-
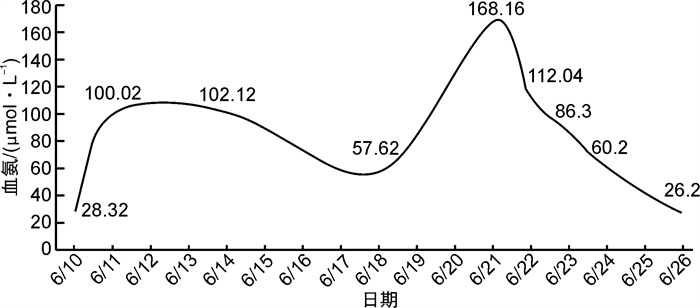
摘要: 回顾性分析合肥市第一人民医院重症医学科ICU收治的1例复杂高氨血症老年患者的临床资料并进行总结。患者因脑外伤伴癫痫发作收住入院,既往有胆管癌伴肝转移病史,入院后予丙戊酸钠控制癫痫发作,病程中患者肺部感染严重,肝功能正常,血氨升高,加用苯巴比妥肌内注射联合丙戊酸钠缓释片口服后出现血氨迅速升高。停用抗癫痫药物后,患者血氨逐步降至正常。高氨血症的病因不易鉴别,尤其是丙戊酸钠引起的非肝硬化性高氨血症临床不常见,在诊疗工作中需高度重视,避免漏诊、误诊。Abstract: To study the clinical diagnosis and treatment characteristics of sodium valproate-related hyperammonemia. To retrospectively analyze and summarize the clinical data of an elderly patient with complex hyperammonemia in ICU of our hospital. Thepatient was admitted to the hospital due to brain trauma and seizures. He had a history of cholangiocarcinoma with liver metastasis. After admission, sodium valproate was used to control the seizures. During the course of the disease, the patient had severe lung infection, normal liver function, and elevated blood ammonia. After oral administration of phenobarbital combined with sodium valproate sustained-release tablets, blood ammonia rapidly increased. After stopping the antiepileptic drugs, the patient's blood ammonia gradually decreased to normal. The etiology of hyperammonemia is not easy to identify, especially non-hepatic hyperammonemiacaused by sodium valproate is not common in clinical practice. It is necessary to attach great importance to clinical diagnosis and treatment to avoid missed diagnosis and misdiagnosis.
-
Key words:
- non-hepatic hyperammonemia /
- valproate /
- adverse reactions
-

-
[1] Lee S, Cheong J, Kim C, et al. Valproic Acid-Induced Hyperammonemic Encephalopathy as a Cause of Neurologic Deterioration after Unruptured Aneurysm Surgery[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2015, 58(2): 159-162. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.2.159
[2] Smith KM, Britton JW, Hocker SE, et al. Hyperammonemia in Patients With Status Epilepticus Treated With or Without Valproic Acid[J]. Neurologist, 2021, 26(3): 80-82. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0000000000000335
[3] Woo P, Woo A, Lam SW, et al. Incidence, Presentation, and Risk Factors for Sodium Valproate-Associated Hyperammonemia in Neurosurgical Patients: A Prospective, Observational Study[J]. World Neurosurg, 2020, 144: e597-e604. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.09.027
[4] Stergachis AB, Mogensen KM, Khoury CC, et al. A retrospective study of adult patients with noncirrhotic hyperammonemia[J]. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2020, 43(6): 1165-1172. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12292
[5] Kido J, Matsumoto S, Sugawara K, et al. Variants associated with urea cycle disorders in Japanese patients: Nationwide study and literature review[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2021, 185(7): 2026-2036. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62199
[6] García-García R, Guerrero JF, Lavilla-Miyasato M, et al. Hyperammonemia alters the mismatch negativity in the auditory evoked potential by altering functional connectivity and neurotransmission[J]. J Neurochem, 2020, 154(1): 56-70. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14941
[7] Drews L, Zimmermann M, Westhoff P, et al. Ammonia inhibits energy metabolism in astrocytes in a rapid and glutamate dehydrogenase 2-dependent manner[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2020, 13(10): dmm047134. doi: 10.1242/dmm.047134
[8] 陈曦, 付春毅, 张新超. 肺炎克雷伯菌肝脓肿侵袭性综合征10例临床分析[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2020, 21(6): 451-455. http://zzlc.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=ff1ebb82-d695-4af2-96e7-7ab12a531c9b
[9] 刘晓蕾, 黄欢, 朱长清, 等. 肺炎克雷伯菌导尿管相关性尿路感染单中心临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2021, 22(5): 339-343. http://zzlc.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=84e68c94-e449-4a3b-a19a-e33481f375bc
[10] Hashiguchi M, Tamai T, Kiyama K, et al. Two cases of liver cirrhosis with hyperammonemic encephalopathy caused by urease-producing bacteria in the urinary tract[J]. Clin J Gastroenterol, 2021, 14(2): 650-655. doi: 10.1007/s12328-020-01313-2
[11] Mazzoglio YNMJ, Munoz S, Muniz M, et al. Clinical Pharmacology of Hyperammonemia by Sodium Valproate and Carbamazepine in People Living with HIV. [J]. CNS Spectr, 2021, 26(2): 143.
[12] Abily-Donval L, Dupic L, Joffre C, et al. Management of 35 critically ill hyperammonemic neonates: Role of early administration of metabolite scavengers and continuous hemodialysis[J]. Arch Pediatr, 2020, 27(5): 250-256. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2020.05.002
[13] Wu J, Li J, Jing W, et al. Valproic acid-induced encephalopathy: A review of clinical features, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2021, 120: 107967. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2021.107967
[14] Habhab SF, Ulvin LB, Taubll E, et al. Influence of valproate-induced hyperammonemia on treatment decision in an adult status epilepticus cohort[J]. Epilepsy Behav, 2020, 111: 107193. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107193
[15] 崔荣周, 詹彦, 谢延风, 等. 丙戊酸钠致高氨血症脑病性意识障碍(附5例报告)[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2011, 37(7): 430-432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0152.2011.07.015
[16] Li Y, Zhou Q, Song JN, et al. Analysis of clinical prognosis in patients with non-hepatic hyperammonemia[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100(3): e24157. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000024157
[17] Tarazona S, Carmona H, Conesa A, et al. A multi-omic study for uncovering molecular mechanisms associated with hyperammonemia-induced cerebellar function impairment in rats[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2021, 37(3): 129-149.
[18] Zhao L, Gao Y, Guo S, et al. Prognosis of Patients with Sepsis and Non-Hepatic Hyperammonemia: A Cohort Study[J]. J Exp Clin Res,2020, 26: e928573.
[19] Naorungroj T, Yanase F, Eastwood GM, et al. Extracorporeal Ammonia Clearance for Hyperammonemia in Critically Ill Patients: A Scoping Review[J]. Blood Purification, 2020: 1-9.
[20] 程媛, 甘大楠, 叶永安. 血氨水平与肝性脑病的相关性研究进展[J]. 肝脏, 2019, 24(10): 1202-1204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-1704.2019.10.038
[21] Pérez LMP, Rivada LM, Villaroya EC, et al. Use of carglumic acid in valproate-induced hyperammonemia: 25 pediatric cases[J]. J Inherited Metabolic Dis, 2020, 55(1): 3-11.
-

| 引用本文: | 余菲, 叶友胜, 张琳. 丙戊酸钠致高氨血症1例[J]. 临床急诊杂志, 2022, 23(5): 359-361. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2022.05.012 |
| Citation: | YU Fei, YE Yousheng, ZHANG Lin. Hyperammonemia caused by sodium valproate: a case report[J]. J Clin Emerg, 2022, 23(5): 359-361. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1009-5918.2022.05.012 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: