 8.51±1.08 好转 57 3.34±0.79 15.63±2.96 16.54±3.91 33.31±6.25 7.57±0.61 t 3.745 5.592 5.568 5.050 5.016 P < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 表 4 HMGB1、miR-223对SP预后的预测价值
指标 AUC 95%CI χ2 P cut-off值 敏感度/% 特异度/% HMGB1 0.757 0.649~0.846 4.220 < 0.001 >3.92 60.87 80.70 miR-223 0.829 0.763~0.894 5.527 < 0.001 >16.28 82.61 75.44 联合预测 0.889 0.794~0.939 7.853 < 0.001 95.65 70.11 -
[1] 卢薇, 郑相, 田福, 等. 等热卡不同蛋白质含量肠内营养支持对老年重症肺炎患者蛋白质代谢的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2018, 25(1): 53-56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2018.01.013
[2] Liu C, Feng M, Zhu J, et al. Severe pneumonia due to Nocardia otitidiscaviarum identified by mass spectroscopy in a cotton farmer: A case report and literature review[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2017, 96(13): e6526.
[3] 高延秋, 张根生, 李双凤, 等. 血管外肺水指数联合血管内皮生长因子受体1对重症肺炎ARDS合并感染性休克患者预后的评估[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2018, 27(12): 1381-1387. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2018.12.013
[4] Rao Y, Wan Q, Su H, et al. ROS-induced HSP70 promotes cytoplasmic translocation of high-mobility group box 1b and stimulates antiviral autophagy in grass carp kidney cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2018, 293(45): 17387-17401. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003840
[5] 邱潇, 程爱萍, 李永梅, 等. 血清高迁移率族蛋白1, 可溶性CD163分子, 粒细胞集落刺激因子对新生儿重症肺炎的预后评估价值[J]. 实用预防医学, 2020, 27(2): 121-123. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYY202002034.htm
[6] 王昭君, 刘勤富, 王晓红, 等. 重症肺炎患者支气管肺泡灌洗液微小RNA-127-5p的表达及诊断价值[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2017, 29(7): 592-595. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.07.004
[7] 刘红新, 孟舰, 武小娟, 等. 血必净注射液辅助治疗对脓毒症患者病情及微小高迁移率族蛋白B1、微小RNA-223表达的影响[J]. 解放军医药杂志, 2021, 33(2): 93-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-140X.2021.02.021
[8] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会. 中国成人社区获得性肺炎诊断和治疗指南(2016年版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2016, 60(2): 97-107.
[9] Lau VI, Cook DJ, Fowler R, et al. Economic evaluation alongside the Probiotics to Prevent Severe Pneumonia and Endotracheal Colonization Trial(E-PROSPECT): study protocol[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(6): e036047. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-036047
[10] 储芳芳, 王亚亭, 毕良学, 等. 重症肺炎合并呼吸衰竭患儿的病原学特征及支气管镜肺泡灌洗术的疗效分析[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2020, 30(8): 1275-1280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202008032.htm
[11] 吴文涛, 魏鲲鹏, 陈文红, 等. 高迁移率族蛋白B1肿瘤坏死因子-α和白介素-6在老年人病毒性肺炎中的表达和临床意义[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2021, 40(5): 591-595. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2021.05.010
[12] Sarsu SB, Erbagci AB, Ulusal H, et al. The Place of Calprotectin, Lactoferrin, and High-Mobility Group Box 1 Protein on Diagnosis of Acute Appendicitis with Children[J]. Indian J Surg, 2017, 79(2): 131-136. doi: 10.1007/s12262-015-1441-2
[13] 闫百灵, 唐颖, 付尧, 等. HMGB1-IL-17信号传导轴在老年重症肺炎患者中作用及机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2018, 38(14): 3380-3382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2018.14.020
[14] 吴述光, 侯小丽, 马胜喜. 重症肺炎并发脓毒症患者血清高迁移率族蛋白B1检测的临床意义[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2018, 35(2): 143-145, 150-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXYX201802019.htm
[15] 高晶晶, 潘超. 多沙普仑联合连续性血液净化治疗重症肺炎并发呼吸衰竭对血清sTREM-1与HMGB1的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2019, 36(8): 1356-1361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYD201908034.htm
[16] 刘道莹, 刘笛, 尹昆. 重症肺炎患者血清NT-proBNP和HMGB1水平的变化及其意义[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2017, 27(17): 58-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.17.012
[17] 王瑾, 王加强, 邱洪, 等. miR-223通过调控NLRP3炎症小体减轻免疫球蛋白A肾病大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(24): 2960-2965. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2020.24.004
[18] 麻贞贞, 赵萍, 吕继彩, 等. 系统性红斑狼疮患者外周血单个核细胞中微RNA-223及核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体家族蛋白3炎性小体的表达及临床意义[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2019, 23(1): 10-14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-7480.2019.01.003
[19] Dhungel BP, Monteuuis G, Giardina C, et al. The Fusion of CLEC12A and MIR223HG Arises from a trans-Splicing Event in Normal and Transformed Human Cells[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 12178. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212178
[20] 邵慧芝, 吕勤, 陈赫赫. microRNA-223在重症肺炎患儿血浆中的表达意义及其与预后的关系[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2016, 18(3): 402-405, 409-409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-1372.2016.03.020
[21] 李大勇, 刘冠兰, 袁新科. 脓毒症合并急性肾损伤患者血清miR-21、miR-233和miR-107的表达水平及临床意义[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2018, 18(12): 1580-1584. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3619.2018.12.010
[22] Bunthi C, Rhodes J, Thamthitiwat S, et al. Etiology and Clinical Characteristics of Severe Pneumonia Among Young Children in Thailand: Pneumonia Etiology Research for Child Health (PERCH) Case-Control Study Findings, 2012-2013[J]. Pediatr Infect Dis J, 2021, 40(9S): S91-S100. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002768
[23] Li G, Zong X, Cheng Y, et al. miR-223-3p contributes to suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Streptococcus equi ssp. zooepidemicus infection[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2022, 269(1): 109430.
[24] Szilágyi B, Fejes Z, Rusznyák á, et al. Platelet Microparticles Enriched in miR-223 Reduce ICAM-1-Dependent Vascular Inflammation in Septic Conditions[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12(1): 658524.
[25] Cong PD, Leelahavanichkul A. Over-expression of miR-223 induces M2 macrophage through glycolysis alteration and attenuates LPS-induced sepsis mouse model, the cell-based therapy in sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(7): e0236038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236038
[26] 黄林枫, 熊岚, 吴奎, 等. 脓毒症患儿血浆miR-146a、miR-223表达与IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α水平变化的临床意义分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(32): 6324-6327, 6344-6344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201732027.htm
[27] Jiao P, Wang XP, Luoreng ZM, et al. miR-223: An Effective Regulator of Immune Cell Differentiation and Inflammation[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(9): 2308-2322. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.59876
-




 下载:
下载: