Diagnostic value of serum Gas6 and SDF-1 in the occurrence of abdominal infection in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
-
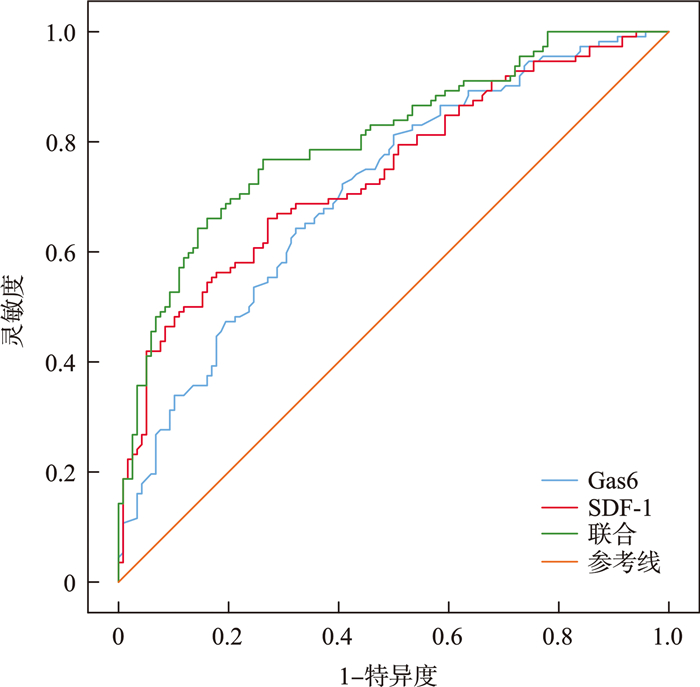
摘要: 目的 探讨血清生长停滞特异性蛋白6(growth arrest specific protein 6,Gas6)、基质细胞衍生因子-1(stromal cell-derived factor-1,SDF-1)对重症急性胰腺炎(severe acute pancreatitis,SAP)患者发生腹腔感染的诊断价值。 方法 选取2021年11月—2023年11月收治的112例发生腹腔感染的SAP患者为研究对象(研究组),选择本院同期收治的118例SAP未发生腹腔感染患者作为对照组。采用ELISA试剂盒测定2组患者血清Gas6、SDF-1的水平,采用全自动血液分析仪测定患者血清降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)、C-反应蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP)和D-二聚体的水平,收集临床资料。采用Pearson分析血清Gas6、SDF-1水平与PCT、CRP、D-二聚体的相关性,采用多因素logistic回归分析影响SAP患者发生腹腔感染的因素,采用ROC分析血清Gas6、SDF-1水平对SAP患者发生腹腔感染的诊断价值。 结果 2组间性别、年龄、合并器官功能不全或衰竭情况比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);研究组入院时Rason评分、PCT、住院天数、CRP、D-二聚体、入院时急性生理与慢性健康评分及血清Gas6、SDF-1水平均明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);研究组血清Gas6、SDF-1水平与PCT、CRP、D-二聚体水平均呈正相关(P < 0.05);Gas6和SDF-1水平升高是SAP患者发生腹腔感染的独立危险因素(P < 0.05);血清Gas6、SDF-1单独及联合诊断SAP患者发生腹腔感染的曲线下面积分别为0.694、0.743、0.803,二者联合优于Gas6、SDF-1各自单独诊断(Z=3.679、2.508,P < 0.001、P=0.012)。 结论 发生腹腔感染的SAP患者血清中Gas6、SDF-1水平均升高,血清Gas6、SDF-1水平对于SAP患者发生腹腔感染具有一定的诊断价值。
-
关键词:
- 重症急性胰腺炎 /
- 腹腔感染 /
- 生长停滞特异性蛋白6 /
- 基质细胞衍生因子-1 /
- 诊断
Abstract: Objective To explore the diagnostic value of serum growth arrest specific protein 6(Gas6) and stromal cell-derived factor-1(SDF-1) in the development of abdominal infection(AI) in patients with severe acute pancreatitis(SAP). Methods A total of 112 SAP patients with AI admitted from November 2021 to November 2023 were collected as the study subjects(study group), and 118 SAP patients who did not develop AI admitted from the same time were regarded as the control group. The serum levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 were measured using ELISA kits, and the levels of serum procalcitonin(PCT), C-reactive protein(CRP), and D-dimer were determined using a fully automated blood analyzer. Clinical data were collected. Pearson correlation analysis was used to assess the relationship between serum Gas6 and SDF-1 levels and PCT, CRP, and D-dimer. Multivariate logistic regression was applied to analyze the factors influencing the occurrence of AI in SAP patients. Receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic value of serum Gas6 and SDF-1 levels for AI in SAP patients. Results There was no significant difference in gender, age, and combined with organ insufficiency or failure between two groups(P>0.05). The Rason score, PCT, length of hospital stay, CRP, D-dimer, Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation score on admission, and serum levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 were significantly higher in the study group compared to the control group(P < 0.05). Serum levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 in the study group were positively correlated with the levels of PCT, CRP and D-dimer(P < 0.05). Elevated levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 were identified as independent risk factors for AI in SAP patients(P < 0.05). The area under the curve of serum Gas6 and SDF-1 for diagnosing AI in SAP patients alone and in combination was 0.694, 0.743, and 0.803, respectively. The combination of Gas6 and SDF-1 showed superior diagnostic performance compared to either marker alone(Z=3.679, 2.508, P < 0.001, P=0.012). Conclusion The serum levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 are elevated in SAP patients with AI, and serum levels of Gas6 and SDF-1 have certain diagnostic value for the occurrence of AI in SAP patients. -

-
表 1 2组临床资料及血清指标比较
X±S,例(%) 临床资料 对照组(118例) 研究组(112例) t/χ2 P 年龄/岁 46.35±6.76 46.13±6.58 0.250 0.803 性别 0.006 0.941 男 68(57.63) 64(57.14) 女 50(42.37) 48(42.86) 住院天数/d 8.71±1.79 14.53±2.52 20.273 < 0.001 入院时Rason评分/分 3.47±0.53 4.04±0.71 6.923 < 0.001 入院时APACHEⅡ评分/分 12.53±1.74 14.19±2.05 6.632 < 0.001 合并器官功能不全或衰竭 1.256 0.262 是 38(32.20) 44(39.29) 否 80(67.80) 68(60.71) PCT/(ng/mL) 0.57±0.07 0.85±1.04 2.918 0.004 CRP/(mg/L) 15.41±1.75 23.44±4.04 19.731 < 0.001 D-二聚体/(g/L) 8.15±1.17 13.58±1.72 28.119 < 0.001 表 2 2组血清Gas6、SDF-1水平比较
X±S 指标 对照组(118例) 研究组(112例) t P Gas6/(ng/mL) 4.13±0.58 4.66±0.60 6.811 < 0.001 SDF-1/(pg/mL) 150.20±18.02 166.63±19.42 6.655 < 0.001 表 3 研究组血清Gas6、SDF-1水平与血清指标的相关性分析
指标 Gas6 SDF-1 r P r P PCT 0.666 < 0.001 0.522 < 0.001 CRP 0.501 < 0.001 0.426 < 0.001 D-二聚体 0.606 < 0.001 0.405 < 0.001 表 4 影响SAP患者发生AI的多因素logistic回归分析
影响因素 B SE Wald χ2 OR 95%CI P Gas6 1.201 0.287 17.508 3.323 1.893~5.832 < 0.001 SDF-1 0.941 0.290 10.524 2.562 1.451~4.523 0.001 Rason评分 0.074 0.245 0.092 1.077 0.666~1.741 0.762 PCT 0.579 0.344 2.837 1.785 0.909~3.503 0.092 住院天数 0.218 0.265 0.674 1.243 0.739~2.090 0.412 CRP 0.202 0.234 0.746 1.224 0.774~1.936 0.388 D-二聚体 0.345 0.196 3.098 1.412 0.962~2.073 0.078 入院时APACHEⅡ评分 0.320 0.206 2.412 1.377 0.920~2.062 0.120 表 5 血清Gas6、SDF-1水平诊断SAP患者发生AI的价值
指标 AUC 95%CI 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 截断值 Gas6 0.694 0.630~0.752 60.71 74.58 4.44 ng/mL SDF-1 0.743 0.681~0.798 66.07 72.88 159.26 pg/mL 联合 0.803 0.746~0.853 64.29 80.51 0.49 -
[1] Huang Y, Badurdeen DS. Acute Pancreatitis Review[J]. Turk J Gastroenterol, 2023, 34(8): 795-801. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2023.23175
[2] 李玉蓉, 邓炜, 王新刚, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎合并腹腔感染患者病原菌分布、药物敏感性分析及其院内死亡的危险因素探讨[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2023, 23(18): 3504-3509.
[3] Napolitano LM. Intra-abdominal Infections[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med, 2022, 43(1): 10-27. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1741053
[4] Baskol G, Özel M, Saracoglu H, et al. New Avenues to Explore in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Both TRIM25 and TRIM56 Positively Correlate with VEGF, GAS6, and sAXL in COVID-19 Patients[J]. Viral Immunol, 2022, 35(10): 690-699. doi: 10.1089/vim.2022.0112
[5] 林秋满. 热休克因子1对雨蛙素诱导的小鼠急性胰腺炎的保护作用及对SDF-1/CXCR4表达的影响[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2021.
[6] 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2021)[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2021, 59(7): 578-587.
[7] 中华医学会外科学分会外科感染与重症医学学组, 中国医师协会外科医师分会肠瘘外科医师专业委员会. 中国腹腔感染诊治指南(2019版)[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2020, 40(1): 1-16.
[8] 王真珍, 邬明杰, 方雪玲, 等. 急性生理和慢性健康评分Ⅱ对成人复杂腹腔感染死亡预测准确性的荟萃分析[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志, 2018, 18(4): 345-351.
[9] 周巍, 陈尉华, 张星宇, 等. 改良的早期预警评分在急性胰腺炎中的应用[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2009, 18(7): 747-750.
[10] 毛恩强, 车在前. 《急性胰腺炎急诊诊治专家共识》解读[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2024, 25(7): 325-328. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2024.07.001
[11] Jaber S, Garnier M, Asehnoune K, et al. Guidelines for the management of patients with severe acute pancreatitis, 2021[J]. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med, 2022, 41(3): 1-10.
[12] Mohammadzadeh P, Amberg GC. AXL/Gas6 signaling mechanisms in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis[J]. Front Endocrinol(Lausanne), 2023, 14(3): 1-8.
[13] Bellomo G, Rainer C, Quaranta V, et al. Chemotherapy-induced infiltration of neutrophils promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis via Gas6/AXL signalling axis[J]. Gut, 2022, 71(11): 2284-2299. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325272
[14] Bassyouni RH, Gomaa AA, Hassan EA, et al. Possible Association of Elevated Plasma Levels of Growth Arrest-Specific Protein 6 and the Soluble Form of Tyrosine Kinase Receptor Axl with Low Hepatitis C Viral Load in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus[J]. Viral Immunol, 2020, 33(2): 105-111. doi: 10.1089/vim.2019.0127
[15] 南文波, 王亚红, 白雪芬, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎合并腹腔感染患者血浆线粒体DNA水平与感染程度及预后的关系[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(16): 2496-2500.
[16] Ngamsri KC, Jans C, Putri RA, et al. Inhibition of CXCR4 and CXCR7 Is Protective in Acute Peritoneal Inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11(1): 1-19.
[17] Sremac M, Luo H, Deng H, et al. Short-term function and immune-protection of microencapsulated adult porcine islets with alginate incorporating CXCL12 in healthy and diabetic non-human primates without systemic immune suppression: A pilot study[J]. Xenotransplantation, 2023, 30(6): 1-18.
[18] Gui M, Huang J, Sheng H, et al. High-Dose Vitamin C Alleviates Pancreatic Necrosis by Inhibiting Platelet Activation Through the CXCL12/CXCR4 Pathway in Severe Acute Pancreatitis[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2023, 16(1): 2865-2877.
[19] Mousavi A. CXCL12/CXCR4 signal transduction in diseases and its molecular approaches in targeted-therapy[J]. Immunol Lett, 2020, 217(1): 91-115.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 221
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: