One case of acute right heart insufficiency and liver failure cause by severe amlodipine poisoning
-
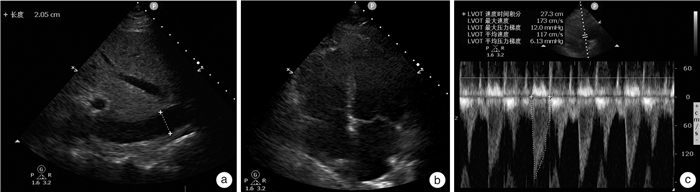
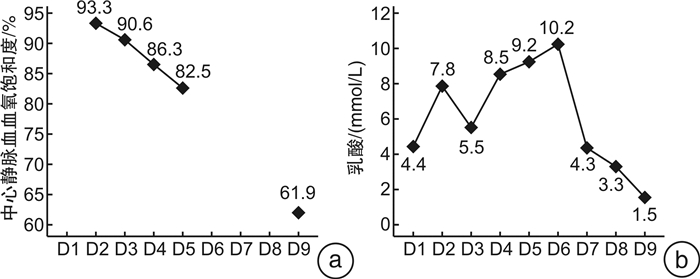
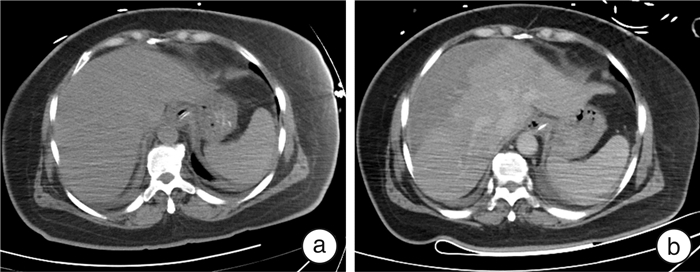
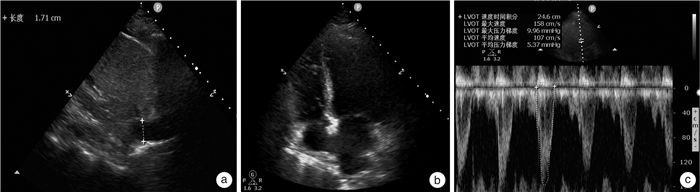
摘要: 重度氨氯地平中毒可导致顽固性休克,救治难度大,病死率高。本文报道1例大剂量氨氯地平中毒致顽固性休克及多脏器功能不全患者的成功抢救过程。该患者病程中合并急性右心功能不全及伴有肝脏影像学改变的肝衰竭,在既往文献中未见报道。血流动力学监测显示患者处于高排低阻状态。中毒早期,患者右心室增大、中心静脉压和中心静脉血氧饱和度显著增高。在大剂量升压药和综合解毒措施后,患者的循环功能逐渐改善。住院第6天,患者肝功能显著异常,CT显示肝脏有斑片状低密度阴影,伴有腹水。经过保肝治疗和血浆置换,患者肝功能逐渐恢复。4个月后CT显示患者肝脏低密度阴影和腹水消失。我们推测氨氯地平引起的矛盾性肺动脉高压是患者急性右心室功能不全的诱因。矛盾性肺动脉高压,高中心静脉压和休克导致的肝脏缺血,共同导致了急性肝衰竭。病程中准确的血流动力学监测有助于解释患者右心室功能不全和肝功能衰竭的原因,使我们能够及时调整治疗方案,取得了良好的疗效。Abstract: Severe amlodipine poisoning can lead to refractory shock, which is difficult to treat and has a high mortality. We report the successful rescue of a patient with refractory shock and multiple organ dysfunction caused by high dose amlodipine poisoning. This case complicated with acute right ventricular dysfunction and liver failure with liver imaging changes, which has not been reported in previous literature. Hemodynamic monitoring showed that the patient was in a state of high output and low resistance. At the early stage of poisoning, the right ventricle, central venous pressure and central venous blood oxygen saturation increased significantly. The patient's circulatory function gradually improved after large doses of vasopressors and detoxification measures. On the sixth day of hospitalization, the patient showed significant liver dysfunction, and CT showed patchy low-density shadows in the liver with ascites. After protective treatment and plasma exchange, the patient's liver function gradually recovered. A CT scan four months later showed that the shadows on her liver as well as her ascites all disappeared. We speculate that the contradictory pulmonary hypertension caused by amlodipine was the inducement of acute right ventricular dysfunction in this patient. Contradictory pulmonary hypertension, high central venous pressure and liver ischemia caused by shock all jointly led to acute liver failure. Accurate hemodynamic monitoring during the course of the disease helped to explain the causes of the patient's right ventricular dysfunction and liver failure, which enabled us to make timely adjustments to the treatment plan, resulting in a favorable outcome.
-
Key words:
- amlodipine /
- shock /
- liver failure /
- poisoning /
- blood purification /
- heart failure
-

-
[1] St-Onge M, Anseeuw K, Cantrell FL, et al. Experts Consensus Recommendations for the Management of Calcium Channel Blocker Poisoning in Adults[J]. Crit Care Med, 2017, 45(3): e306-e315. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000002087
[2] 崔继耀, 尹永杰. 苯磺酸氨氯地平片中毒致急性心力衰竭1例[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2015, 16(6): 482-483. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2015.06.029
[3] Koliastasis L, Lampadakis I, Milkas A, et al. Refractory Shock from Amlodipine Overdose Overcomed with Hyperinsulinemia[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2022, 22(1): 63-66. doi: 10.1007/s12012-021-09699-2
[4] Krenz JR, Kaakeh Y. An overview of hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic therapy in calcium channel blocker and β-blocker overdose[J]. Pharmacotherapy, 2018, 38(11): 1130-1142. doi: 10.1002/phar.2177
[5] Tale S, Kumar M, Ghosh S, et al. A Case of Life-threatening Amlodipine and Atenolol Overdose[J]. Indian J Crit Care Med, 2019, 23(6): 281-283. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23181
[6] Cole JB, Lee SC, Prekker ME, et al. Vasodilation in patients with calcium channel blocker poisoning treated with high-dose insulin: a comparison of amlodipine versus non-dihydropyridines[J]. Clin Toxicol (Phila), 2022, 60(11): 1205-1213. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2022.2131565
[7] Kumar K, Biyyam M, Bajantri B, et al. Critical Management of Severe Hypotension Caused by Amlodipine Toxicity Managed With Hyperinsulinemia/Euglycemia Therapy Supplemented With Calcium Gluconate, Intravenous Glucagon and Other Vasopressor Support: Review of Literature[J]. Cardiol Res, 2018, 9(1): 46-49. doi: 10.14740/cr646w
[8] Gautam S, Chamlagain M, Yadav GK, et al. Once was not enough: A case report of the concomitant intoxication of amlodipine (calcium channel blocker) and clonazepam (benzodiazepine)[J]. Clin Case Rep, 2022, 10(7): e6042. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6042
[9] Kumar S, Thakur D, Gupta RK, et al. Unresponsive shock due to amlodipine overdose: An unexpected cause[J]. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res, 2018, 10(4): 246-247. doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2018.43
[10] 张云, 张晶, 高霏, 等. ECMO在心血管药物中毒救治中的应用[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2020, 21(10): 832-839. https://lcjz.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2020.10.013
[11] Hong IZ, Ng M, Sewa DW, et al. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in massive amlodipine overdose[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2022, 96(12): 3403-3405. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03364-5
[12] Mahmoud SH, Buhler J, Chu E, et al. Drug Dosing in Patients Undergoing Therapeutic Plasma Exchange[J]. Neurocrit Care, 2021, 34(1): 301-311. doi: 10.1007/s12028-020-00989-1
[13] Ramanathan K, Mohanty B, Tang S, MacLaren G. Extracorporeal therapy for amlodipine poisoning[J]. J Artif Organs, 2020, 23(2): 183-186. doi: 10.1007/s10047-019-01132-4
[14] Li R, Xu YW, Xue Y, et al. Plasmapheresis in the treatment of multi-drug intoxication involving levothyroxine sodium and calcium channel blockers: a case report[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(5): 5839-5845. doi: 10.21037/apm-20-190
[15] Katlan B, Kesici S, Bayrakci B. Intravenous Lipid Emulsion Treatment for Calcium-Channel Blocker Intoxication: Pediatric Case Series and Review of the Literature[J]. Pediatr Emerg Care, 2023, 39(3): 120-124. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000002703
[16] Chou YJ, Lee CH. Success in early treatment with lipid emulsion for antihypertension drug overdose patient[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2021, 50: 814.e3-e814.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.06.043
[17] Garg SK, Goyal PK, Kumar R, et al. Management of life-threatening calcium channel blocker overdose with continuous venove noushemodiafiltration with charcoal hemoperfusion[J]. Indian Crit Care Med, 2014, 18(6): 399-401. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.133939
[18] Lindeman E, Ålebring J, Johansson A, et al. The unknown known: non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema in amlodipine poisoning, a cohort study[J]. Clin Toxicol(Phila), 2020, 58(11): 1042-1049. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2020.1725034
[19] Yet Kwong Horman J, Patel P, Schultz M, et al. Amlodipine-Induced Liver Injury[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(3): e23441.
[20] Varghese G, Madi L, Ghannam M, et al. A possible increase in liver enzymes due to amlodipine: A case report[J]. SAGE Open Med Case Rep, 2020, 8: 2050313X20917822.
[21] Kawahira M, Tamaki S, Yamada T, et al. Prognostic value of impaired hepato-renal function and liver fibrosis in patients admitted for acute heart failure[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2021, 8(2): 1274-1283. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13195
-




 下载:
下载: