Expert consensus on prevention and blocking of severe acute pancreatitis in emergency department
-
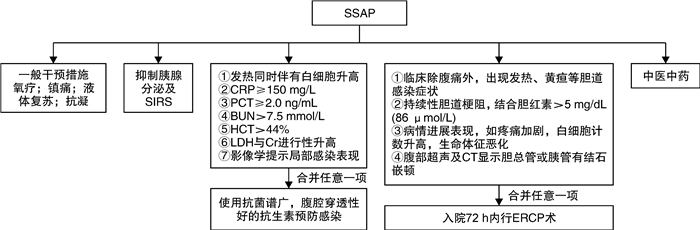
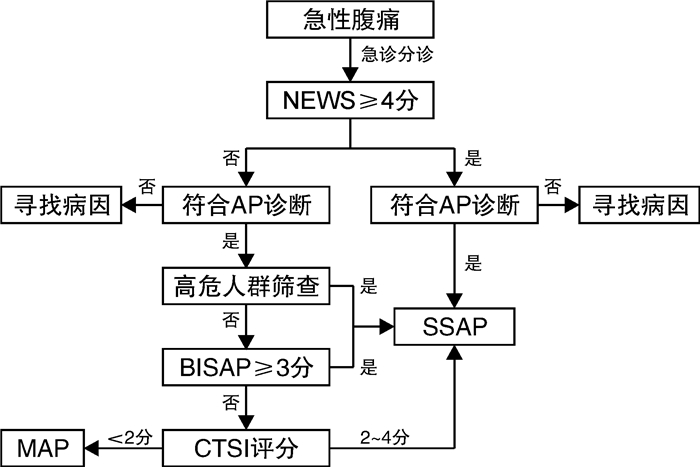
摘要: 急性胰腺炎是急诊科常见的严重消化系统疾病之一,近年来急诊科收治的急性胰腺炎患者有增无减。急诊科早期积极有效地处理可以减轻胰腺炎带来的器官功能损害,改善患者预后。目前急性胰腺炎的严重程度分型需要在发病后48 h才能确定,这种诊断时间上的“滞后性”,无法为急诊科急性胰腺炎分级诊疗提供帮助。该共识通过文献整理、专家讨论,根据患者的基础病情、来急诊时全身和胰腺局部表现等,提出“疑似重症急性胰腺炎(SSAP)”的概念,为急性胰腺炎的早期规范化处理提出了病理生理学依据,为预防与阻断重症急性胰腺炎的发生提供了基础。本共识总结既往研究,从高危患者筛选到细胞因子测定,联合多项重症患者通用评分和胰腺炎专项评分,使急性胰腺炎患者在急诊科得到充分评估,并提出一系列包括液体复苏、器官支持、中医中药等SSAP阻断方案,促进急性胰腺炎患者早期康复。Abstract: Acute pancreatitis is one of the common serious digestive system diseases in emergency department, recently, the number of acute pancreatitis patients admitted to emergency department is increasing.Early active and effective management in emergency department can reduce organ function damage caused by pancreatitis and improve the prognosis of patients.At present, the severity of acute pancreatitis can only be determined 48 hours after the onset of the disease.This "lag" in diagnosis time cannot provide help for the graded diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis in the emergency department.Through literature review and expert discussion, the concept of "suspicious severe acute pancreatitis(SSAP)" was proposed according to patients' basic conditions, systemic and local pancreatic manifestations when they came to the emergency department, so as to provide a pathophysiological theory for the early standardized management of acute pancreatitis, and to provide a basis for the prevention and blocking of severe acute pancreatitis.Consensus summarizes the previous studies, from screening high-risk patients to the determination of cytokines, combined a number of patients with severe general special score, score and pancreatitis make full assessment of the patients with acute pancreatitis in the emergency department, and put forward a series include: liquid recovery, organ support, such as Chinese medicine SSAP blocking scheme, promote early rehabilitation of acute pancreatitis.
-
Key words:
- suspicious severe acute pancreatitis /
- early recogmition /
- prevention /
- treatment
-

-
表 1 急性胰腺炎腹痛特征
腹痛 特征 性质 急性发作,持续性,可严重疼痛 部位 上腹或左上腹 放射 背部、胸部和左侧腹部 伴随症状 恶心、呕吐、黄疸、腹胀及发热 表 2 中国急性胰腺炎分类诊断及预后
分类诊断 特征 预后 MAP 具备急性胰腺炎表现和生化变化,不伴有局部或全身并发症 通常在1~2周内就可恢复,病死率极低 MSAP 具备急性胰腺炎表现和生化变化,伴有一过性器官功能衰竭(48 h内可以恢复)和(或)局部并发症 早期病死率低,如坏死组织合并感染,则病死率增高 SAP 具备急性胰腺炎表现和生化变化,伴有持续(>48 h)器官功能衰竭 病死率高,如合并感染则病死率极高 表 3 急性胰腺炎病情判断评分系统
评分系统 评分名称 Glasgow昏迷评分 急重症通用评分 急性生理与慢性健康评分Ⅱ(APACHEⅡ) 序贯器官衰竭评分(SOFA) JSS Ranson评分 改良Marshall评分 胰腺炎专项评分 简化急性生理评分(SAPSⅡ) BISAP 胰腺炎活动度评分系统(pancreatitis activity scoring system,PASS) 表 4 BISAP评分标准
评分指标 评分/分 血BUN>8.9 mmol/L 1 精神异常 1 存在SIRS 1 年龄>60岁 1 影像学检查显示胸腔积液 1 注:评分1~2分为低危患者,≥3分为高危患者。 表 5 CTSI评分标准
项目 评分标准 评分/分 A级:胰腺正常 0 B级:胰腺局限性渗出肿大 1 急性胰腺炎分级 C级:胰腺实质异常伴有轻度胰腺周围炎症改变 2 D级:1处胰周积液、蜂窝织炎,通常位于肾前间隙 3 E级:≥2处区域胰周积液,或胰腺内、胰周炎症内积气 4 胰腺无坏死 0 胰腺坏死程度 胰腺坏死<30% 2 胰腺坏死30%~50% 4 胰腺坏死>50% 6 注:CTSI评分=急性胰腺炎分级+胰腺坏死程度评分;Ⅰ级:0~3分, Ⅱ级:4~6分, Ⅲ级:7~10分;CTSI>4分为重症。 表 6 血气分析对急性胰腺炎严重程度的判断
项目 变化 分级 含义 PaCO2 下降 Ⅰ级 轻度肺损伤,代偿期 PaO2 下降 Ⅱ级 肺损伤 碱剩余、HCO3- 下降 Ⅲ级 组织灌注下降 乳酸 升高 Ⅳ级 组织缺氧 -
[1] 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2021)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2021, 41(7): 739-746. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNK201307012.htm
[2] EI Halabi M, Bou Daher H, Rustom L, et al. Characteristics and outcome of patients presenting with acute Pancreatitis: A one-year descriptive study from a tertiary care center in Lebanon[J]. Arab J Gastroenterol, 2020, 21(2): 106-110. doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2020.04.015
[3] Yadav D, Lowenfels AB. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2013, 144(6): 1252-1261. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.068
[4] Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2021[J]. Gastroenterology, 2022, 162(2): 621-644. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.017
[5] Lankisch PG, Apte M, Banks PA. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(9988): 85-96. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60649-8
[6] 急性胰腺炎协作组. 中国6 223例急性胰腺炎病因及病死率分析[J]. 胰腺病学, 2006, 6(6): 321-325. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXBX200606000.htm
[7] Gapp J, Hall AG, Walters RW, et al. Trends and Outcomes of Hospitalizations Related to Acute Pancreatitis: Epidemiology From 2001 to 2014 in the United States[J]. Pancreas, 2019, 48(4): 548-554. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001275
[8] Garg SK, Sarvepalli S, Campbell JP, et al. Incidence, Admission Rates, and Predictors, and Economic Burden of Adult Emergency Visits for Acute Pancreatitis: Data From the National Emergency Department Sample, 2006 to 2012[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2019, 53(3): 220-225. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000001030
[9] Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis, 2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus[J]. Gut, 2013, 62(1): 102-111. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779
[10] Berger Z, Mancilla C, Tobar E, et al. Acute pancreatitis in Chile: A multicenter study on epidemiology, etiology and clinical outcome. Retrospective analysis of clinical files[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20(4): 637-643. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.04.016
[11] Garg SK, Campbell JP, Anugwom C, et al. Incidence and Predictors of Readmissions in Acute Pancreatitis: A Nationwide Analysis[J]. Pancreas, 2018, 47(1): 46-54. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000952
[12] Bolourani S, Diao L, Thompson DA, et al. Risk Factors for Early Readmission After Acute Pancreatitis: Importance of Timely Interventions[J]. J Surg Res, 2020, 252: 96-106. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.03.003
[13] Forsmark CE, Vege SS, Wilcox CM. Acute Pancreatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016, 375(20): 1972-1981. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1505202
[14] Phillip V, Huber W, Hagemes F, et al. Incidence of acute pancreatitis does not increase during Oktoberfest, but is higher than previously described in Germany[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 9(11): 995-1000.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.06.016
[15] Hong S, Qiwen B, Ying J, et al. Body mass index and the risk and prognosis of acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 23(12): 1136-1143. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32834b0e0e
[16] Maheshwari R, Subramanian RM. Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Necrotizing Pancreatitis[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2016, 32(2): 279-290. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2015.12.006
[17] Ikarashi S, Kawai H, Hayashi K, et al. Risk factors for walled-off necrosis associated with severe acute pancreatitis: A multicenter retrospective observational study[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2020, 27(11): 887-895. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.787
[18] Tenner S, Baillie J, Dewitt J, et al. American College of Gastroenterology guideline: management of acute pancreatitis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2013, 108(9): 1400-1415, 1416-1416. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2013.218
[19] Liang Y, Zhao X, Meng F. Procalcitonin, C-Reactive Protein, and Neutrophil Ratio Contribute to the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Severe Acute Pancreatitis[J]. Iran J Public Health, 2019, 48(12): 2177-2186.
[20] Forsmark CE, Vege SS, Wilcox CM. Acute Pancreatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 376(6): 598-599.
[21] Zhao K, Adam SZ, Keswani RN, et al. Acute Pancreatitis: Revised Atlanta Classification and the Role of Cross-Sectional Imaging[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2015, 205(1): 32-41. doi: 10.2214/AJR.14.14056
[22] Hines OJ, Pandol SJ. Management of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. BMJ, 2019, 367: 6227.
[23] Yokoe M, Takada T, Mayumi T, et al. Japanese guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis: Japanese Guidelines 2015[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2015, 22(6): 405-432. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.259
[24] Meher S, Mishra TS, Sasmal PK, et al. Role of Biomarkers in Diagnosis and Prognostic Evaluation of Acute Pancreatitis[J]. J Biomark, 2015, 2015: 519534.
[25] 徐冬梅, 季孝, 周雪芬, 等. 白细胞介素-6、血清淀粉样A蛋白、唾液酸、HBP在发热患者中的诊断价值[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2019, 29(24): 3027-3029. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ201924026.htm
[26] 冯所远, 符史健. 血清淀粉酶、C反应蛋白、降钙素原与尿胰蛋白酶原激活肽联合检测对急性胰腺炎的诊断价值[J]. 中国普通外科杂志, 2018, 27(3): 377-381. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWZ201803024.htm
[27] Sternby H, Hartman H, Johansen D, et al. IL-6 and CRP are superior in early differentiation between mild and non-mild acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2017, 17(4): 550-554. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.05.392
[28] Staubli SM, Oertli D, Nebiker CA. Laboratory markers predicting severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 2015, 52(6): 273-283. doi: 10.3109/10408363.2015.1051659
[29] 邱渊, 李莉, 曾来星. 重症急性胰腺炎患者C反应蛋白及血清降钙素原的变化[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2019, 23(12): 62-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYZL201912018.htm
[30] Ivanusa SY, Ivanov AM, Lazutkin MV, et al. Opportunities of modern laboratory diagnostics of infectious complications of acute pancreatitis(review)[J]. Klin Lab Diagn, 2019, 64(3): 145-152. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2019-64-3-145-152
[31] Vasudevan S, Goswami P, Sonika U, et al. Comparison of Various Scoring Systems and Biochemical Markers in Predicting the Outcome in Acute Pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2018, 47(1): 65-71. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000957
[32] 陈方莹, 柏小寅, 吴东. 预测急性胰腺炎严重程度的评分系统及生物标志物[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2019, 58(8): 615-619. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2019.08.016
[33] Valverde-Lopez F, Matas-Cobos AM, Alegria-Motte C, et al. BISAP, RANSON, lactate and others biomarkers in prediction of severe acute pancreatitis in a European cohort[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2017, 32(9): 1649-1656. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13763
[34] 黄莚庭. 急性胰腺炎细胞内的早期事件[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2000(4): 75-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHWK200004039.htm
[35] Charalabopoulos A, Davakis S, Lambropoulou M, et al. Apigenin Exerts Anti-inflammatory Effects in an Experimental Model of Acute Pancreatitis by Down-regulating TNF-α[J]. In Vivo, 2019, 33(4): 1133-1141. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11583
[36] Frohlich M, Wafaisade A, Mansuri A, et al. Which score should be used for posttraumatic multiple organ failure? Comparison of the MODS, Denver-and SOFA-Scores[J]. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med, 2016, 24(1): 130. doi: 10.1186/s13049-016-0321-5
[37] Gliem N, Ammer-Herrmenau C, Ellenrieder V, et al. Management of Severe Acute Pancreatitis: An Update[J]. Digestion, 2021, 102(4): 503-507. doi: 10.1159/000506830
[38] Sharma V, Shanti Devi T, Sharma R, et al. Arterial pH, bicarbonate levels and base deficit at presentation as markers of predicting mortality in acute pancreatitis: a single-centre prospective study[J]. Gastroenterol Rep(Oxf), 2014, 2(3): 226-231.
[39] Levy MM, Evans LE, Rhodes A. The Surviving Sepsis Campaign Bundle: 2018 update[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2018, 44(6): 925-928. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5085-0
[40] Gardner TB, Vege SS, Chari ST, et al. Faster rate of initial fluid resuscitation in severe acute pancreatitis diminishes in-hospital mortality[J]. Pancreatology, 2009, 9(6): 770-776. doi: 10.1159/000210022
[41] Brown A, Baillargeon JD, Hughes MD, et al. Can fluid resuscitation prevent pancreatic necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis?[J]. Pancreatology, 2002, 2(2): 104-107. doi: 10.1159/000055899
[42] Trikudanathan G, Navaneethan U, Vege SS. Current controversies in fluid resuscitation in acute pancreatitis: a systematic review[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(6): 827-834. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31824c1598
[43] Wu BU, Conwell DL. Acute pancreatitis part Ⅰ: approach to early management[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2010, 8(5): 410-416. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.10.033
[44] Yi XL, Hu J, Wu QT, et al. Effect of Different-Volume Fluid Resuscitation on Organ Functions in Severe Acute Pancreatitis and Therapeutic Effect of Poria cocos[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2020, 2020: 6408202.
[45] Sah RP, Saluja A. Molecular mechanisms of pancreatic injury[J]. Curr Opin Gastroenterol, 2011, 27(5): 444-451. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0b013e328349e346
[46] Moggia E, Koti R, Belgaumkar AP, et al. Pharmacological interventions for acute pancreatitis[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2017, 4: CD011384.
[47] Wang R, Yang F, Wu H, et al. High-dose versus low-dose octreotide in the treatment of acute pancreatitis: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Peptides, 2013, 40: 57-64. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2012.12.018
[48] Yoo JH, Kwon CI, Yoo KH, et al. Effect of proton pump inhibitor in patients with acute pancreatitis-pilot study[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2012, 60(6): 362-367. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2012.60.6.362
[49] Italian Association for the Study of the Pancreas(AISP), Pezzilli R, Zerbi A, et al. Consensus guidelines on severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2015, 47(7): 532-543. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2015.03.022
[50] Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H, Hashimoto H, et al. Effect and cost of treatment for acute pancreatitis with or without gabexate mesylate: a propensity score analysis using a nationwide administrative database[J]. Pancreas, 2013, 42(2): 260-264. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e31826495a0
[51] Chen S, Shi H, Zou X, et al. Role of ulinastatin in preventing post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: the Emperor's New Clothes or Aladdin's Magic Lamp?[J]. Pancreas, 2010, 39(8): 1231-1237. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181dc67e7
[52] Wang G, Liu Y, Zhou SF, et al. Effect of Somatostatin, Ulinastatin and Gabexate on the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis[J]. Am J Med Sci, 2016, 351(5): 506-512. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2016.03.013
[53] 杨柯君. 中国医师协会发布《2013中国急诊急性胰腺炎临床实践指南》[J]. 上海医药, 2014, 35(4): 42-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYIY201404020.htm
[54] Pekgoz M. Post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: A systematic review for prevention and treatment[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(29): 4019-4042. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i29.4019
[55] Tang LP, Xiao W, Li YF, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Reduning Injection on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury of rats[J]. Chin J Integr Med, 2014, 20(8): 591-599. doi: 10.1007/s11655-014-1758-x
[56] 常秀娟, 张帅, 江益平, 等. 从细胞因子风暴探讨热毒宁注射液抗大鼠急性肺损伤作用机制[J]. 中草药, 2015, 46(2): 236-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCYO201502020.htm
[57] Leppaniemi A, Tolonen M, Tarasconi A, et al. 2019 WSES guidelines for the management of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. World J Emerg Surg, 2019, 14: 27. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0247-0
[58] Wittau M, Wagner E, Kaever V, et al. Intraabdominal tissue concentration of ertapenem[J]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2006, 57(2): 312-316. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki459
[59] Wacke R, Forster S, Adam U, et al. Penetration of moxifloxacin into the human pancreas following a single intravenous or oral dose[J]. J Antimicrob Chemother, 2006, 58(5): 994-999. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl353
[60] 中华中医药学会脾胃病分会, 刘凤斌, 胡玲, 等. 消化系统常见病急性胰腺炎中医诊疗指南(基层医生版)[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2020, 35(4): 1906-1913. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BXYY202004079.htm
[61] 孟秋菊. 急性胰腺炎的病机演变与中医证治思路探析[J]. 浙江中西医结合杂志, 2014, 24(2): 116-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJZH201402011.htm
[62] 王翔, 刘祥树, 宋亚君. 中医辨证治疗ICU重症急性胰腺炎的临床疗效研究[J]. 湖北中医药大学学报, 2019, 21(4): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZXX201904028.htm
[63] 高霞, 张昔伟, 王婷玉, 等. 清胰汤联合早期肠内营养治疗重症急性胰腺炎临床疗效Meta分析[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2020, 22(9): 152-157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LZXB202009037.htm
[64] 潘洋, 白琬璇. 加减清胰汤治疗肝郁气滞型急性水肿性胰腺炎60例临床观察[J]. 黑龙江中医药, 2020, 49(2): 62-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLZY202002044.htm
[65] 项红, 尚东. 茵陈蒿汤加味化裁治疗急性胰腺炎[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2015, 21(6): 626-628. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZX201506033.htm
[66] 任晓芳, 阮艳, 王敏. 龙胆泻肝汤联合西医疗法治疗急性胰腺炎临床观察[J]. 新中医, 2015, 47(4): 115-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REND201504059.htm
[67] 王军. 清胰利胆颗粒联合乌司他丁和生长抑素治疗急性重症胰腺炎的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2016, 31(9): 1477-1481. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWZW201609037.htm
[68] 贾楠, 何茵, 赵海颖, 等. 清胰利胆颗粒对重症急性胰腺炎患者血清HMGB1, HSP70, HSP27, IL-8水平的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(24): 4650-4652, 4675-4675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201724011.htm
[69] 郑蕊, 张莉, 田然, 等. 血必净注射液治疗重症急性胰腺炎的Meta分析[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2015, 27(8): 682-686. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTCT202101049.htm
[70] 蔡北源, 李建华, 杨丽明, 等. 复方丹参注射液治疗急性胰腺炎的系统评价[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2012, 29(4): 470-473, 477-477. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-REST201204041.htm
[71] 张春漪, 逯阳, 张良登. 参附注射液治疗急性胰腺炎的系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 中国中医急症, 2015, 24(7): 1200-1202, 1205-1205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYJZ201507027.htm
[72] Chen X, Yang K, Jing G, et al. Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Rhubarb Combined With Early Enteral Nutrition for the Treatment of Severe Acute Pancreatitis[J]. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr, 2020, 44(6): 1066-1078.
[73] 戈宏焱, 陈博. 穴位贴敷配合药物治疗急性胰腺炎临床观察[J]. 中国针灸, 2012, 32(7): 602-604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZE201207012.htm
[74] 郑西, 何文华, 吕农华. 急性胰腺炎的治疗: 近5年进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2018, 38(3): 245-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYNK201803019.htm
[75] Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2013, 13(4 Suppl 2): e1-15.
[76] Crockett SD, Wani S, Gardner TB, et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on Initial Management of Acute Pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2018, 154(4): 1096-1101.
[77] Gottlieb M, Koyfman A, Long B. Evaluation and Management of Abdominal Compartment Syndrome in the Emergency Department[J]. J Emerg Med, 2019, 58(1): 43-53.
[78] Mowery NT, Bruns BR, Macnew HG, et al. Surgical management of pancreatic necrosis: A practice management guideline from the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg, 2017, 83(2): 316-327.
[79] 王春友, 杨明. 急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2014)解读——急性胰腺炎外科诊治难点分析[J]. 临床外科杂志, 2015, 23(1): 11-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCWK201501007.htm
[80] Hollemans RA, Bakker OJ, Boermeester MA, et al. Superiority of Step-up Approach vs Open Necrosectomy in Long-term Follow-up of Patients With Necrotizing Pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 156(4): 1016-1026.
[81] van Santvoort HC, Besselink MG, Bakker OJ, et al. A step-up approach or open necrosectomy for necrotizing pancreatitis[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(16): 1491-1502.
[82] Cao F, Duan N, Gao C, et al. One-Step verse Step-Up Laparoscopic-Assisted Necrosectomy for Infected Pancreatic Necrosis[J]. Dig Surg, 2020, 37(3): 211-219.
-




 下载:
下载: