Serum CDC42 and TRAF6 levels and their predictive value in patients with severe acute pancreatitis complicated by acute gastrointestinal injury
-
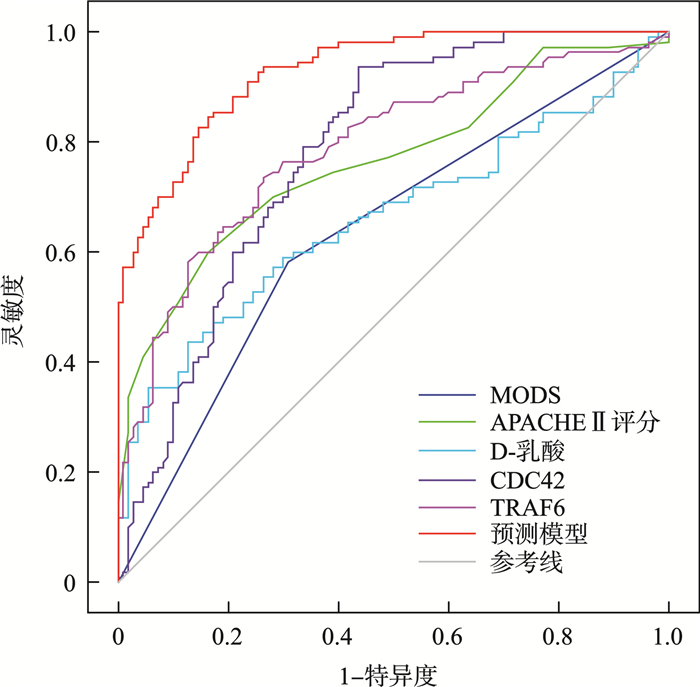
摘要: 目的 探讨重症急性胰腺炎(severe acute pancreatitis,SAP)并发急性胃肠损伤(acute gastrointestinal injury,AGI)患者血清细胞分裂周期蛋白42(cell division cycle protein 42,CDC42)、肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6,TRAF6)水平变化及预测价值。方法 选取2019年10月—2024年7月铜川市人民医院急诊科收治的SAP并发AGI患者110例(AGI组),按照1∶1比例选取同期收治的未并发AGI的SAP患者110例(非AGI组),SAP并发AGI患者根据AGI程度分为Ⅰ级组(25例)、Ⅱ级组(33例)、Ⅲ级组(29例)、Ⅳ级组(23例)。采用酶联免疫吸附法检测血清CDC42、TRAF6水平。通过多因素条件logistic回归分析血清CDC42、TRAF6水平与SAP并发AGI的关系并构建预测模型,受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线分析各独立影响因素及预测模对SAP并发AGI的预测价值。结果 与非AGI组比较,AGI组血清CDC42水平降低,TRAF6水平升高,差异有统计学(P<0.05)。Ⅰ级组、Ⅱ级组、Ⅲ级组、Ⅳ级组血清CDC42水平依次降低,TRAF6水平依次升高(P<0.05)。调整混杂因素后,CDC42高为SAP并发AGI的独立保护因素,TRAF6高为独立危险因素(P<0.05)。SAP并发AGI的预测模型[Logit(P)=-8.913+1.509×多器官功能障碍综合征(multiple organ dysfunction syndrome,MODS)+0.296×急性生理和慢性健康评估Ⅱ(acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ,APACHEⅡ)评分+0.060×D-乳酸-0.163×CDC42+1.424×TRAF6]。预测模型预测SAP并发AGI的曲线下面积为0.928,大于MODS、APACHEⅡ评分、D-乳酸、CDC42、TRAF6单独预测的0.636、0.765、0.662、0.782、0.789(P<0.05)。结论 血清CDC42水平降低、TRAF6水平升高与SAP并发AGI及AGI程度加重有关,基于此构建的预测模型对SAP并发AGI有较高的预测价值。
-
关键词:
- 重症急性胰腺炎 /
- 急性胃肠损伤 /
- 细胞分裂周期蛋白42 /
- 肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6 /
- 预测价值 /
- 独立危险因素
Abstract: Objective To investigate the changes in serum cell division cycle protein 42(CDC42) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6(TRAF6) levels in patients with severe acute pancreatitis(SAP) complicated by acute gastrointestinal injury(AGI) and evaluate their predictive value.Methods A total of 110 patients with SAP complicated by AGI(AGI group) admitted to the Emergency Department of Tongchuan People's Hospital between October 2019 and July 2024 were selected. Additionally, 110 SAP patients without AGI(non-AGI group) were matched 1∶1. The AGI group was further divided into Grade Ⅰ(25 cases), Grade Ⅱ(33 cases), Grade Ⅲ(29 cases), and Grade Ⅳ(23 cases) according to the severity of AGI. Serum CDC42 and TRAF6 levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The relationship between serum CDC42, TRAF6 levels, and SAP complicated with AGI was analyzed through multivariate conditional logistic regression, and a predictive model was constructed. The receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve was used to analyze the predictive value of independent influencing factors and the model for SAP complicated with AGI.Results Compared with the non-AGI group, the AGI group had significantly lower serum CDC42 levels and higher TRAF6 levels(P < 0.05). As the severity of AGI increased from Grade Ⅰ to Ⅳ, CDC42 levels progressively decreased, while TRAF6 levels increased(P < 0.05). After adjusting for confounding factors, elevated CDC42 was identified as an independent protective factor, while elevated TRAF6 was an independent risk factor for SAP complicated by AGI(P < 0.05). The prediction model for SAP complicated with AGI was established as follows: Logit(P)=-8.913 + 1.509×multiple organ dysfunction syndrome(MODS)+ 0.296×acute physiology and chronic health evaluation Ⅱ(APACHE Ⅱ) score + 0.060×D-lactate-0.163×CDC42 + 1.424×TRAF6. The area under the curve(AUC) of the predictive model was 0.928, which was significantly higher than that of MODS(0.636), APACHE Ⅱ score(0.765), D-lactate(0.662), CDC42(0.782), and TRAF6(0.789) alone(P < 0.05).Conclusion Decreased serum CDC42 levels and increased TRAF6 levels are associated with the occurrence and severity of AGI in SAP patients. The combined measurement of CDC42 and TRAF6 has high predictive value for SAP complicated by AGI. -

-
表 1 AGI组与非AGI组血清CDC42、TRAF6水平比较
X±S 组别 例数 CDC42/(ng/mL) TRAF6/(μg/mL) AGI组 110 47.52±5.24 7.11±0.87 非AGI组 110 55.54±7.63 6.09±0.64 t - -8.389 8.315 P - <0.001 <0.001 表 2 不同分级SAP并发AGI患者血清CDC42、TRAF6水平比较
X±S 组别 例数 CDC42/(ng/mL) TRAF6/(μg/mL) Ⅰ级组 25 54.20±2.00 6.08±0.43 Ⅱ级组 33 49.45±1.481) 6.88±0.201) Ⅲ级组 29 45.33±1.141)2) 7.54±0.171)2) Ⅳ级组 23 40.87±1.921)2)3) 8.18±0.301)2)3) F趋势 - 892.433 731.381 P - <0.001 <0.001 与Ⅰ级组比较,1)P<0.05;与Ⅱ级组比较,2)P<0.05;与Ⅲ级组比较,3)P<0.05。 表 3 AGI组与非AGI组临床资料比较
X±S 项目 AGI组(110例) 非AGI组(110例) χ2/t/Z P 性别/例(%) 2.268 0.132 男 70(63.64) 59(53.64) 女 40(36.36) 51(46.36) 年龄/岁 59.63±8.95 57.82±8.75 1.516 0.131 饮酒史/例(%) 44(40.00) 34(30.91) 1.986 0.159 吸烟史/例(%) 40(36.36) 30(27.27) 2.095 0.148 基础疾病/例(%) 冠心病 17(15.45) 14(12.73) 0.338 0.561 糖尿病 25(22.73) 21(19.09) 0.440 0.507 高血压 51(46.36) 39(35.45) 2.708 0.100 急性胰腺炎病因/例(%) 酒精性 9(8.18) 9(8.18) 0.594 0.964 脂源性 36(32.73) 31(28.18) 胆源性 40(36.36) 44(40.00) 特发性 9(8.18) 9(8.18) 其他 16(14.55) 17(15.45) 腹部表现/例(%) 排气排便停止 32(29.09) 30(27.27) 0.090 0.764 腹膜刺激征 70(63.64) 66(60.00) 0.308 0.579 肠鸣音减弱 103(93.64) 99(90.00) 0.968 0.325 腹痛 109(99.09) 106(96.36) 0.819 0.366 腹胀 103(93.64) 96(87.27) 2.580 0.108 MODS/例(%) 有 64(58.18) 34(30.91) 16.561 <0.001 无 46(41.82) 76(69.09) ICU停留时间/d 10.53±4.11 7.24±3.53 6.371 <0.001 APACHEⅡ评分/分 16.46±4.32 12.54±3.02 7.811 <0.001 D-乳酸/(mg/L) 50.63±17.89 40.68±10.91 4.979 <0.001 血肌酐/(μmol/L) 128.78±37.18 125.34±41.27 0.649 0.517 血淀粉酶/(U/L) 969.74±253.66 927.87±199.18 1.361 0.175 血尿素氮/(mmol/L) 6.65±1.77 6.40±1.46 1.132 0.259 C反应蛋白/(mg/L) 127.96±52.95 109.40±40.28 2.926 0.004 血红蛋白/(g/L) 141.02±13.77 145.42±14.27 -2.327 0.021 白细胞计数/(×109/L) 13.33±2.53 12.35±4.77 1.903 0.059 血小板计数/(×109/L) 237.17±72.02 258.70±72.34 -2.212 0.028 表 4 血清CDC42、TRAF6水平与SAP并发AGI的多因素条件logistic回归分析
变量 β SE Wald χ2 P OR 95%CI MODS 1.837 0.514 12.751 <0.001 6.278 2.290~17.208 ICU停留时间长 1.291 0.721 3.207 0.073 3.638 0.885~14.950 APACHEⅡ评分高 0.295 0.065 20.468 <0.001 1.343 1.182~1.526 D-乳酸高 0.066 0.020 11.276 0.001 1.069 1.028~1.111 C反应蛋白高 0.002 0.005 0.168 0.682 1.002 0.992~1.012 血小板计数高 -0.039 0.032 1.464 0.226 0.962 0.903~1.024 CDC42高 -0.155 0.043 12.928 <0.001 0.857 0.787~0.932 TRAF6高 1.479 0.339 19.019 <0.001 4.389 2.258~8.532 表 5 各指标及预测模型对SAP并发AGI的预测价值
指标 曲线下面积 95%CI P 截断值 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 约登指数 MODS 0.636 0.569~0.700 <0.001 是 58.18 69.09 0.273 APACHEⅡ评分 0.765 0.704~0.820 <0.001 15分 60.00 83.64 0.436 D-乳酸 0.662 0.595~0.724 <0.001 46.96 mg/L 43.64 87.27 0.309 CDC42 0.782 0.722~0.835 <0.001 51.13 ng/mL 93.64 56.36 0.500 TRAF6 0.789 0.729~0.841 <0.001 6.62 μg/mL 73.64 73.64 0.473 预测模型 0.928 0.885~0.958 <0.001 - 85.45 82.73 0.682 -
[1] 中华医学会急诊医学分会, 上海市医学会急诊专科分会. 急性胰腺炎急诊诊治专家共识[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2024, 33(4): 470-479.
[2] 中华中医药学会《重症急性胰腺炎中西医结合诊疗指南》起草组. 重症急性胰腺炎中西医结合诊疗指南[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2024, 40(6): 1114-1125.
[3] Tao FZ, Jiang RL, Jin SF. Implementation of gastrointestinal function protection in severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2024, 23(5): 521-522. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2024.04.006
[4] 温聪聪, 王颖, 吴德卿, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎胃肠功能障碍的诊治和发生机制研究进展[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2019, 19(2): 143-145.
[5] Lechuga S, Marino-Melendez A, Davis A, et al. Coactosin-like protein 1 regulates integrity and repair of model intestinal epithelial barriers via actin binding dependent and independent mechanisms[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2024, 7(12): 1405454.
[6] Bement WM, Goryachev AB, Miller AL, et al. Patterning of the cell cortex by Rho GTPases[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2024, 25(4): 290-308. doi: 10.1038/s41580-023-00682-z
[7] Yang J, Li X, Yang X, et al. Aberrant blood cell division cycle 42 expression and its correlation with disease severity, inflammation and mortality risk in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2022, 24(1): 458.
[8] Li T, Lei Z, Wei L, et al. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 and human cancer: a systematic review of mechanistic insights, functional roles, and therapeutic potential[J]. J Cancer, 2024, 15(2): 560-576.
[9] 尹成龙, 周鹏飞. 急性胰腺炎患者血TRAF6和NF-кB水平变化对胰外并发症急性肺损伤的预测价值[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(11): 590-596. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.11.007
[10] 中华医学会, 中华医学会杂志社, 中华医学会消化病学分会, 等. 急性胰腺炎基层诊疗指南(2019年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(9): 819-826.
[11] Reintam Blaser A, Malbrain ML, et al. Gastrointestinal function in intensive care patients: Terminology, definitions and management. Recommendations of the ESICM working group on abdominal problems[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2012, 38(3): 384-394.
[12] Harshit Kumar A, Singh Griwan M. A comparison of APACHE Ⅱ, BISAP, Ranson's score and modified CTSI in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis based on the 2012 revised Atlanta Classification. Gastroenterol Rep(Oxf), 2018, 6(2): 127-131.
[13] 上海市中西医结合学会急救专业委员会, 上海市中西医结合学会重症医学专业委员会, 上海市医师协会急诊科医师分会, 等. 脓毒症急性胃肠功能障碍中西医结合临床专家共识[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2022, 34(2): 113-120.
[14] 谢胜, 严静, 黎丽群, 等. 中西医协同治疗重症急性胰腺炎的进展述评[J]. 中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2024, 32(2): 98-104.
[15] 毛恩强, 车在前. 《急性胰腺炎急诊诊治专家共识》解读[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2024, 25(7): 325-328. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2024.07.001
[16] 黄学盼, 刘琦. 急性胰腺炎肠黏膜屏障功能障碍的研究进展[J]. 大连医科大学学报, 2024, 46(1): 51-56.
[17] Zhen J, Chen W, Liu Y, et al. Baicalin protects against acute pancreatitis involving JNK signaling pathway via regulating miR-15a[J]. Am J Chin Med, 2021, 49(1): 147-161.
[18] Cheng K, Larabee SM, Tolaymat M, et al. Targeted intestinal deletion of Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 7, βPIX, impairs enterocyte proliferation, villus maturation, and mucosal defenses in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2021, 320(4): G627-G643.
[19] Aihara R, Kunimura K, Watanabe M, et al. DOCK8 controls survival of group 3 innate lymphoid cells in the gut through Cdc42 activation[J]. Int Immunol, 2021, 33(3): 149-160.
[20] Woode RA, Strubberg AM, Liu J, et al. Increased activity of epithelial Cdc42 Rho GTPase and tight junction permeability in the Cftr knockout intestine[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2024, 327(4): G545-G557.
[21] Wang H, Jiang Y, Li H, et al. Carbachol protects the intestinal barrier in severe acute pancreatitis by regulating Cdc42/F-actin cytoskeleton[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 20(3): 2828-2837.
[22] Zhang D, Tang W, Niu H, et al. Monogenic deficiency in murine intestinal Cdc42 leads to mucosal inflammation that induces crypt dysplasia[J]. Genes Dis, 2023, 11(1): 413-429.
[23] Wei B, Su Z, Yang H, et al. Inhibition of TRAF6 improves hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis by alleviating pyroptosis in vitro and in vivo rat models[J]. Biol Direct, 2023, 18(1): 23.
[24] Tian Y, Fu M, Su J, et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal barrier impairment in diarrhea caused by cold drink and high-fat diet[J]. Toxicology, 2024, 2(502): 153728.
[25] Cheng B, Du M, He S, et al. Inhibition of platelet activation suppresses reactive enteric glia and mitigates intestinal barrier dysfunction during sepsis[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 149.
[26] 倪维, 蒲玟静, 陈涛, 等. HMGB1-TLR9-MyD88-TRAF6-NF-κB信号通路在急性胰腺炎肠粘膜屏障损伤中的作用[J]. 现代预防医学, 2022, 49(8): 1514-1520.
[27] 谭贞菊, 周翔宇, 陈霞. 急性胰腺炎小鼠胰腺和远隔脏器组织TRAF6、XIAP表达变化及其与细胞凋亡的关系[J]. 山东医药, 2023, 63(32): 45-49.
[28] Ni W, Ma YF, Chen T, et al. Toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway contributes to intestinal mucosal barrier injury in mice with severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreas, 2022, 51(9): 1194-1200.
[29] 姚朝光, 黄杰安, 黄理, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎急性胃肠损伤的危险因素分析及相关预测模型的构建[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2023, 28(12): 1543-1547.
[30] Chen JH, Zhang MF, Du WC, et al. Risk factors and their interactive effects on severe acute pancreatitis complicated with acute gastrointestinal injury[J]. World J Gastrointest Surg, 2023, 15(8): 1712-1718.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 195
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: