-
摘要: 脓毒症是由创伤、感染等引起的临床急危重综合征,其患病率和死亡率在全球范围内居高不下。随着对脓毒症病理生理机制研究的深入,免疫调节逐渐成为该领域研究热点,而T淋巴细胞是机体免疫状态的关键特征指标,其功能受损和数量锐减是导致脓毒症患者后期免疫麻痹甚至死亡的重要因素。本文综述了CD8+、CD4+及调节性T细胞在脓毒症中的变化情况和致病机制,同时分析了各类T细胞抑制性免疫检查点在脓毒症中的分子作用机制,最后阐述了脓毒症免疫治疗的相关研究进展,以期为脓毒症临床监测和治疗提供新的研究靶点和思路。Abstract: Sepsis is a clinical acute and critical syndrome resulting from trauma, infection, etc., and its morbidity and mortality rates are still high worldwide. Further studies on the pathophysiology of sepsis indicate that immunoregulation is a research hotspot. T lymphocytes are the key indicator of immune status, and the function impairment and depletion of T cells are important cause of immune paralysis and even death for sepsis patients at later stage. In this review, we summarized the changes and pathogenic mechanisms of CD8+, CD4+and regulatory T cells in sepsis, we meanwhile analyzed the molecular mechanism of various inhibitory immune checkpoints in sepsis. The relevant research progress of immunotherapy in sepsis was also reviewed. We hope this article can provide new research targets and ideas for clinical monitoring and treatment of sepsis.
-
Key words:
- sepsis /
- immunosuppression /
- T lymphocytes /
- inhibitory immune checkpoint /
- immunotherapy
-

-
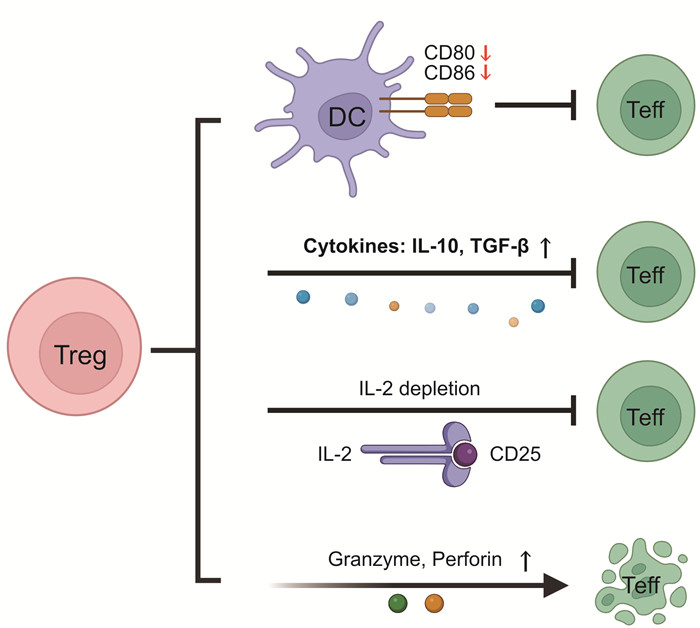
表 1 CD4+辅助T细胞与脓毒症免疫抑制
T细胞亚群 与脓毒症相关的生理功能 脓毒症引起的免疫抑制 CD4+辅助T细胞[17, 30-32, 35-36] Th1 分泌INF-γ、IL-2、TNF-α;促进Tc细胞增殖、分化和成熟;促进巨噬细胞吞噬作用;加强NK细胞杀伤能力;抑制Th2分化 Th2分化增加,分泌炎症抑制因子诱导免疫抑制;Th2/Th1比例增加,且比例失衡程度与脓毒症预后显著相关 Th2 分泌IL-4,IL-5、IL-6、IL-10、IL-13;促进B细胞增殖分化为浆细胞并产生抗体;抑制Th1细胞分化。 与脓毒症急性肠屏障损伤有关 Th9 分泌IL-9、IL-10 Th17 分泌IL-17A、IL-17F、IL-21、IL22;促进嗜中性粒细胞募集和激活,并趋化其至感染部位 SIRS主导期显著上升,CARS主导期显著下降;与Treg相互制;Treg/Th17比例失衡提示免疫抑制 Th22 分泌IL-22 脓毒症急性肺损伤患者外周血中Th22比例显著上升 Tfh 分泌IL-21;促进B细胞存活、增殖和成熟;促进生发中心发育 脓毒症患者Tfh细胞显著降低;Tfh细胞与B细胞数量正相关 CD8+细胞毒性T细胞[12, 17] 特异性识别内源pMHC-1复合物后激活;分泌穿孔素/颗粒酶等直接杀伤靶细胞,或表达INF-γ和TNF-α诱导靶细胞凋亡 凋亡增加,增值能力减弱,CD8+T趋于耗竭;分泌细胞因子能力减弱;恢复后的CD8+T免疫响应能力下降 -
[1] Xie J, Wang H, Kang Y, et al. The Epidemiology of Sepsis in Chinese ICUs: A National Cross-Sectional Survey[J]. Crit Care Med, 2020, 48(3): e209-e218. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004155
[2] 王静, 乔佑杰. 脓毒症相关生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2023, 22(5): 540-545. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNBZ202305020.htm
[3] Jensen IJ, Sjaastad FV, Griffith TS, et al. Sepsis-Induced T Cell Immunoparalysis: The Ins and Outs of Impaired T Cell Immunity[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 200(5): 1543-1553. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701618
[4] Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock(Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
[5] Liu Q, Li L, Xu D, et al. Identification of novel immune-related targets mediating disease progression in acute pancreatitis[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 1052466. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1052466
[6] Tujios S, Stravitz RT, Lee WM. Management of Acute Liver Failure: Update 2022[J]. Semin Liver Dis, 2022, 42(3): 362-378. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1755274
[7] Liu D, Huang SY, Sun JH, et al. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: mechanisms, diagnosis and current treatment options[J]. Mil Med Res, 2022, 9(1): 56.
[8] Sendler M, van den Brandt C, Glaubitz J, et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Regulates Development of Systemic Inflammatory Response and Compensatory Anti-Inflammatory Response Syndromes in Mice With Acute Pancreatitis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(1): 253-269. e214. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.040
[9] 陈正钢, 刘励军. 急诊脓毒症患者早期筛查生物标志物的研究现状与展望[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(2): 99-104. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.02.010
[10] 付绪哲, 柳英杰, 牛明明, 等. 脓毒症免疫抑制机制的研究进展[J]. 中国临床研究, 2023, 36(5): 741-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGCK202305022.htm
[11] Wik JA, Skålhegg BS. T Cell Metabolism in Infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 840610. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.840610
[12] Reina-Campos M, Scharping NE, Goldrath AW. CD8(+)T cell metabolism in infection and cancer[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2021, 21(11): 718-738. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00537-8
[13] Darden DB, Dong X, Brusko MA, et al. A Novel Single Cell RNA-seq Analysis of Non-Myeloid Circulating Cells in Late Sepsis[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 696536. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696536
[14] Liu J, Li G, Chen YZ, et al. Effects of rhubarb on the expression of glucocorticoids receptor and regulation of cellular immunity in burn-induced septic rats[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2019, 132(10): 1188-1193.
[15] Wang J, Zhou J, Bai S. Combination of Glutamine and Ulinastatin Treatments Greatly Improves Sepsis Outcomes[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2020, 13: 109-115. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S234122
[16] 黄鑫波, 刘端绘, 莫旻龙, 等. 脓毒症患者T淋巴细胞亚群水平与炎症状态动态变化的关系及对预后的影响[J]. 广西医学, 2021, 43(23): 2779-2784. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYYX202123003.htm
[17] Martin MD, Badovinac VP, Griffith TS. CD4 T Cell Responses and the Sepsis-Induced Immunoparalysis State[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1364. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01364
[18] Bai G, Cui N, Wang H, et al. T-lymphocyte subtyping: an early warning and a potential prognostic indicator of active cytomegalovirus infection in patients with sepsis[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2022, 100(10): 777-790. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12586
[19] 李兆芳, 林青伟, 张昕, 等. 大黄素对盲肠结扎穿孔小鼠CD4+、CD8+T细胞的影响[J]. 医学动物防制, 2023, 39(4): 379-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXDZ202304017.htm
[20] 黄丽, 曹殿青. 脓毒症中CD4+T淋巴细胞凋亡的研究进展[J]. 海南医学, 2021, 32(5): 651-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HAIN202105031.htm
[21] Espinosa Gonzalez M, Volk-Draper L, Bhattarai N, et al. Th2 Cytokines IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10 Promote Differentiation of Pro-Lymphatic Progenitors Derived from Bone Marrow Myeloid Precursors[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2022, 31(11-12): 322-333. doi: 10.1089/scd.2022.0004
[22] Muhammad Yusoff F, Wong KK, Mohd Redzwan N. Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Autoimmunity, 2020, 53(1): 8-20. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2019.1693545
[23] 骆付丽, 华维, 钱民, 等. T淋巴细胞亚群及Th1/Th2细胞因子谱早期鉴别细菌尿源性脓毒症[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(4): 502-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202104007.htm
[24] Zhao GJ, Yang XY, Zhang C, et al. Supplementation with Nicotinamide riboside attenuates T cell exhaustion and improves survival in sepsis[J]. Shock, 2023, 60(2): 238-247. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002153
[25] Xu J, Li J, Xiao K, et al. Dynamic changes in human HLA-DRA gene expression and Th cell subsets in sepsis: Indications of immunosuppression and associated outcomes[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2020, 91(1): e12813. doi: 10.1111/sji.12813
[26] Dutzan N, Kajikawa T, Abusleme L, et al. A dysbiotic microbiome triggers T(H)17 cells to mediate oral mucosal immunopathology in mice and humans[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2018, 10(463): eaat0797. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat0797
[27] 徐晨, 何精选, 石珍, 等. 急性胰腺炎患者外周血lncRNA H19表达与Th17/Treg平衡的关系[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2022, 23(5): 316-320, 326. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2022.05.004
[28] Zhou X, Yao J, Lin J, et al. Th17/Regulatory T-Cell Imbalance and Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Sepsis[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(14): 4027. doi: 10.3390/jcm11144027
[29] 徐玲文, 王华兵, 王倩, 等. 黄芩苷对脓毒症急性肺损伤小鼠TLR4/NF-κB通路及Treg/Th17平衡的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2022, 38(15): 1813-1818, 1823. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZMXZ202215005.htm
[30] Sun JK, Zhang Q, Shen X, et al. Integrin αEβ7 is involved in the intestinal barrier injury of sepsis[J]. Aging(Albany NY), 2022, 14(2): 780-788.
[31] Li G, Zhang L, Han N, et al. Increased Th17 and Th22 Cell Percentages Predict Acute Lung Injury in Patients with Sepsis[J]. Lung, 2020, 198(4): 687-693. doi: 10.1007/s00408-020-00362-1
[32] Noto A, Suffiotti M, Joo V, et al. The deficiency in Th2-like Tfh cells affects the maturation and quality of HIV-specific B cell response in viremic infection[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 960120. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960120
[33] Taylor MD, Brewer MR, Nedeljkovic-Kurepa A, et al. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Prevent Depletion of Follicular B Cells in Response to Cecal Ligation and Puncture[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 1946. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01946
[34] Duan S, Jiao Y, Wang J, et al. Impaired B-Cell Maturation Contributes to Reduced B Cell Numbers and Poor Prognosis in Sepsis[J]. Shock, 2020, 54(1): 70-77. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001478
[35] Lv L, Chen Z, Bai W, et al. Taurohyodeoxycholic acid alleviates trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced ulcerative colitis via regulating Th1/Th2 and Th17/Treg cells balance[J]. Life Sci, 2023, 318: 121501. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121501
[36] Wang B, Hu S, Fu X, et al. CD4(+) Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes in Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy[J]. Adv Biol (Weinh), 2023, 7(4): e2200169. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200169
[37] Tian X, Ning Q, Yu J, et al. T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain in cancer immunotherapy: A focus on tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells[J]. Mol Immunol, 2022, 147: 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.04.014
[38] Rowshanravan B, Halliday N, Sansom DM. CTLA-4: a moving target in immunotherapy[J]. Blood, 2018, 131(1): 58-67. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-741033
[39] Shankar-Hari M, Fish M, Azoulay E. Should we consider blocking the inhibitory immune checkpoint molecules for treating T cell exhaustion in sepsis?[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2020, 46(1): 119-121. doi: 10.1007/s00134-019-05814-8
[40] 张思也, 侯粲, 钟燕军, 等. 脓毒症T淋巴细胞亚群免疫监测的研究进展[J]. 中华重症医学电子杂志(网络版), 2021, 7(1): 48-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZYD202101009.htm
[41] 朱红俊, 陈佳琦. Tfr细胞及炎性因子对脓毒症患者的影响[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志, 2023, 33(16): 1963-1967. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWJZ202316013.htm
[42] 吴健锋. 脓毒症免疫抑制的监测和治疗进展[J]. 中山大学学报(医学版), 2020, 41(1): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSYK202001006.htm
[43] 李秋林, 范骏. TIGIT对脓毒症免疫细胞影响的研究进展[J]. 南昌大学学报(医学版), 2023, 63(2): 80-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXYB202302015.htm
[44] Lou JS, Wang JF, Fei MM, et al. Targeting Lymphocyte Activation Gene 3 to Reverse T-Lymphocyte Dysfunction and Improve Survival in Murine Polymicrobial Sepsis[J]. J Infect Dis, 2020, 222(6): 1051-1061. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa191
[45] 张登容, 刘春瑶, 卜婷婷, 等. PD-1/PD-L1信号通路在脓毒症不同器官免疫调控中的研究进展[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2023, 39(3): 1-8.
[46] Huang S, Liu D, Sun J, et al. Tim-3 regulates sepsis-induced immunosuppression by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in CD4 T cells[J]. Mol Ther, 2022, 30(3): 1227-1238. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.12.013
[47] Wang WD, Yang XR, Guo MF, et al. Up-regulation of BTLA expression in myeloid dendritic cells associated with the treatment outcome of neonatal sepsis[J]. Mol Immunol, 2021, 134: 129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.03.007
[48] Lesnik P, Janc J, Mierzchala-Pasierb M, et al. Interleukin-7 and interleukin-15 as prognostic biomarkers in sepsis and septic shock: Correlation with inflammatory markers and mortality[J]. Cytokine, 2023, 169: 156277. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156277
[49] Delwarde B, Peronnet E, Venet F, et al. Low Interleukin-7 Receptor Messenger RNA Expression Is Independently Associated With Day 28 Mortality in Septic Shock Patients[J]. Crit Care Med, 2018, 46(11): 1739-1746. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003281
[50] Venet F, Demaret J, Blaise BJ, et al. IL-7 Restores T Lymphocyte Immunometabolic Failure in Septic Shock Patients through mTOR Activation[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 199(5): 1606-1615. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700127
[51] Francois B, Jeannet R, Daix T, et al. Interleukin-7 restores lymphocytes in septic shock: the IRIS-7 randomized clinical trial[J]. JCI Insight, 2018, 3(5): e98960. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98960
[52] Laterre PF, François B, Collienne C, et al. Association of Interleukin 7 Immunotherapy With Lymphocyte Counts Among Patients With Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19)[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(7): e2016485. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.16485
[53] Saito M, Inoue S, Yamashita K, et al. IL-15 Improves Aging-Induced Persistent T Cell Exhaustion in Mouse Models of Repeated Sepsis[J]. Shock, 2020, 53(2): 228-235. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001352
[54] Zhao X, Qi H, Zhou J, et al. Treatment with Recombinant Interleukin-15(IL-15) Increases the Number of T Cells and Natural Killer(NK)Cells and Levels of Interferon-γ(IFN-γ) in a Rat Model of Sepsis[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 4450-4456. doi: 10.12659/MSM.914026
[55] Sari MI, Ilyas S. The Expression Levels and Concentrations of PD-1 and PD-L1 Proteins in Septic Patients: A Systematic Review[J]. Diagnostics(Basel), 2022, 12(8): 2004.
[56] Marques A, Torre C, Pinto R, et al. Treatment Advances in Sepsis and Septic Shock: Modulating Pro-and Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(8): 2892. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082892
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 370
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: