Interpretation of 2021 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute heart failure
-
-
关键词:
- 急性心力衰竭 /
- 急性失代偿性心力衰竭 /
- 指南解读
-
Key words:
- acute heart failure /
- acute decompensated heart failure /
- interpretation
-

-
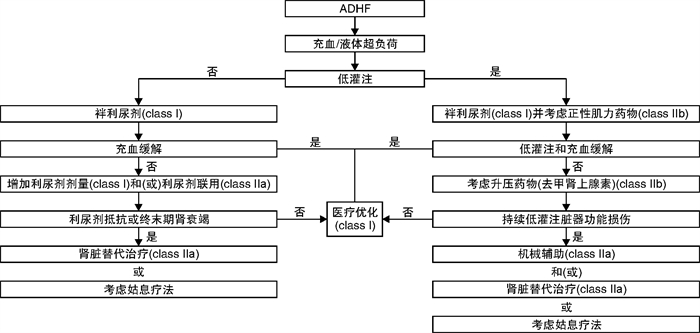
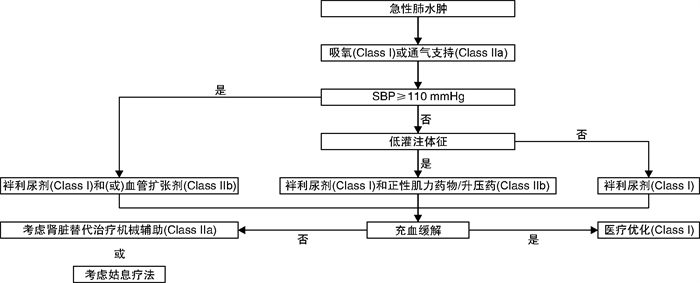
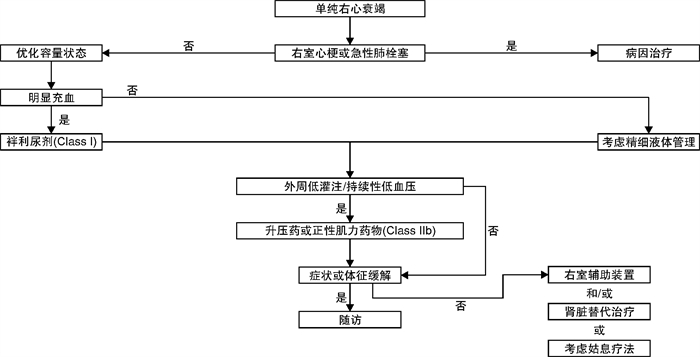
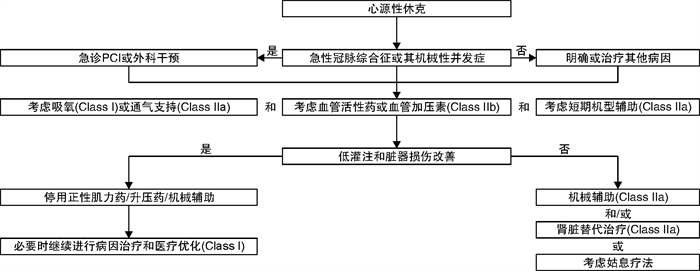
表 1 AHF的相关临床表现
ADHF 急性肺水肿 单纯右心衰竭 心源性休克 主要机制 左心室功能障碍
肾脏水钠潴留后负荷增加和(或)显著左室舒张功能障碍/心脏瓣膜病 右心室功能障碍和(或)毛细血管前肺动脉高压 严重心功能不全 主要原因 液体积聚,心室内压力增高 液体再分布至肺,急性呼吸衰竭 中心静脉压升高,常伴有全身灌注不足 全身灌注不足 发病 逐渐(数天) 迅速(数小时) 逐渐或迅速 逐渐或迅速 主要血流动力学异常 左室舒张末压和肺毛细血管楔压增加
心排量正常或降低
收缩压正常或降低左室舒张末压和肺毛细血管楔压增加
心排量正常
收缩压正常或升高右心室舒张末压增加
心排量降低
收缩压降低左室舒张末压和肺毛细血管楔压增加
心排量降低
收缩压降低临床表现 湿暖或湿冷 湿暖 湿冷 湿冷 主要治疗 利尿剂
正性肌力药物/升压药(如有外周低灌注/低血压)
必要时短期机械循环支持或肾脏替代治疗利尿剂
血管扩张剂利尿剂治疗外周淤血
正性肌力药物/升压药(如有外周低灌注/低血压)
必要时短期机械循环支持或肾脏替代治疗正性肌力药物/升压药
短期机械循环支持
肾脏替代治疗 -
[1] McDonagh TA, Metra M, Adamo M, et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(36): 3599-3726. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab368
[2] Ezekowitz JA, McMurtry MS. Reader Commentary on 2017 Comprehensive Update of the Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines for the Management of Heart Failure[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2018, 34(6): 813.
[3] Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA Focused Update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(6): e137-e161.
[4] 王华, 梁延春. 中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2018[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2018, 46(10): 760-789. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.10.004
[5] Price S, Platz E, Cullen L, et al. Expert consensus document: Echocardiography and lung ultrasonography for the assessment and management of acute heart failure[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2017, 14(7): 427-440. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.56
[6] Chow SL, Maisel AS, Anand I, et al. Role of Biomarkers for the Prevention, Assessment, and Management of Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2017, 135(22): e1054-e1091.
[7] 中国医师协会急诊医师分会, 中国心胸血管麻醉学会急救与复苏分会. 中国急性心力衰竭急诊临床实践指南(2017)[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2017, 26(12): 1347-1357. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2017.12.003
[8] Masip J, Peacock WF, Price S, et al. Indications and practical approach to non-invasive ventilation in acute heart failure[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(1): 17-25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx580
[9] Taylor CJ, Rutten FH, Brouwer JR, et al. Practical guidance on heart failure diagnosis and management in primary care: recent EPCCS recommendations[J]. Br J Gen Pract, 2017, 67(660): 326-327. doi: 10.3399/bjgp17X691553
[10] Mullens W, Verbrugge FH, Nijst P, et al. Rationale and design of the ADVOR(Acetazolamide in Decompensated Heart Failure with Volume Overload)trial[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2018, 20(11): 1591-1600. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1307
[11] Cox ZL, Hung R, Lenihan DJ, et al. Diuretic Strategies for Loop Diuretic Resistance in Acute Heart Failure: The 3T Trial[J]. JACC Heart Fail, 2020, 8(3): 157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2019.09.012
[12] Mullens W, Damman K. Response to letters on "The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion-a position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology"[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2019, 21(7): 949-950.
[13] Damman K, Ter Maaten JM, Coster JE, et al. Clinical importance of urinary sodium excretion in acute heart failure[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2020, 22(8): 1438-1447. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1753
[14] Kozhuharov N, Goudev A, Flores D, et al. Effect of a Strategy of Comprehensive Vasodilation vs Usual Care on Mortality and Heart Failure Rehospitalization Among Patients With Acute Heart Failure: The GALACTIC Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA, 2019, 322(23): 2292-2302. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.18598
[15] Freund Y, Cachanado M, Delannoy Q, et al. Effect of an Emergency Department Care Bundle on 30-Day Hospital Discharge and Survival Among Elderly Patients With Acute Heart Failure: The ELISABETH Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA, 2020, 324(19): 1948-1956. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.19378
[16] Mebazaa A, Motiejunaite J, Gayat E, et al. Long-term safety of intravenous cardiovascular agents in acute heart failure: results from the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Long-Term Registry[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2018, 20(2): 332-341. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.991
[17] Levy B, Mebazaa A, Vignon P, et al. Reply: Norepinephrine Versus Epinephrine in Cardiogenic Shock After Acute Myocardial Infarction: Do We Have an Answer?[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2018, 72(19): 2413. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.008
[18] Léopold V, Gayat E, Pirracchio R, et al. Correction to: Epinephrine and short-term survival in cardiogenic shock: an individual data meta-analysis of 2583 patients[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2018, 44(11): 2022-2023. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5372-9
[19] Gil V, Domínguez-Rodríguez A, Masip J, et al. Morphine Use in the Treatment of Acute Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema and Its Effects on Patient Outcome: A Systematic Review[J]. Curr Heart Fail Rep, 2019, 16(4): 81-88. doi: 10.1007/s11897-019-00427-0
[20] Caspi O, Naami R, Halfin E, et al. Adverse dose-dependent effects of morphine therapy in acute heart failure[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2019, 293 131-136. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.06.015
[21] Tehrani BN, Truesdell AG, Sherwood MW, et al. Standardized Team-Based Care for Cardiogenic Shock[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2019, 73(13): 1659-1669. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.12.084
[22] Basir MB, Kapur NK, Patel K, et al. Improved Outcomes Associated with the use of Shock Protocols: Updates from the National Cardiogenic Shock Initiative[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2019, 93(7): 1173-1183.
[23] Tehrani BN, Truesdell AG, Psotka MA, et al. A Standardized and Comprehensive Approach to the Management of Cardiogenic Shock[J]. JACC Heart Fail, 2020, 8(11): 879-891. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2020.09.005
-




 下载:
下载: