-
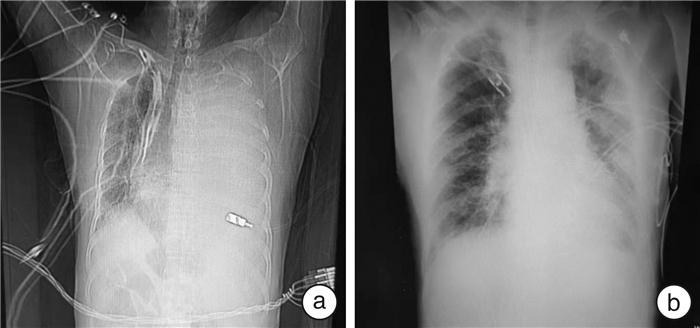
摘要: 梗阻性休克是由大血管或心脏本身阻塞引起的临床症状,常见于大面积肺栓塞、心包积液、气胸、腔静脉梗阻等病因。尽管其发病症状类似于心源性休克,但梗阻性休克需要与后者明确区分开来,因为两者的治疗方式截然不同。本文回顾性分析解放军总医院第六医学中心急诊医学科抢救室收治的1例以大量胸腔积液为罕见病因的梗阻性休克患者的临床资料并进行总结,旨在扩展对梗阻性休克临床表现及病因的认知,为临床诊疗提供经验,避免出现误诊及漏诊。Abstract: Obstructive shock is a clinical symptom caused by obstruction of large blood vessels or the heart itself. Although its symptoms are similar to those of cardiogenic shock, obstructive shock needs to be clearly distinguished from the latter because the two have completely different treatment methods. This paper retrospectively analyzes and summarizes the clinical data of a patient with obstructive shock with massive pleural effusion as a rare cause admitted to the emergency department of the Sixth Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital, aiming to expand the cognition to the clinical manifestations and etiology of obstructive shock, provide experience for clinical diagnosis and treatment, and avoid misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis.
-
Key words:
- obstructive shock /
- etiology /
- pleural effusion
-

-
[1] Blumlein D, Griffiths I. Shock: aetiology, pathophysiology and management[J]. Br J Nurs, 2022, 31(8): 422-428. doi: 10.12968/bjon.2022.31.8.422
[2] Kislitsina ON, Rich JD, Wilcox JE, et al. Shock-classification and pathophysiological principles of therapeutics[J]. Curr Cardiol Rev, 2019, 15(2): 102-113. doi: 10.2174/1573403X15666181212125024
[3] Patel S, Holden K, Calvin B, et al. Shock[J]. Crit Care Nurs Q, 2022, 45(3): 225-232. doi: 10.1097/CNQ.0000000000000407
[4] Wartenweiler M, Dellas Buser T, Joerg L, et al. Pulmonary embolism in a patient with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy: think outside"the box"[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2021, 37(8): 1275-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2021.02.019
[5] Margaretha PA, Rusmawatiningtyas D, Makrufardi F, et al. Obstructive shock in pediatric patient with congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation: A case report[J]. Ann Med Surg(Lond), 2021, 68: 102614. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34381602/
[6] Baig M, Nada K, Aboueisha A, et al. An atypical cause of obstructive shock[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2021, 203(4): e7-e8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202004-1136IM
[7] 张志民, 江涛, 黄渊旭. 左房粘液瘤脱落导致梗阻性休克1例[J]. 实用休克杂志(中英文), 2019, 3(4): 251-253. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYW201904016.htm
[8] Morgan C. Obstructive shock[J]. Open Pediatr Med J, 2013, 7(1): 35-37. doi: 10.2174/1874309901307010035
[9] Marik PE, Weinmann M. Optimizing fluid therapy in shock[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2019, 25(3): 246-251. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000604
[10] Standl T, Annecke T, Cascorbi I, et al. The nomenclature, definition and distinction of types of shock[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2018, 115(45): 757-768. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30573009/
[11] Mallett I, Watsjold B, Chipman AK. Young man with cardiac arrest secondary to undiagnosed mediastinal mass: a case report[J]. Clin Pract Cases Emerg Med, 2021, 5(1): 62-65. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/349056852_Young_Man_with_Cardiac_Arrest_Secondary_to_Undiagnosed_Mediastinal_Mass_A_Case_Report
[12] Mendelson J. Emergency department management of pediatric shock[J]. Emerg Med Clin North Am, 2018, 36(2): 427-440. doi: 10.1016/j.emc.2017.12.010
[13] McKiernan CA, Lieberman SA. Circulatory shock in children: an overview[J]. Pediatr Rev, 2005, 26(12): 451-460. doi: 10.1542/pir.26-12-451
[14] Pich H, Heller AR. Obstructive shock[J]. Anaesthesist, 2015, 64(5): 403-419. doi: 10.1007/s00101-015-0031-9
[15] Sharma A, Sonny A, Panaich S, et al. Analysis of the 2019 American heart association(AHA)focused update on advanced cardiovascular life support[J]. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, 2021, 35(5): 1516-1523. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053077020304924
-

| 引用本文: | 杨文军, 单毅. 大量胸腔积液致梗阻性休克1例[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(6): 323-325. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.06.009 |
| Citation: | YANG Wenjun, SHAN Yi. A case of obstructive shock caused by massive pleural effusion[J]. J Clin Emerg, 2023, 24(6): 323-325. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.06.009 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: