-
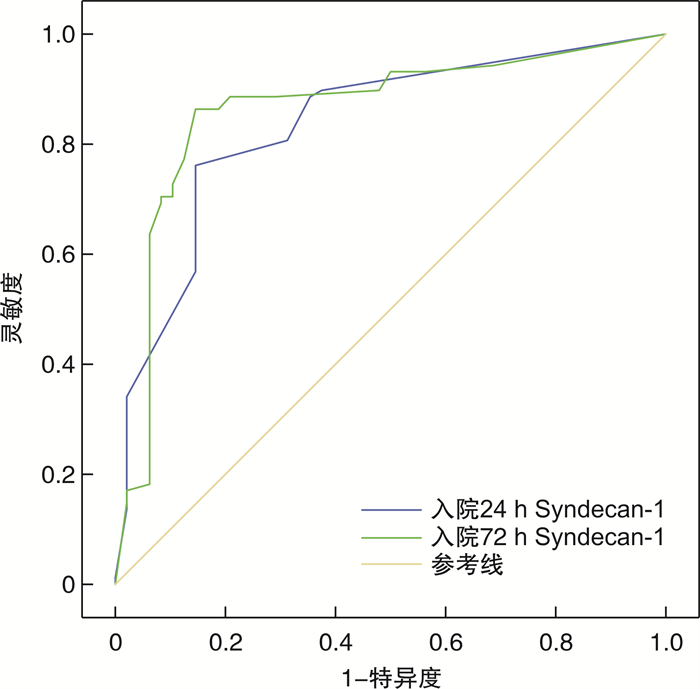
摘要: 目的 探讨多配体蛋白聚糖-1(Syndecan-1)在急性百草枯中毒(acute paraquat poisoning,APP)肺损伤患者中的表达意义。方法 选取2018年1月—2020年12月衡水市第二人民医院收治的APP患者136例,根据患者住院期间生存情况分为死亡组87例和存活组49例。分别在入院后24、72 h,检测C反应蛋白(CRP)、白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-10(IL-10)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α);同时采用ELISA法检测Syndecan-1、透明质酸(hyaluronic acid,HA)、硫酸类肝素(heparan sulfate,HS)。入院后72 h用Murray肺损伤评分系统对肺损伤程度进行评估。结果 生存组和死亡组患者性别、年龄、体质量比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。死亡组服毒剂量、就诊时间与生存组比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。入院后24 h,生存组和死亡组CRP、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。死亡组HA、Syndecan-1、HS高于生存组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。入院后72 h,死亡组CRP、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α、HA、Syndecan-1、HS明显高于生存组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。生存组和死亡组入院后72 h的CRP、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α、HA、Syndecan-1、HS均高于入院后24 h,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。相关性分析:入院后72 h,APP患者多糖包被降解产物HA、Syndecan-1、HS与Murray肺损伤评分之间呈正相关(r=0.667,P=0.013;r=0.732,P=0.004;r=0.661,P=0.014)。ROC曲线显示,入院24 h Syndecan-1对肺损伤患者预后有一定预测价值;入院72 h Syndecan-1对肺损伤患者预后的预测价值最大。结论 Syndecan-1在APP患者急性肺损伤早期升高,与Murray肺损伤评分有一定相关性,对评估APP肺损伤有临床预测价值。Abstract: Objective To investigate the significance of Syndecan-1(SDC-1) expression in patients with acute paraquat poisoning(APP) lung injury.Methods A total of 136 patients with APP admitted to our hospital from January 2018 to December 2020 were selected, and the patients were divided into 87 cases in the death group and 49 cases in the survival group according to their during hospitalization. C-reactive protein(CRP), interleukin-6(IL-6), interleukin-10(IL-10), and tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α) were detected at 24 h and 72 h after admission, respectively; hyaluronic acid(HA), multiligand proteoglycan-1(SDC-1), and heparan sulfate(HS) were also detected by ELISA. The degree of lung injury was assessed by the Murray Lung Injury Scoring System 72 h after admission.Results There was no statistically significant difference in gender, age, and body mass of patients in the survival and death groups(P>0.05). There was a statistically significant difference in the dose of toxicity and the time of consultation in the death group compared with the survival group(P < 0.05). There was no statistical difference in CRP, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α between the survival and death groups at 24 h after admission(P>0.05). HA, SDC-1, and HS were higher in the death group than in the survival group, and the differences were statistically significant(P < 0.05). At 72 h after admission, CRP, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, HA, SDC-1, and HS were significantly higher in the death group than in the survival group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). In both the survival and death groups, CRP, IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, HA, SDC-1, and HS were higher at 72 h after admission than at 24 h after admission, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Correlation analysis: 72 h after admission, there was a positive correlation between polysaccharide-encapsulated degradation products HA, SDC-1, HS and Murray's lung injury score in APP patients(r=0.667, P=0.013; r=0.732, P=0.004; r=0.661, P=0.014). OC showed that Syndecan-1 at 24 h after admission had lung injury patients; Syndecan-1 at 72 hours of admission had the greatest predictive value for prognosis of lung injury patients.Conclusion Syndecan-1 is elevated early in acute lung injury in APP patients and is of good clinical value in assessing the condition and prognosis.
-
Key words:
- acute paraquat poisoning /
- acute lung injure /
- Syndecan-1 /
- prognosis
-

-
表 1 生存组和死亡组临床资料的比较
X±S 项目 生存组(49例) 死亡组(87例) t/χ2 P 性别(女)/例(%) 26(53.06) 50(57.47) 0.247 0.375 年龄/岁 61.70±12.34 64.87±11.98 0.485 0.627 体质量/kg 71.01±5.51 67.63±6.34 1.324 0.212 服毒剂量/mL 11.62±5.27 43.25±5.80 9.875 0.001 就诊时间/h 2.83±0.95 4.87±1.64 4.517 0.001 表 2 生存组和死亡组炎性因子的比较
X±S 项目 生存组(49例) 死亡组(87例) t P IL-6/(ng/L) 入院24 h 30.61±2.14 31.75±3.48 1.471 0.169 入院72 h 41.10±5.521) 65.59±7.761) 10.451 0.001 IL-10/(ng/L) 入院24 h 10.40±1.16 11.62±2.34 1.836 0.094 入院72 h 19.42±5.891) 36.33±7.151) 8.975 0.001 TNF-α/(ng/L) 入院24 h 33.32±5.13 31.26±6.29 2.040 0.086 入院72 h 45.27±7.551) 80.37±10.841) 11.266 0.001 CRP/(mg/L) 入院24 h 17.16±5.73 17.97±6.19 0.247 0.810 入院72 h 25.21±6.651) 47.58±9.231) 13.925 0.001 与入院24 h比较,1)P < 0.05。 表 3 生存组和死亡组Syndecan-1的比较
X±S 项目 生存组(49例) 死亡组(87例) t P HA/(μg/L) 入院24 h 17.82±9.64 23.64±8.90 4.429 0.001 入院72 h 41.28±12.531) 74.77±11.641) 14.003 0.001 Syndecan-1/(μg/L) 入院24 h 22.05±4.03 26.92±6.18 3.403 0.011 入院72 h 46.39±11.321) 93.88±13.561) 13.398 0.001 HS/(μg/L) 入院24 h 27.26±6.19 33.14±8.27 3.524 0.005 入院72 h 51.65±7.841) 80.85±9.631) 15.290 0.001 与入院24 h比较,1)P < 0.05。 -
[1] Chen CK, Chen YC, Mégarbane B, et al. The acute paraquat poisoning mortality(APPM)score to predict the risk of death in paraquat-poisoned patients[J]. Clin Toxicol(Phila), 2022, 60(4): 446-450. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2021.1979234
[2] Patterson EK, Cepinskas G, Fraser DD. Endothelial glycocalyx degradation in critical illness and injury[J]. Front Med(Lausanne), 2022, 9: 898592.
[3] Suzuki A, Tomita H, Okada H. Form follows function: the endothelial glycocalyx[J]. Transl Res, 2022, 247: 158-167. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2022.03.014
[4] 段琬钰, 樊卓, 张文迪, 等. 我国2008-2018年急性百草枯中毒患者的流行病学分析[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2022, 43(1): 80-83.
[5] 闫永吉, 李双, 马瑞敏, 等. 吡非尼酮干预百草枯所致大鼠肺纤维化实验研究[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2023, 41(2): 104-111.
[6] Wu M, Zhou C, Li M, et al. Depletion of NK cells attenuates paraquat-induced acute lung injury by manipulating macrophage polarization[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2020, 86: 106698. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106698
[7] Kumar S, Gupta S, Bansal YS, et al. Pulmonary histopathology in fatal paraquat poisoning[J]. Autops Case Rep, 2021, 11: e2021342. doi: 10.4322/acr.2021.342
[8] Xu F, Liu C, Zhou QZ, et al. Effects of sequential blood purification on the organ function and lethality in patients with paraquat-induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2022, 14(3): 1818-1825.
[9] 陈东方, 郑海, 刘树峰, 等. 不同细菌感染引起的脓毒血症患者炎症因子水平[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2022, 32(3): 351-355. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHYY202203007.htm
[10] Yuan HM, Liu Q, Yu YL. Dynamic changes of serum cytokines in acute paraquat poisoning and changes in patients' immune function[J]. IET Syst Biol, 2022, 16(3-4): 132-143. doi: 10.1049/syb2.12045
[11] 靳妍, 刘志, 孙宁, 等. 内皮祖细胞移植对百草枯中毒所致急性肺损伤大鼠炎性因子表达的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(1): 6-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYQY202101003.htm
[12] 陈庆贤, 刘立伟, 吴茂森. 泮托拉唑对急性肺损伤模型大鼠和人肺微血管内皮细胞损伤的作用及作用机制[J]. 中国药业, 2022, 31(3): 65-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYGZ202203016.htm
[13] Villalba N, Baby S, Yuan SY. The endothelial glycocalyx as a double-edged sword in microvascular homeostasis and pathogenesis[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 711003.
[14] 陈加弟, 龚迪, 易玉虎, 等. 血管内皮糖萼在脓毒症急性肺损伤病理机制及诊断治疗中的作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021, 46(4): 398-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JFJY202104013.htm
[15] Masola V, Zaza G, Arduini A, et al. Endothelial glycocalyx as a regulator of fibrotic processes[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2996.
[16] Zhang D, Zhang JT, Pan Y, et al. Syndecan-1 shedding by matrix metalloproteinase-9 signaling regulates alveolar epithelial tight junction in lipopolysaccharide-induced early acute lung injury[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 5801-5816.
[17] Ali MM, Mahmoud AM, Le Master E, et al. Role of matrix metalloproteinases and histone deacetylase in oxidative stress-induced degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2019, 316(3): H647-H663.
[18] Sugita S, Naito Y, Zhou L, et al. Hyaluronic acid restored protein permeability across injured human lung microvascular endothelial cells[J]. FASEB Bioadv, 2022, 4(9): 619-631.
-

| 引用本文: | 李英, 韩丽, 柴成国. Syndecan-l在急性百草枯中毒肺损伤的表达意义[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2023, 24(5): 249-252. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.05.005 |
| Citation: | LI Ying, HAN Li, CHAI Chengguo. Significance of Syndecan-1 expression in acute paraquat poisoning lung injury[J]. J Clin Emerg, 2023, 24(5): 249-252. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2023.05.005 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: