共识注册编号:PREPARE-2025CN304
Expert consensus on coagulant function tests in the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary thromboembolism
-
摘要: 目的 制定肺血栓栓塞症(pulmonary thromboembolism,PTE)诊疗全流程出凝血功能检测专家共识(简称《共识》)。方法 充分借鉴急性PTE诊治和管理指南,参考国内外近10年的循证医学依据,并整合现有的最佳临床证据和分别来自全国的84名急诊医学、重症医学、检验医学、呼吸病学以及护理学等不同领域的专家经验。通过系统查阅文献资料、德尔菲专家调查及专家论证会议,共同制定本《共识》。结果 《共识》包括PTE临床表现、出凝血功能检测在PTE诊断和治疗决策中的作用、PTE护理中的关键作用以及出凝血功能检测的准确性评估等。结论 《共识》以其特有的科学性和实用性,为各级医院在PTE的诊治领域,提供基于出凝血功能指标检测的指导和实践性参考。Abstract: Objective To formulate the expert consensus on the coagulant function tests throughout the entire process of pulmonary thromboembolism(PTE)(hereinafter referred to as the "Consensus").Methods The consensus thoroughly draw on the latest evidence-based medical data from both domestic and international sources over the past decade regarding the diagnosis, treatment, and management of acute PTE and integrate the best available clinical evidence with expert consensus from 84 specialists spanning emergency medicine, critical care medicine, laboratory medicine, respiratory medicine, and nursing science across nationwide. This "Consensus" was developed through systematic literature review, Delphi expert survey, and expert argumentation meetings.Results The "Consensus" includes the clinical manifestations of PTE, the role of coagulant function tests in the diagnosis, treatment and nursing of PTE, the assessment of the accuracy of coagulant function tests.Conclusion The "Consensus", with its unique scientific nature and practicality, provides guidance and practical references based on the detection of coagulation function indicators for hospitals at all levels in the field of diagnosis and treatment of PTE.
-

-
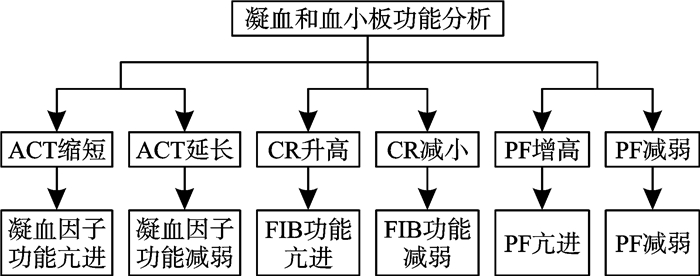
图 1 CPA评估凝血功能紊乱的流程图[72]
表 1 共识推荐分级及其代表意义
推荐分级 代表意义 Ⅰ级(一致推荐或一致不推荐) 投票100%一致,所有专家完全达成共识 Ⅱ级(强推荐或强不推荐) 投票75%~99%一致,绝大多数专家达成共识 Ⅲ级(弱推荐或弱不推荐) 投票50%~74%一致,多数专家达成共识,但少数专家存在分歧 Ⅳ级(专家未达成一致性结论) 投票<50%一致,专家未达成一致性结论 APTT检测 初始剂量及调整剂量 下次APTT测定的时间间隔/h 治疗前基础值 初始计量:80 IU/kg静脉注射,然后按照18 IU/kg/h静脉滴注 4~6 <35 s(<1.2倍基础值) 予80 IU/kg静脉注射,然后增加静脉滴注剂量4 IU/kg/h 6 35~45 s(1.2~1.5倍基础值) 予40 IU/kg静脉注射,然后增加静脉滴注剂量2 IU/kg/h 6 46~70 s(1.5~2.3倍基础值) 无须调整剂量 6 71~90 s(2.3~3.0倍基础值) 减少静脉滴注剂量2 IU/kg/h 6 >90 s(>3倍基础值) 停药1 h,然后减少剂量3 IU/kg/h后恢复静脉滴注 6 表 3 直接口服抗凝剂在VTE强化治疗和维持治疗期间的用药方法[53]
药物 强化治疗 维持治疗(急性发作治疗至少3~6个月内) 达比加群 胃肠外抗凝≥5 d 150 mg bid (高龄患者可减量) 利伐沙班 15 mg bid,21 d 20 mg qd 阿哌沙班 10 mg bid,7 d 5 mg bid 艾多沙班 胃肠外抗凝≥5 d 60 mg qd 活动性出血 具体表现 大出血 ①致死性出血;②某些重要部位或器官的出血,如颅内、脊柱内、腹膜后、关节内、心包等,及因出血引起的骨筋膜室综合征;③出血导致血流动力学不稳定,和(或)在24~48 h内引起血红蛋白水平下降20 g/L以上,或需要输至少2个单位全血或红细胞;④手术部位出血需要再次进行切开,关节镜或血管内介入等,或关节腔内出血致活动或伤口恢复推迟,使住院时间延长或伤口加深 临床相关非大出血 ①自发性皮肤出血面积>25 cm2;②自发性鼻出血时间>5 min;③持续24 h肉眼血尿;④便血(厕纸可见出血点);⑤牙龈出血时间>5 min;⑥因出血住院治疗;⑦出血需要输血但少于2个单位;⑧观察者认为影响临床治疗 小出血 其他类型的出血 表 5 常见凝血指标及其临床意义参考
凝血指标 正常参考值 延长/升高临床意义 缩短/降低临床意义 PT 11.5~14.5 s 延长>3 s,纤溶亢进,抗凝阶段,存在出血风险 血栓前状态 INR 0.8~1.2 抗凝阶段,>3时存在出血风险 血栓形成状态 APTT 20~40 s 延长>10 s,抗凝阶段,存在出血风险 血栓形成及血液呈高凝状态 TT 11~14 s 延长>3 s,AT升高,FDP/D-Dimer增多,抗凝阶段,存在出血风险 存在微小凝块,可以粗略用于检测肝素抗凝治疗 FIB 2~4 g/L 血栓高凝状态 <1.5 g/L,低凝血期及纤溶期,溶栓治疗的监测,存在出血风险 FDP 0~5 mg/L 原发性纤溶亢进,血栓高凝状态 - D-Dimer <500 μg/L 继发性纤溶亢进,血栓高凝状态,提示发生PTE的风险增加 对于低可能性的患者,可基本排除PTE AT 80%~120% 血液抗凝活性增强 血栓形成状态,抗凝能力下降及肝素抗凝作用减弱 血小板计数 (125~320)×109/L 血小板易发生黏附、聚集及释放反应,可能形成血小板性血栓 <100×109/L,出血风险增加 PC 70%~140% 病理性异常 易形成血栓 PS 63.5%~149% 病理性异常 易形成血栓 -
[1] Huisman MV, Barco S, Cannegieter SC, et al. Pulmonary embolism[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2018, 4: 18028.
[2] Lutsey PL, Zakai NA. Epidemiology and prevention of venous thromboembolism[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2023, 20(4): 248-262.
[3] Cao Y, Geng C, Li Y, et al. In situ pulmonary artery thrombosis: a previously overlooked disease[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 671589.
[4] Konstantinides SV, Wärntges S. Acute phase treatment of venous thromboembolism: advanced therapy. Systemic fibrinolysis and pharmacomechanical therapy[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2015, 113(6): 1202-1209.
[5] Diamond IR, Grant RC, Feldman BM, et al. Defining consensus: a systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 2014, 67(4): 401-409.
[6] Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2021, 143(8): e254-e743.
[7] Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al. 2024 Heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(8): e347-e913.
[8] Zhang Z, Lei J, Shao X, et al. Trends in Hospitalization and In-Hospital Mortality From VTE, 2007 to 2016, in China[J]. Chest, 2019, 155(2): 342-353. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.10.040
[9] Essien EO, Rali P, Mathai SC. Pulmonary embolism[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2019, 103(3): 549-564. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2018.12.013
[10] Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society(ERS)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2020, 41(4): 543-603. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz405
[11] Zhai Z, Wang D, Lei J, et al. Trends in risk stratification, in-hospital management and mortality of patients with acute pulmonary embolism: an analysis from the China pUlmonary thromboembolism REgistry Study(CURES)[J]. Eur Respir J, 2021, 58(4): 2002963. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02963-2020
[12] Morrone D, Morrone V. Acute pulmonary embolism: focus on the clinical picture[J]. Korean Circ J, 2018, 48(5): 365-381. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2017.0314
[13] 陈升汶, 黄平. 实用急性肺栓塞诊疗手册[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2016.
[14] Sharma GV, McIntyre KM, Sharma S, et al. Clinical and hemodynamic correlates in pulmonary embolism[J]. Clin Chest Med, 1984, 5(3): 421-437. doi: 10.1016/S0272-5231(21)00267-7
[15] Konstantinides SV, Meyer G. The 2019 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(42): 3453-3455. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz726
[16] Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Derivation of a simple clinical model to categorize patients probability of pulmonary embolism: increasing the models utility with the SimpliRED D-dimer[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2000, 83(3): 416-420. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1613830
[17] Le Gal G, Righini M, Roy PM, et al. Prediction of pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: the revised Geneva score[J]. Ann Intern Med, 2006, 144(3): 165-171. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-144-3-200602070-00004
[18] Koziatek CA, Simon E, Horwitz LI, et al. Automated pulmonary embolism risk classification and guideline adherence for computed tomography pulmonary angiography ordering[J]. Acad Emerg Med, 2018, 25(9): 1053-1061. doi: 10.1111/acem.13442
[19] 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会肺血管疾病学组, 中国肺栓塞救治团队(PERT)联盟. 急性肺栓塞多学科团队救治中国专家共识[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2022, 50(1): 25-35. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20210527-00455
[20] Kline JA, Jimenez D, Courtney DM, et al. Comparison of four bleeding risk scores to Iidentify rivaroxaban-treated patients with venous thromboembolism at low risk for major bleeding[J]. Acad Emerg Med, 2016, 23(2): 144-150. doi: 10.1111/acem.12865
[21] 唐慧琴, 王伟鑫, 于宝丹, 等. 血栓弹力图联合凝血功能指标在肺血栓栓塞症患者中的应用研究[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2022, 19(8): 1118-1121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2022.08.028
[22] Wu YY, Tan Y, Yan M, et al. Analysis of CRP, antithrombin, fibrinogen, and hematological changes in 433 patients with PTE[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2021, 14: 7181-7185. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S333747
[23] Shi M, Gao W, Jin Y, et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome-related pulmonary embolism: clinical characteristics and early recognition[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 872523. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.872523
[24] Zhou Q, Huang R, Xiong X, et al. Prediction of pulmonary embolism by an explainable machine learning approach in the real world[J]. Sci Rep, 2025, 15(1): 835. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75435-9
[25] Yang C, Zhu L. Coagulation and deep vein flow changes following laparoscopic total extraperitoneal inguinal hernia repair: a single-center, prospective cohort study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2019, 33(12): 4057-4065. doi: 10.1007/s00464-019-06700-6
[26] Tian B, Song C, Li H, et al. The significance of perioperative coagulation and fibrinolysis related parameters after lung surgery for predicting venous thromboembolism: a prospective, single center study[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2018, 10(4): 2223-2230.
[27] Ben SQ, Ni SS, Shen HH, et al. The dynamic changes of LDH isoenzyme 3 and D-dimer following pulmonary thromboembolism in canine[J]. Thromb Res, 2007, 120(4): 575-583.
[28] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺栓塞与肺血管病学组, 中国医师协会呼吸医师分会肺栓塞与肺血管病工作委员会, 全国肺栓塞与肺血管病防治协作组. 肺血栓栓塞症诊治与预防指南[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(14): 1060-1087. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.14.007
[29] 中国研究型医院学会血栓与止血专业委员会. D-二聚体实验室检测与临床应用中国专家共识[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103(35): 2743-2756. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20230721-00066
[30] Bass AR, Fields KG, Goto R, et al. Clinical decision rules for pulmonary embolism in hospitalized patients: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2017, 117(11): 2176-2185.
[31] Rivera-Lebron B, McDaniel M, Ahrar K, et al. Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow Up of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Consensus Practice from the PERT Consortium[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2019, 25: 1-16.
[32] Righini M, Van Es J, Den Exter PL, et al. Age-adjusted D-dimer cutoff levels to rule out pulmonary embolism: the ADJUST-PE study[J]. Jama, 2014, 311(11): 1117-1124. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.2135
[33] Fuchs E, Asakly S, Karban A, et al. Age-adjusted cutoff D-Dimer level to rule out acute pulmonary embolism: a validation cohort study[J]. Am J Med, 2016, 129(8): 872-878. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.02.043
[34] Penaloza A, Roy PM, Kline J, et al. Performance of age-adjusted D-dimer cut-off to rule out pulmonary embolism[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2012, 10(7): 1291-1296. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04769.x
[35] Lozano-Polo L, Puig-Campmany M, Herrera-Mateo S, et al. Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism in the elderly: adherence to guidelines and age-adjusted D-dimer concentration values[J]. Emergencias, 2018, 30(5): 321-327.
[36] Liu P, Yu H, Liu W, et al. Distinct age-adjusted D-dimer threshold to rule out acute pulmonary embolism in outpatients and inpatients[J]. Clin Respir J, 2024, 18(2): e13728.
[37] 夏书月. 急性肺血栓栓塞症的规范化抗凝和溶栓治疗[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(6): 501-507.
[38] Stewart LK, Kline JA. Fibrinolytics for the treatment of pulmonary embolism[J]. Transl Res, 2020, 225: 82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.05.003
[39] Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(12): e344-e418.
[40] Berge E, Whiteley W, Audebert H, et al. European Stroke Organisation(ESO)guidelines on intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke[J]. Eur Stroke J, 2021, 6(1): I-lxii.
[41] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会, 王辰. 肺血栓栓塞症的诊断与治疗指南(草案)[J]. 中华医学会呼吸病学分会, 2001, 24(5): 259-264.
[42] 中国静脉介入联盟, 中国医师协会介入医师分会外周血管介入专业委员会, 国际血管联盟中国分部护理专业委员会. 致命性肺血栓栓塞症急救护理专家共识[J]. 中华现代护理杂志, 2023, 29(17): 2241-2250. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115682-20221115-05533
[43] Ortel TL, Neumann I, Ageno W, et al. American Society of Hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism[J]. Blood Adv, 2020, 4(19): 4693-4738. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001830
[44] Favaloro EJ, Kershaw G, Mohammed S, et al. How to optimize activated partial thromboplastin time(APTT)testing: solutions to establishing and verifying normal reference intervals and assessing APTT reagents for sensitivity to heparin, lupus anticoagulant, and clotting factors[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2019, 45(1): 22-35.
[45] Pineo GF, Hull RD. Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolism[J]. Drugs, 1996, 52(1): 71-92.
[46] Raschke RA, Reilly BM, Guidry JR, et al. The weight-based heparin dosing nomogram compared with a "standard care" nomogram. A randomized controlled trial[J]. Ann Intern Med, 1993, 119(9): 874-881.
[47] Hull RD, Raskob GE, Rosenbloom D, et al. Optimal therapeutic level of heparin therapy in patients with venous thrombosis[J]. Archives of Internal Medicine, 1992, 152(8): 1589-1595.
[48] Kearon C, Akl EA, Comerota AJ, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines[J]. Chest, 2012, 141(2 Suppl): e419S-e496S.
[49] 中国医师协会心血管内科医师分会血栓防治专业委员会, 《中华医学杂志》编辑委员会. 肝素诱导的血小板减少症中国专家共识(2017)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(6): 408-417. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.06.003
[50] Ridker PM, Goldhaber SZ, Danielson E, et al. Long-term, low-intensity warfarin therapy for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism[J]. N Engl J Med, 2003, 348(15): 1425-1434. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa035029
[51] 中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中国老年学学会心脑血管病专业委员会. 华法林抗凝治疗的中国专家共识[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2013, 52(1): 76-82. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2013.01.027
[52] Cuker A, Arepally GM, Chong BH, et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia[J]. Blood Adv, 2018, 2(22): 3360-3392. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018024489
[53] 《口服抗凝药物治疗管理路径专家共识》编写组, 林阳. 口服抗凝药物治疗管理路径专家共识[J]. 临床药物治疗杂志, 2024, 22(9): 1-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3384.2024.09.001
[54] Duffett L, Castellucci LA, Forgie MA. Pulmonary embolism: update on management and controversies[J]. Bmj, 2020, 370 m2177.
[55] Patnaik MM, Moll S. Inherited antithrombin deficiency: a review[J]. Haemophilia, 2008, 14(6): 1229-1239. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2516.2008.01830.x
[56] 中华医学会血液学分会血栓与止血学组. 易栓症诊断与防治中国指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42(11): 881-888. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2021.11.001
[57] 门剑龙, 徐菲亚, 翟振国. 肝素抵抗的发生机制及临床处理策略[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2023, 103(10): 707-713. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20220830-01838
[58] Koster A, Nagler M, Erdoes G, et al. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: perioperative diagnosis and management[J]. Anesthesiology, 2022, 136(2): 336-344. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004090
[59] Pouplard C, Gueret P, Fouassier M, et al. Prospective evaluation of the '4Ts' score and particle gel immunoassay specific to heparin/PF4 for the diagnosis of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2007, 5(7): 1373-1379. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02524.x
[60] 范庆坤, 张真路. 如何面对肝素诱导血小板减少症诊断的困惑[J]. 中国检验医学杂志, 2019, 42(4): 227-231.
[61] 闫姝洁, 卞璐瑜, 滕媛, 等. 肝素诱导血小板减少症成人体外循环管理临时专家共识[J]. 中国体外循环杂志, 2024, 22(2): 82-86.
[62] 刘芳, 诸兰艳, 陈平, 等. 蛋白C/蛋白S缺乏症相关的肺动脉血栓栓塞症. 中华医学会第六届全国肺栓塞与肺血管病学术会议暨第四届国际肺循环病研讨会论文集, 重庆, 2013, 192-193.
[63] Alshehri FS, Bashmeil AA, Alamar IA, et al. The natural anticoagulant protein S: hemostatic functions and deficiency[J]. Platelets, 2024, 35(1): 2337907.
[64] Patel AB, Mai V, Caiano L, et al. Fatal pulmonary embolism, fatal bleeding and intracranial hemorrhage with systemic and catheter-directed thrombolysis in intermediate-high and high-risk pulmonary embolism: a systematic review with meta-analysis[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 2644-2644.
[65] Zhang RS, Maqsood MH, Sharp ASP, et al. Efficacy and safety of anticoagulation, catheter-directed thrombolysis, or systemic thrombolysis in acute pulmonary embolism[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2023, 16(21): 2644-2651.
[66] Klok FA, Hösel V, Clemens A, et al. Prediction of bleeding events in patients with venous thromboembolism on stable anticoagulation treatment[J]. Eur Respir J, 2016, 48(5): 1369-1376.
[67] Schulman S, Angerås U, Bergqvist D, et al. Definition of major bleeding in clinical investigations of antihemostatic medicinal products in surgical patients[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2010, 8(1): 202-204. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2009.03678.x
[68] Lim HY, O'Malley C, Donnan G, et al. A review of global coagulation assays-Is there a role in thrombosis risk prediction?[J]. Thromb Res, 2019, 179: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.04.033
[69] 中国医师协会介入医师分会, 中华医学会放射学分会介入专业委员会, 中国静脉介入联盟. 下肢深静脉血栓形成介入治疗规范的专家共识(第2版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(23): 1813-1821. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.23.003
[70] Benes J, Zatloukal J, Kletecka J. Viscoelastic methods of blood clotting assessment-a multidisciplinary review[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2015, 2: 62.
[71] 天津市输血协会围术期输血专业委员会, 于泳浩, 苏林, 等. 床旁血液黏弹性检测围术期应用专家共识[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2023, 30(4): 385-391.
[72] 中国医药教育协会. 《凝血障碍诊断规范》团体标准: T/CMEAS 019-2024[S]. 2024.
[73] Schiffer S, Schwers S, Heitmeier S. The effect of rivaroxaban on biomarkers in blood and plasma: a review of preclinical and clinical evidence[J]. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2023, 55(3): 449-463.
[74] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 血栓与止血检验常用项目的标本采集与处理: WS/T 359-2024[S]. 2024.
[75] Kitchen S, Adcock DM, Dauer R, et al. International Council for Standardization in Haematology(ICSH)recommendations for processing of blood samples for coagulation testing[J]. Int J Lab Hematol, 2021, 43(6): 1272-1283.
[76] 吴瑶瑶, 徐武敏, 黄筱燕, 等. 不同采血方法对血透半永久导管华法林抗凝者出凝血指标的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2016, 14(4): 3.
[77] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 静脉血液标本采集指南[J]. 中国实用乡村医生杂志, 2020, 27(5): 7-11.
[78] 中华医学会检验医学分会. 不合格静脉血标本管理中国专家共识[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2020, 43(10): 956-963.
[79] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 凝血因子活性测定技术标准: WS/T 220-2021[S]. 2021.
[80] Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, et al. WFH guidelines for the management of hemophilia, 3rd edition[J]. Haemophilia, 2020, 26 Suppl 61-158.
[81] Davie EW, Ratnoff OD. Waterfall sequence for intrinsic blood clotting[J]. Science, 1964, 145(3638): 1310-1312.
[82] Lippi G, Salvagno GL, Montagnana M, et al. Quality standards for sample collection in coagulation testing[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2012, 38(6): 565-575.
[83] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 临床血液检验常用项目分析质量标准: WS/T406—2024[S]. 2024.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 550
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: