Comparison of renal resistance index and biomarkers in predicting acute kidney injury in patients with sepsis
-
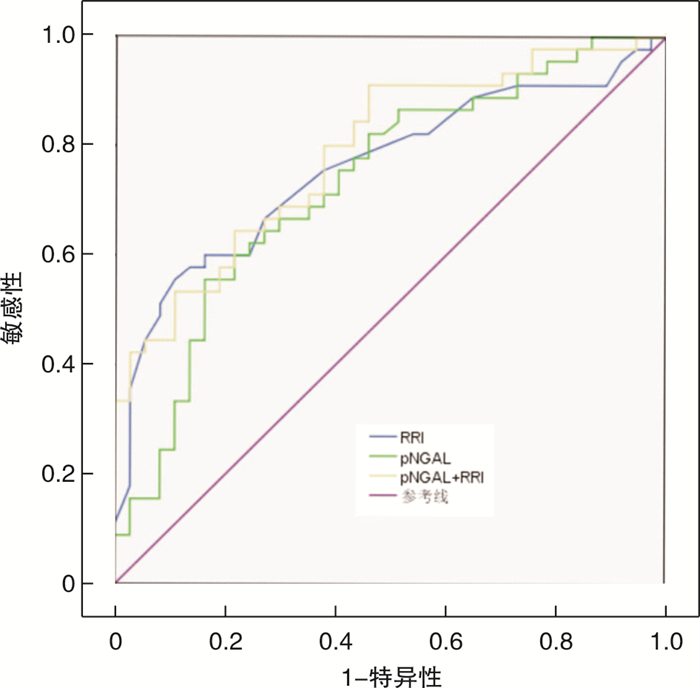
摘要: 目的 比较肾阻力指数(RRI)、血浆中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂蛋白(pNGAL)及血浆前脑啡肽(pPENK)对于脓毒症患者发生急性肾损伤(AKI)的早期预测价值,发现对脓毒症患者AKI早期预测的最佳方法。方法 测量入组脓毒症患者6 h内的RRI,检测pNGAL、pPENK水平,根据入组患者7 d内是否发生AKI分成2组:AKI组和未发生AKI(N-AKI)组,绘制受试者工作特征曲线(ROC),计算曲线下面积(AUC),评价3个指标对于脓毒症患者发生AKI的早期预测价值。结果 RRI(AUC=0.762)在脓毒症患者发生AKI的早期预测中优于pNGAL(AUC=0.714)。RRI联合pNGAL预测AKI的准确性(AUC=0.790)高于单一指标,但两者差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。pPENK在AKI组和N-AKI组中比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);进一步剔除肿瘤患者后发现,pPENK在AKI组中明显高于N-AKI组,差异有统计学意义(P< 0.05)。结论 在脓毒症患者发生AKI的早期预测中,RRI的检测准确性优于pNGAL,RRI联合pNGAL并不明显优于单一指标。在肿瘤患者中,pPENK对于脓毒症AKI的早期预测受到限制。
-
关键词:
- 脓毒症 /
- 急性肾损伤 /
- 肾阻力指数 /
- 血浆中性粒细胞明胶酶相关脂蛋白 /
- 血浆前脑啡肽
Abstract: Objective Objective to compare the early predictive value of renal resistance index(RRI), plasma neutrophil gelatinase associated lipoprotein(pNGAL) and plasma preenkephalin(pPENK) for acute kidney injury(AKI) in patients with sepsis, and to find the best method for early prediction of AKI in patients with sepsis.Methods The patients were divided into two groups: AKI group and no AKI(N-AKI) group according to the occurrence of AKI within 7 days. The receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC) was drawn to evaluate the early predictive value of the three indicators for AKI in patients with sepsis.Results RRI(AUC=0.762) was better than pNGAL(AUC=0.714) in the early prediction of AKI in sepsis patients. The accuracy of RRI combined with pngal in predicting AKI(AUC=0.790) was higher than that of single index, but the difference between them was not statistically significant(P>0.05). There was no significant difference between the two groups(P>0.05), but after further removal of tumor patients, it was found that the difference of pepink in AKI group was significantly higher than that in N-AKI group(P< 0.05).Conclusion In the early prediction of AKI in patients with sepsis, the accuracy of RRI is better than pngal, and the combination of RRI and pNGAL is not significantly better than a single index. In cancer patients, the early prediction of septic AKI by pPENK is limited. -

-
表 1 AKI组与N-AKI组患者一般资料的比较
例(%),M(Q1, Q3) 一般资料 AKI组(n=45) N-AKI组(n=37) P 年龄/岁 69(61, 77) 65(61, 70) 0.096 男性/% 29(64.44) 29(78.38) 0.076 APACHE-Ⅱ评分 16.00(13.50,20.00) 13.00(10.00,18.00) 0.020 RRI 0.71(0.65,0.74) 0.64(0.60,0.67) < 0.001 pNGAL/(ng·mL-1) 1.76(1.41,2.12) 1.33(1.12,1.71) 0.001 pPENK/(pg·mL-1) 70.44(63.06,139.46) 72.02(63.81,100.21) 0.885 表 2 pPENK在肿瘤患者和非肿瘤患者中对脓毒症AKI的预测价值
pg/mL,M(Q1, Q3) 组别 pPENK P AKI N-AKI 肿瘤患者 68.46
(63.03,89.06)73.09
(64.25,148.76)0.216 非肿瘤患者 142.92
(66.74,549.80)64.27
(62.27,77.40)0.028 P 0.062 0.084 -
[1] Joannidis M, Druml W, Forni LG, et al. Prevention of acute kidney injury and protection of renal function in the intensive care unit: update: Expert opinion of the Working Group on Prevention, AKI section, European Society of Intensive Care Medicine[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2017, 43(6): 730-749. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4832-y
[2] Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock(Sepsis-3)[J]. JAMA, 2016, 315(8): 801-10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
[3] Zarjou A, Agarwal A, et al. Sepsis and acute kidney injury[J]. Am Soc Nephrol, 2011, 22: 999-1006. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010050484
[4] Gomez H, Ince C, DeBacker D, et al. Aunifiedtheory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: infiammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury[J]. Shock, 2014, 41(1): 3-11. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000052
[5] Song JQ, Wu W, He YZ, et al. Value of the combination of renal resistance index and central venous pressure in the early prediction of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury[J]. J Crit Care, 2018, 45: 204-208. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2018.03.016
[6] Xing ZQ, Liu DW, Wang XT, et al. The value of renal resistance index and urine oxygen pressure for prediction of acute kidney injury in patients with septic shock[J]. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi, 2019, 58(5): 349-354.
[7] Charlton JR, Portilla D. OkusaA basic science view of acute kidney injury biomarkers[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2014, 29(7): 1301-1311. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gft510
[8] Zappitelli M, Washburn KK, Arikan AA, et al. Urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is an early marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study[J]. Crit Care, 2007, 11(4): R84. doi: 10.1186/cc6089
[9] Zhang A, Cai Y, Wang PF, et al. Diagnosis and prognosis of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20: 41-53. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1212-x
[10] Alge JL, Arthur JM. Biomarkers of AKI: A Review of Mechanistic Relevance and Potential Therapeutic Implications[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2015, 10(1): 147-155. doi: 10.2215/CJN.12191213
[11] Wong MCY, Piaggio G, Damasio MB, et al. Hydronephrosis and crossing vessels in children: Optimization of diagnostic-therapeutic pathway and analysis of color Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance urography diagnostic accuracy[J]. Pediatr Urol, 2018, 14(2): 204-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jpurol.2017.12.020
[12] Meola M, Samoni S, Petrucci I, et al. Imaging in Chronic Kidney Disease[J]. Contrib Nephrol, 2016, 188: 69-80.
[13] Deruddre S, Cheisson G, Mazoit JX, et al. Renal arterial resistance in septic shock: effects of increasing mean arterial pressure with norepinephrine on the renal resistive index assessed with Doppler ultrasonography[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2007, 33(9): 1557-1562. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0665-4
[14] Moman RN, Ostby SA, Akhoundi A, et al. Impact of individualized target mean arterial pressure for septic shock resuscitation on the incidence of acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2018, 8(1): 124. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0468-5
[15] Emmens JE, Ter Maaten JM, Damman M, et al. K Proenkephalin, an Opioid System Surrogate, as a Novel Comprehensive Renal Marker in Heart Failure[J]. Circ Heart Fail, 2019, 12(5): e005544. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.118.005544
[16] Molvin J, Jujic A, Navarin S, et al. Bioactive adrenomedullin, proenkephalin A and clinical outcomes in an acute heart failure setting[J]. Open Heart, 2019, 6(2): e001048. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2019-001048
[17] Schulz CA, Christensson A, Ericson U, et al. High Level of Fasting Plasma Proenkephalin-A Predicts Deterioration of Kidney Function and Incidence of CKD[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017, 28(1): 291-303. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015101177
[18] Breidthardt T, Jaeger C, Christ A, et al. Proenkephalin for the Early Detection of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2018, 48(10): e12999. doi: 10.1111/eci.12999
[19] Rosenqvist M, Bronton K, Hartmann O, et al. Proenkephalin a 119-159(penKid)-a novel biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis: an observational study[J]. BMC Emerg Med, 2019, 19(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1186/s12873-019-0283-9
[20] Marino R, Struck J, Hartmann O, et al. Diagnostic and short-term prognostic utility of plasma pro-enkephalin(pro-ENK)for acute kidney injury in patients admitted with sepsis in the emergency department[J]. Nephrology, 2015, 28(6): 717-724. doi: 10.1007/s40620-014-0163-z
[21] Melander O, Svensson T, Svensson T, et al. Stable Peptide of the Endogenous Opioid Enkephalin Precursor and Breast Cancer Risk[J]. Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(24): 2632-2638.
[22] Balabanova S, Holmberg C, Steele I, et al. The neuroendocrine phenotype of gastric myofibroblasts and its loss with cancer progression[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2014, 35(8): 1798-1806. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu086
-




 下载:
下载: