The value of combined detection of IL-37, PCT and CRP in evaluating the 28-day prognosis of patients with emergency sepsis
-
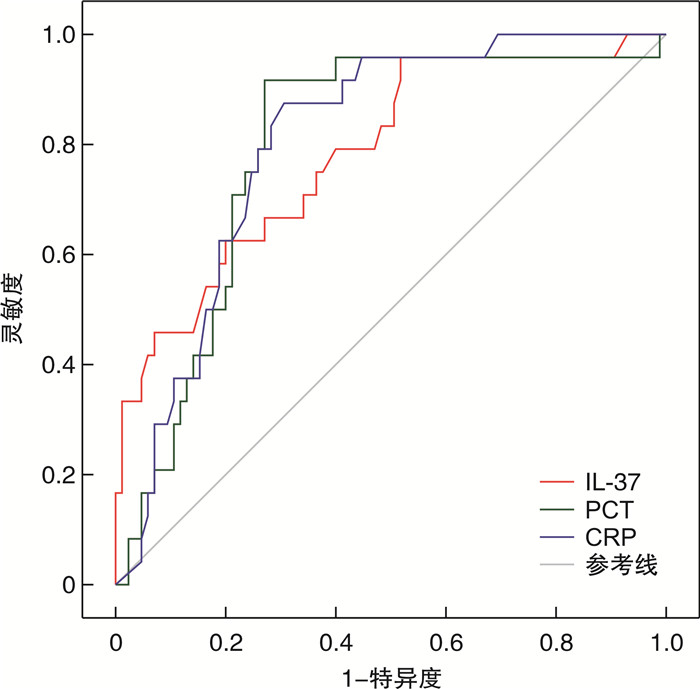
摘要: 目的 回顾性分析早期白细胞介素-37(interleukin-37,IL-37)联合降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、C-反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)对急诊脓毒症患者28 d预后的评估价值。方法 选取2021年10月—2023年8月南京医科大学附属淮安第一医院急诊科收治的109例脓毒症患者,根据脓毒症患者28 d生存情况分为存活组85例和死亡组24例。分别比较两组患者的基础疾病、感染部位、IL-37、PCT、CRP、急性生理与慢性健康评分(acute physiology and chronic health status score Ⅱ,APACHEⅡ)及序贯性器官功能衰竭评分(sequential organ failure assessment,SOFA)。采用二元logistic回归分析影响脓毒症患者28 d预后的危险因素,受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)统计分析IL-37、PCT、CRP单独检测及联合检测对脓毒症患者28 d预后的评估价值。结果 死亡组患者的SOFA评分、APACHE Ⅱ评分、IL-37、PCT、CRP水平均明显高于存活组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);死亡组与存活组之间的高血压、糖尿病、脑梗死、肿瘤等基础疾病和感染部位的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);进一步二元logistic回归分析发现,IL-37、PCT、CRP为急诊脓毒症患者28 d病死率的独立预测因素(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线结果分析显示,IL-37、PCT、CRP三者联合检测对急诊脓毒症患者28 d预后的评估价值明显优于两者联合检测和单独检测的评估价值,其曲线下面积分别为0.783(IL-37)、0.796(PCT)、0.804(CRP)、0.886(IL-37+PCT)、0.877(IL-37+CRP)、0.899(PCT+CRP)、0.912(IL-37+PCT+CRP)。结论 IL-37、PCT、CRP对急诊脓毒症患者28 d预后具有重要的评估价值,且三者联合检测的评估价值明显高于单独检测及两者联合检测的评估价值。Abstract: Objective To retrospectively analyze the value of early interleukin-37(IL-37) combined with procalcitonin(PCT) and C-reactive protein(CRP) in evaluating the 28-day prognosis of emergency sepsis patients.Methods A total of 109 patients with sepsis admitted to the Emergency Department of Huai'an First Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University from October 2021 to August 2023 were selected and divided into a survival group of 85 patients and a death group of 24 patients based on their 28-day survival status. The basic diseases, infection site, IL-37, PCT, CRP, acute physiology and chronic health status score Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ) and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) were compared between the two groups, respectively. Binary logistic regression was used to analyze the risk factors affecting the 28-day prognosis of patients with sepsis. The receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC) was used to statistically analyze the evaluation value of IL-37, PCT, and CRP alone and in combination for the 28-day prognosis of patients with sepsis.Results The levels of SOFA score, APACHEⅡscore, IL-37, PCT and CRP in the death group were significantly higher than those in the survival group(P < 0.05). There was no significant difference between the death group and the survival group in hypertension, diabetes, cerebral infarction, tumor and other basic diseases and infection sites(P>0.05). Further binary logistic regression analysis revealed that IL-37, PCT, and CRP were independent predictors of 28-day mortality in emergency sepsis patients(P < 0.05). The analysis of ROC curve results shows that the combined detection of IL-37, PCT, and CRP has a significantly better evaluation value for the 28-day prognosis of emergency sepsis patients than the combined and individual detection of the two. The area under the curve was 0.783(IL-37), 0.796(PCT), 0.804(CRP), 0.886(IL-37+PCT), 0.877(IL-37+CRP), 0.899(PCT+CRP), and 0.912(IL-37+PCT+CRP), respectively.Conclusion IL-37, PCT, and CRP have important evaluation value for the 28-day prognosis of patients with emergency sepsis, and the evaluation value of IL-37, PCT, and CRP is significantly higher than that of individual detection and their combined detection.
-
Key words:
- sepsis /
- interleukin-37 /
- procalcitonin /
- C-reactive protein /
- 28-day prognosis
-

-
表 1 脓毒症存活组和死亡组一般资料数据分析
项目 总体(109例) 存活组(85例) 死亡组(24例) T/Z/χ2 P 年龄/岁 64.9±13.8 65.8±15.1 64.7±13.6 0.540 0.745 性别/例 0.011 0.915 男 58 45 13 女 51 40 11 基础疾病/例 高血压 56 47 9 0.245 0.621 糖尿病 46 42 4 0.367 0.545 脑梗死 18 14 4 0.267 0.605 肿瘤 13 9 4 0.123 0.726 感染部位/例 肺部 19 11 8 0.073 0.788 泌尿系 47 44 3 0.533 0.465 皮肤软组织 8 5 3 0.067 0.796 其他 25 25 9 0.151 0.697 表 2 脓毒症患者存活组和死亡组相关数据分析
指标 存活组 死亡组 T/Z/χ2 P IL-37/(pg/mL) 114.6(88.6,141.5) 158.9(127.0,224.8) -4.223 < 0.001 PCT/(ng/mL) 23.0(6.0,64.0) 79.3(62.9,91.6) -4.410 < 0.001 CRP/(ng/mL) 133.0(87.5,163.0) 176.0(161.3,192.0) -4.535 < 0.001 SOFA评分/分 7.0(4.5,10.0) 8.5(7.0,12.0) -2.122 0.034 APACHEⅡ评分/分 14.0(11.0,17.5) 20.0(15.0,24.8) -3.846 < 0.001 表 3 脓毒症患者28 d死亡危险因素二元logistic分析
影响因素 β SE Wald χ2 OR P 95%CI IL-37 0.016 0.007 4.787 1.015 0.029 1.002~1.030 PCT 0.031 0.010 8.993 1.031 0.003 1.011~1.053 CRP 0.029 0.011 7.214 1.030 0.007 1.008~1.052 表 4 IL-37、PCT、CRP三者单独检测对脓毒症28 d预后评估价值
变量 AUC 95%CI P 最佳截断值 灵敏度 特异度 IL-37 0.783 0.678~0.888 < 0.010 111.2 pg/mL 0.958 0.482 PCT 0.796 0.699~0.893 < 0.010 55.9 ng/mL 0.917 0.729 CRP 0.804 0.719~0.889 < 0.010 154.5 ng/mL 0.875 0.804 表 5 IL-37、PCT、CRP三者联合检测对脓毒症28 d预后的评估价值
变量 AUC 95%CI P 灵敏度 特异度 IL-37+PCT 0.886 0.820~0.953 < 0.001 0.750 0.894 IL-37+CRP 0.877 0.810~0.944 < 0.001 0.917 0.741 PCT+CRP 0.899 0.824~0.974 < 0.001 0.958 0.835 IL-37+PCT+CRP 0.912 0.844~0.979 < 0.001 0.917 0.871 -
[1] Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock(Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
[2] Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990—2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10219): 200-211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
[3] Xie J, Wang H, Kang Y, et al. The Epidemiology of Sepsis in Chinese ICUs: A National Cross-Sectional Survey[J]. Crit Care Med, 2020, 48(3): e209-e218. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004155
[4] Liu B, Ding X, Yang J. Effect of early goal directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and/or septic shock[J]. Curr Med Res Opin, 2016, 32(11): 1773-1782. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2016.1206872
[5] 刘明娅. IL-37在H1N1感染导致的重症肺炎中发挥的作用及其作用机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国医学科学院, 清华大学医学部, 北京协和医学院动物学, 2021.
[6] Carbonell R, Moreno G, Martin-Loeches I, et al. Prognostic Value of Procalcitonin and C-Reactive Protein in 1608 Critically Ill Patients with Severe Influenza Pneumonia[J]. Antibiotics(Basel), 2021, 10(4): 350.
[7] Kumar J, Singh A. A Comparative Evaluation of Presepsin with Procalcitonin and CRP in Diagnosing Neonatal Sepsis: Correspondence[J]. Indian J Pediatr, 2019, 86(3): 313-314. doi: 10.1007/s12098-018-2744-7
[8] Garvik OS, Povoa P, Magnussen B, et al. C-reactive protein and albumin kinetics before community-acquired bloodstream infections-a Danish population-based cohort study[J]. Epidemiol Infect, 2020, 148: e38. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820000291
[9] 陈正钢, 刘励军. 急诊脓毒症患者早期筛查生物标志物的研究现状与展望[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(2): 99-104. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.02.010
[10] Ali WA, Bazan NS, Elberry AA, et al. A randomized trial to compare procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in assessing severity of sepsis and in guiding antibacterial therapy in Egyptian critically ill patients[J]. Ir J Med Sci, 2021, 190(4): 1487-1495. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02494-y
[11] LaRovere K, Tasker RC. Muscle Weakness After Sepsis in the Critically Ill: Identifiable and Functionally Remediable?[J]. Pediatr Crit Care Med, 2019, 20(9): 888-889. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000002027
[12] Jarczak D, Kluge S, Nierhaus A. Sepsis-Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Concepts[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2021, 8: 628302.
[13] Tete S, Tripodi D, Rosati M, et al. IL-37(IL-1F7) the newest anti-inflammatory cytokine which suppresses immune responses and inflammation[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2012, 25(1): 31-38. doi: 10.1177/039463201202500105
[14] van de Veerdonk FL, Netea MG. New Insights in the Immunobiology of IL-1 Family Members[J]. Front Immunol, 2013, 4: 167.
[15] Wu C, Ma J, Yang H, et al. Interleukin-37 as a biomarker of mortality risk in patients with sepsis[J]. J Infect, 2021, 82(3): 346-354. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.019
[16] 白奎, 王玉珍, 许宏侠, 等. 血小板参数对脓毒症病情评估及预后预测的临床意义[J]. 中国现代医生, 2016, 54(11): 60-62, 65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDYS201611019.htm
[17] 王惠文, 邢柏. 国家早期预警评分联合肾上腺髓质中段肽及降钙素原对脓毒症患者预后的预测价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(21): 2647-2652. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QKYX202021009.htm
[18] 张娅琴, 赵锦宁, 田朝霞, 等. 降钙素原和C反应蛋白在脓毒症诊断及预后评估中的应用[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2019, 16(15): 2205-2207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYYL201915029.htm
[19] 王子文, 王登基, 徐晓梅, 等. APACHE Ⅱ评分联合血清PCT、D-D、LCR对脓毒症患者预后不良的预测研究[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2021, 22(2): 126-130. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2021.02.009
[20] Eschborn S, Weitkamp JH. Procalcitonin versus C-reactive protein: review of kinetics and performance for diagnosis of neonatal sepsis[J]. J Perinatol, 2019, 39(7): 893-903.
[21] Tan M, Lu Y, Jiang H, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(4): 5852-5859.
[22] Pierrakos C, Velissaris D, Bisdorff M, et al. Biomarkers of sepsis: time for a reappraisal[J]. Crit Care, 2020, 24(1): 287.
[23] Wang YC, Weng GP, Liu JP, et al. Elevated serum IL-37 concentrations in patients with sepsis[J]. Medicine(Baltimore), 2019, 98(10): e14756.
[24] 陈君, 王妮, 陈栩栩, 等. ICU脓毒症患者血清Presepsin、内毒素、IL-6、PCT水平与预后的相关性[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(3): 356-359. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202203008.htm
[25] Wu F, Hou XQ, Sun RR, et al. The predictive value of joint detection of serum amyloid protein A, PCT, and Hs-CRP in the diagnosis and efficacy of neonatal septicemia[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(13): 5904-5911.
[26] 李世亮, 陈明. 脓毒症患者血清学指标变化及与预后的相关性[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2022, 50(11): 1301-1304. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202211012.htm
[27] 李雪青, 李文星, 唐英明, 等. 血清Survivin、sFas、IL-37水平对脓毒症患者病情及预后的评估价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2022, 43(11): 1334-1337, 1341. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWSQ202211012.htm
[28] 张志彪, 严丽. PCT、LAC/ScvO2比值对脓毒症患者病情危重程度与预后的评估价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2019, 20(2): 119-123. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2019.02.007
-




 下载:
下载:
