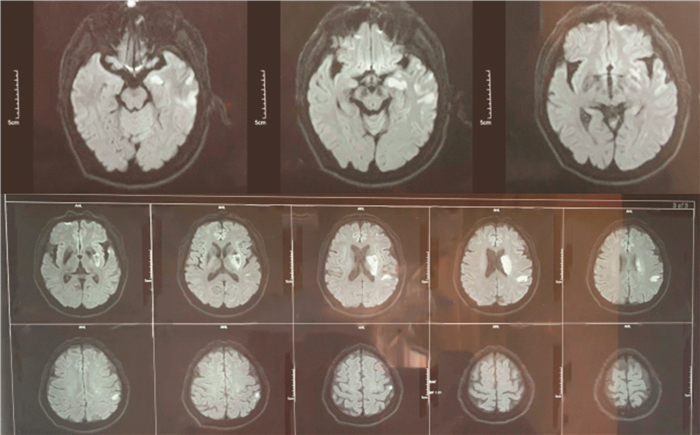
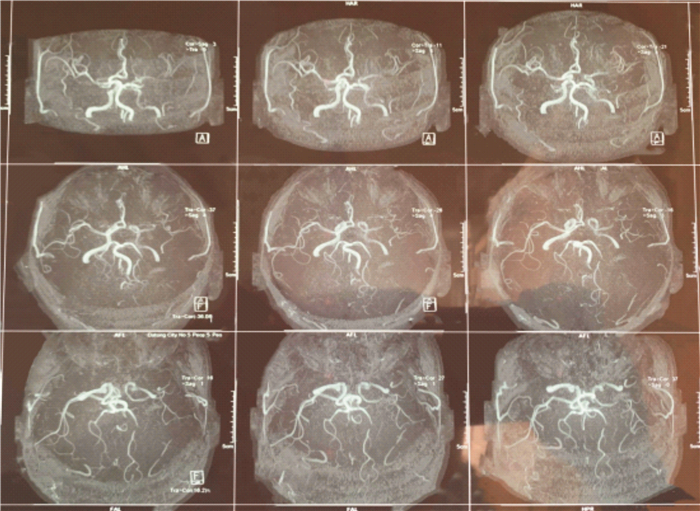
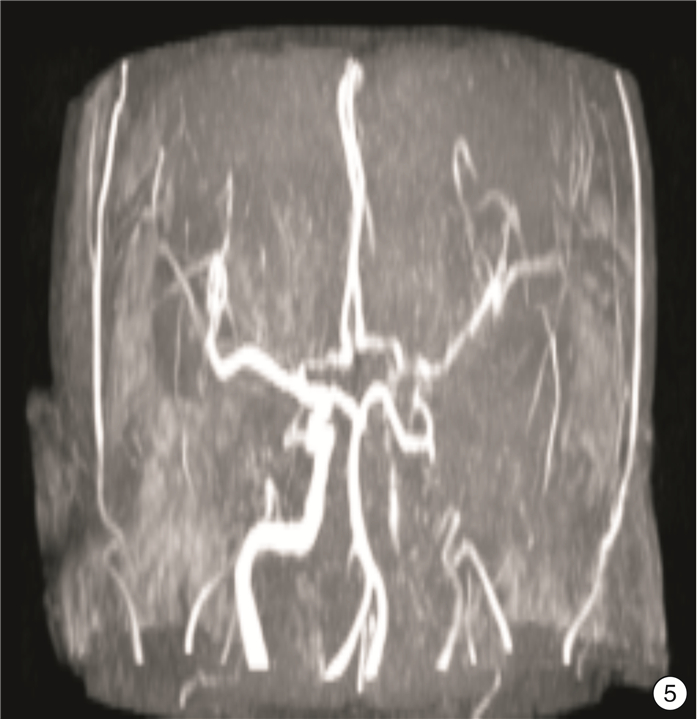
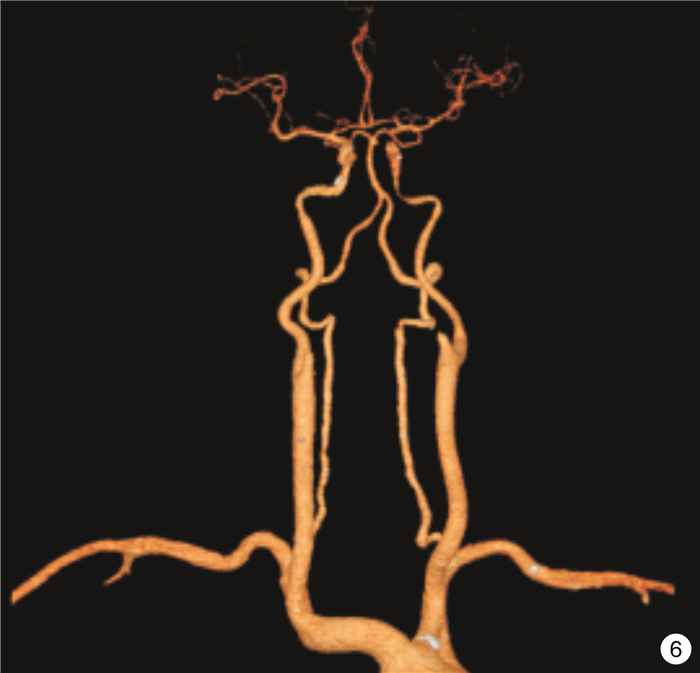
Analysis on evaluation of carotid stenosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke by MRI combined with MRA
-
摘要: 目的 探讨分析磁共振成像(MRI)联合磁共振血管成像(MRA)评估急性缺血性脑卒中(AIS)患者颈动脉狭窄的应用价值。方法 本研究采用前瞻性分析方法,纳入2019年1月—2022年2月我院100例AIS患者为研究对象。全部患者均先后接受MRI、MRA检查,并于1周内进行数字减影血管造影(DSA)检查。以DSA检查结果为“金标准”,分析MRI联合MRA评估AIS患者颈动脉狭窄的应用价值。结果 100例患者经DSA结果证实,共有118条颈动脉血管存在狭窄,其中31条轻度狭窄,48条中度狭窄,29条重度狭窄,10条完全闭塞,占比分别为26.27%、40.68%、24.58%、8.47%;MRI、MRA单独和二者联合评估AIS患者颈动脉狭窄的准确性分别为72.88%、85.59%、96.61%,且以二者联合评估的准确性最高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);以病理学检查结果作为依据,MRI联合MRA评估纤维帽、脂质核、伴有出血、伴有钙化形成和斑块软硬度的符合率比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 MRI联合MRA评估AIS患者颈动脉狭窄与DSA结果具有较高的一致性,有一定的临床应用价值,且还可分析斑块组成成分,具有独特优势。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the value of magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) combined with magnetic resonance angiography(MRA) in the evaluation of carotid stenosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke(AIS).Methods From January 2019 to February 2022, 100 AIS patients in the hospital were included in this study by prospective analysis. All patients underwent MRI and MRA in order, and digital subtraction angiography(DSA) within 1 week. Taking DSA examination results as the"gold standard", the value of MRI combined with MRA in the evaluation of carotid stenosis in patients with AIS was analyzed.Results The results of DSA showed that 118 carotid arteries in 100 patients had stenosis, including 31 mild stenosis, 48 moderate stenosis, 29 severe stenosis and 10 complete occlusion, accounting for 26.27%, 40.68%, 24.58% and 8.47% respectively; the accuracy of MRI, MRA alone and combined assessment of carotid stenosis in patients with AIS were 72.88%, 85.59% and 96.61% respectively, and the accuracy of combined assessment of MRI and MRA was the highest, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05); based on the results of pathological examination, compared the coincidence rate of MRI combined with MRA in evaluating fibrous cap, lipid core, bleeding, calcification and plaque hardness, there was no statistically significant difference(P > 0.05).Conclusion MRI combined with MRA has high consistency with DSA in the evaluation of carotid stenosis in patients with AIS and certain clinical application value. Meanwhile it can also analyze the composition of plaque, with unique advantages.
-

-
表 1 MRI检查颈动脉狭窄结果
例 MRI检查 DSA检查 合计 轻度狭窄 中度狭窄 重度狭窄 完全闭塞 轻度狭窄 21 7 0 0 28 中度狭窄 10 38 4 0 52 重度狭窄 0 3 21 4 28 完全闭塞 0 0 4 6 10 合计 31 48 29 10 118 Kappa值 0.609 表 2 MRA检查颈动脉狭窄结果
例 MRA检查 DSA检查 合计 轻度狭窄 中度狭窄 重度狭窄 完全闭塞 轻度狭窄 27 4 0 0 31 中度狭窄 4 42 2 0 48 重度狭窄 0 2 25 3 30 完全闭塞 0 0 2 7 9 合计 31 48 29 10 118 Kappa值 0.793 表 3 MRI联合MRA检查颈动脉结果
例 MRI联合MRA检查 DSA检查 合计 轻度狭窄 中度狭窄 重度狭窄 完全闭塞 轻度狭窄 30 0 0 0 30 中度狭窄 1 47 0 0 48 重度狭窄 0 1 28 1 30 完全闭塞 0 0 1 9 10 合计 31 48 29 10 118 Kappa值 0.951 表 4 MRI联合MRA评估AIS患者颈动脉斑块特征的价值
例 斑块特征 病理学检查 MRI联合MRA 符合率/ 例(%) χ2 P 纤维帽 113 110 110(97.35) 1.351 0.245 脂质核 92 87 87(94.57) 3.289 0.070 伴有出血 61 58 58(95.08) 1.367 0.242 伴有钙化形成 90 88 88(97.78) 0.506 0.477 表 5 MRI联合MRA评估AIS患者颈动脉斑块软硬度的价值
例(%) 评估方法 软斑块 硬斑块 病理学检查 83(48.26) 89(51.74) MRI联合MRA 80(46.51) 92(53.49) χ2 0.105 P 0.746 -
[1] Ma J, Zhao L, Yuan K, et al. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis after acute ischemic stroke detected by intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Neurol Sci, 2022, 43(2): 1135-1141. doi: 10.1007/s10072-021-05425-6
[2] Yaghi S, de Havenon A, Rostanski S, et al. Carotid Stenosis and Recurrent Ischemic Stroke: A Post-Hoc Analysis of the POINT Trial[J]. Stroke, 2021, 52(7): 2414-2417. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034089
[3] von Reutern GM. Validation of Multiparametric Ultrasonography Criteria with Digital Subtraction Angiography in Carotid Artery Disease: A Prospective Multicenter Study[J]. Ultraschall Med, 2019, 40(4): 516. doi: 10.1055/a-0889-8042
[4] Mori T, Yoshioka K, Tanno Y, et al. Reduced magnetic resonance angiography signal intensity in the middle cerebral artery ipsilateral to severe carotid stenosis may be a practical index of high oxygen extraction fraction[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(3): 2023-2029. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08272-3
[5] 赵永超, 邹智, 李永丽, 等. 四维磁共振血管成像对脑动静脉畸形诊断效能的Meta分析[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(4): 57-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202104011.htm
[6] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-682. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004
[7] North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators, Barnett HJM, Taylor DW, et al. Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis[J]. N Engl J Med, 1991, 325(7): 445-453. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250701
[8] Ren J, Dong X, Nao J. Serum cystatin C is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke[J]. Neurol Sci, 2020, 41(10): 2793-2800. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-04383-9
[9] Pienimäki JP, Sillanpää N, Jolma P, et al. Carotid Artery Stenosis Is Associated with Better Intracranial Collateral Circulation in Stroke Patients[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2020, 49(2): 200-205. doi: 10.1159/000506826
[10] Lehmann A, Alfieri DF, de Araújo M, et al. Carotid intima media thickness measurements coupled with stroke severity strongly predict short-term outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke: a machine learning study[J]. Metab Brain Dis, 2021, 36(7): 1747-1761. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00784-7
[11] Poppe AY, Jacquin G, Roy D, et al. Tandem Carotid Lesions in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Mechanisms, Therapeutic Challenges, and Future Directions[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2020, 41(7): 1142-1148. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6582
[12] Marto JP, Lambrou D, Eskandari A, et al. Associated Factors and Long-Term Prognosis of 24-Hour Worsening of Arterial Patency After Ischemic Stroke[J]. Stroke, 2019, 50(10): 2752-2760. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025787
[13] 黄通, 邹思力, 沈旭, 等. 彩色多普勒超声及数字减影血管造影对颈动脉狭窄患者颈动脉分叉水平及颅外段颈内动脉形态的评估[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2022, 102(11): 781-786. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210605-01285
[14] 李婷, 林雁潮, 王瑶, 等. 颈部血管超声、CT血管成像及磁共振成像在急性缺血性脑卒中患者颈动脉狭窄诊断中的应用比较[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2019, 35(12): 2005-2009. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2019.12.032
[15] 张浩南, 宋清伟, 张钦和, 等. 磁共振血管成像评估颈动脉狭窄的研究进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2021, 12(3): 92-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGZC202103023.htm
[16] 于加贝, 徐刚, 唐雨, 等. 磁共振成像与磁共振血管造影在诊断颈动脉狭窄中的应用价值[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2020, 20(1): 116-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-816x.2020.01.030
[17] 阿力木·吾甫尔, 买买提吐尔·克力木, 张小宁. 磁共振成像对症状性颈动脉狭窄和粥样硬化斑块特征的诊断价值[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2016, 24(1): 72-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KDYZ201601016.htm
[18] Dong L, Underhill HR, Yu W, et al. Geometric and compositional appearance of atheroma in an angiographically normal carotid artery in patients with atherosclerosis[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2010, 31(2): 311-316. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1793
[19] Greve T, Sollmann N, Hock A, et al. Highly accelerated time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography using spiral imaging improves conspicuity of intracranial arterial branches while reducing scan time[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(2): 855-865. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06442-y
[20] 李硕, 高俊华, 梁博, 等. MRI血管造影对颈动脉狭窄程度和斑块组成成分的检测效果[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2021, 39(4): 615-619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GKGH202104025.htm
[21] Lv P, Lin J, Guo D, et al. Detection of carotid artery stenosis: a comparison between 2 unenhanced MRAs and dual-source CTA[J]. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol, 2014, 35(12): 2360-2365. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4073
[22] 姬智艳, 刘德祥, 陈显杰, 等. 能谱CTA分析颈动脉斑块成分及其与脑梗死的关系[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2020, 36(9): 1309-1313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX202009009.htm
-




 下载:
下载: